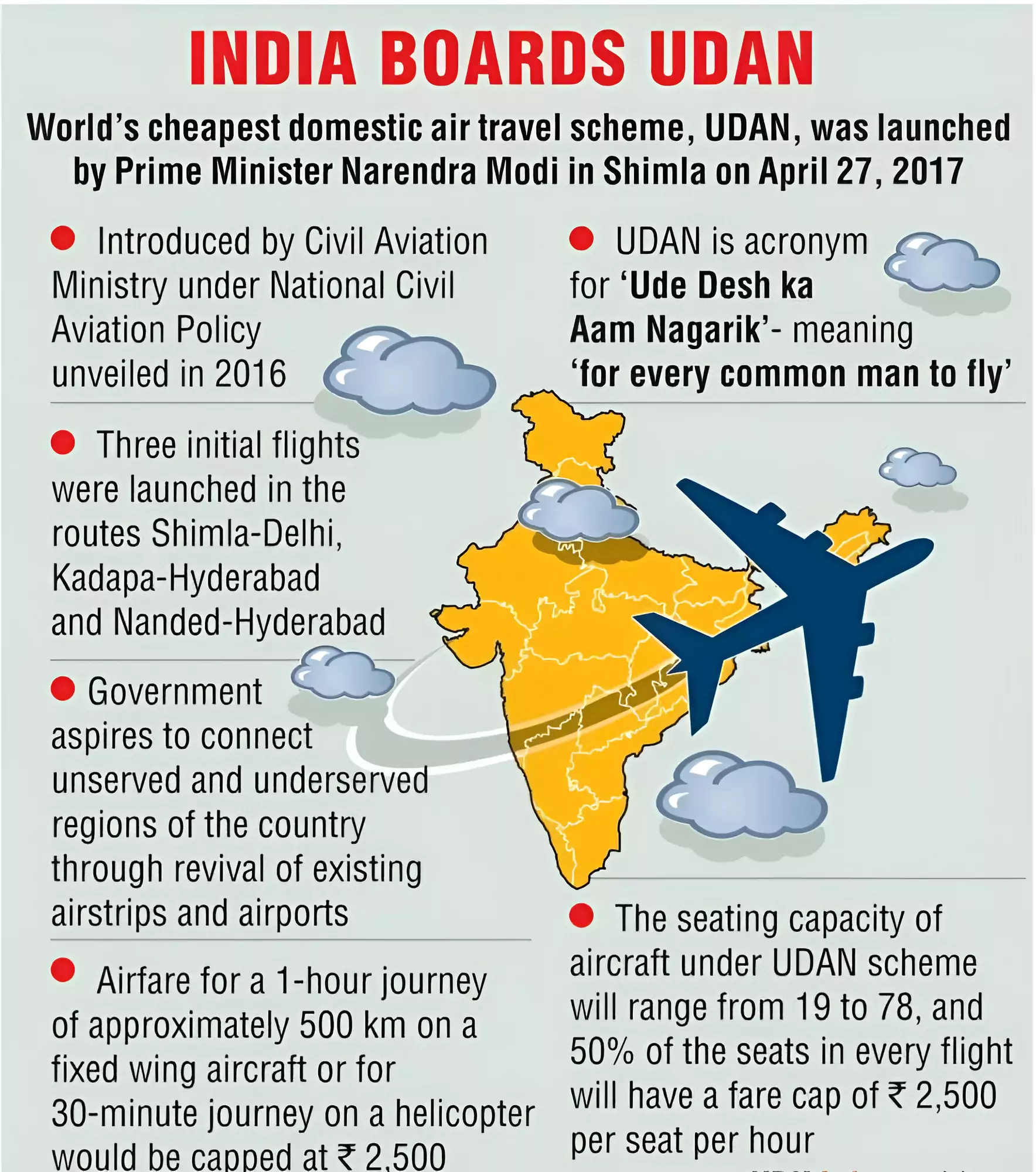
Context: The Regional Connectivity Scheme (RCS) - UDAN (Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik), has completed six years.

| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
RCS Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik is a government-backed initiative to improve air infrastructure and connectivity in India, especially in remote and underserved regions.
Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik scheme is a part of National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP) 2016 and launched by the Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA) under a 10-year vision.
First Component: Develop new airports and enhance the existing regional airports to increase the number of operational airports for civilian flights from 70 to at least 150 airports. Second Component: Adding new flight routes to connect more than 100 underserved airports in smaller towns with each other as well as with well-served airports in bigger cities using the "Viability Gap Funding" (VGF) model.
The scheme aims to provide seamless, cost-effective, time-bound air transportation and associated logistics for all Agri-produce, especially from Northeast, hilly and tribal regions of the country.
International Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik has been introduced with an objective to boost air connectivity from certain States of the country with selected international destinations to promote socio-economic growth.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>