What are El Nino and La Nina? Keep reading to get the inside scoop on El Niño and La Niña and how they affect weather worldwide.
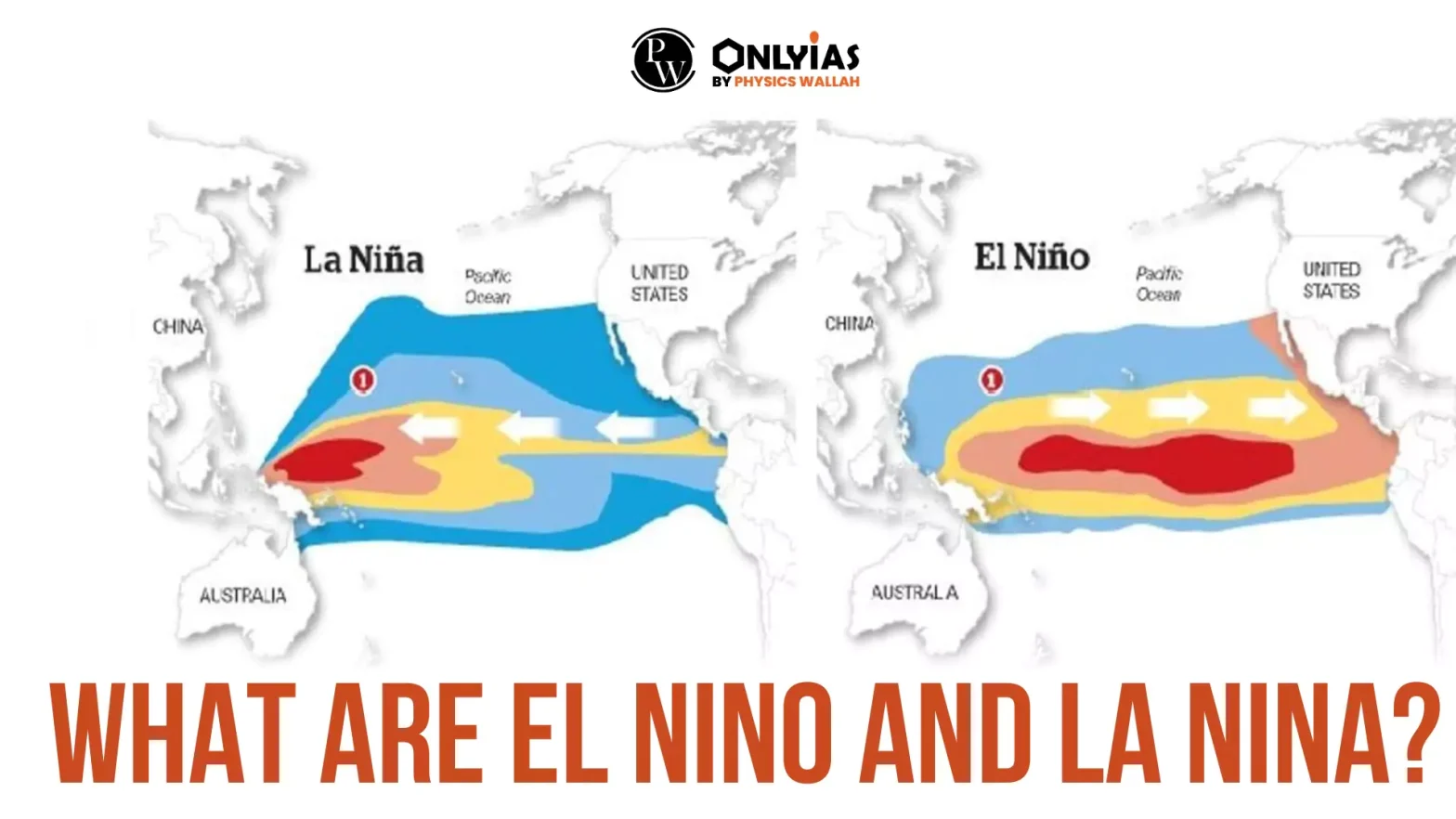
What are El Nino and La Nina: El Niño and La Niña are climatic phenomena that originate in the Pacific Ocean and significantly impact global weather patterns. These events are part of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, which causes changes in sea surface temperatures, winds, and pressure in the tropical Pacific. While El Niño is associated with warming ocean temperatures, La Niña signifies a cooling of the ocean surface. Both events affect weather, rainfall, and temperature worldwide, influencing droughts, floods, and even global food production. Understanding what are El Niño and La Niña in geography is essential for climate studies, disaster preparedness, and agriculture planning.
The Southern Oscillation refers to changes in atmospheric pressure across the Pacific, directly linked to El Niño and La Niña. These events cause shifts in normal weather conditions. El Niño leads to warmer ocean temperatures, while La Niña results in colder-than-average sea surface temperatures. Their effects aren’t limited to the Pacific; they disrupt weather patterns across continents. Regions like India, Australia, and the United States often experience droughts or floods due to these phenomena. The study of what is El Niño and La Niña in geography is crucial for meteorology and environmental science.
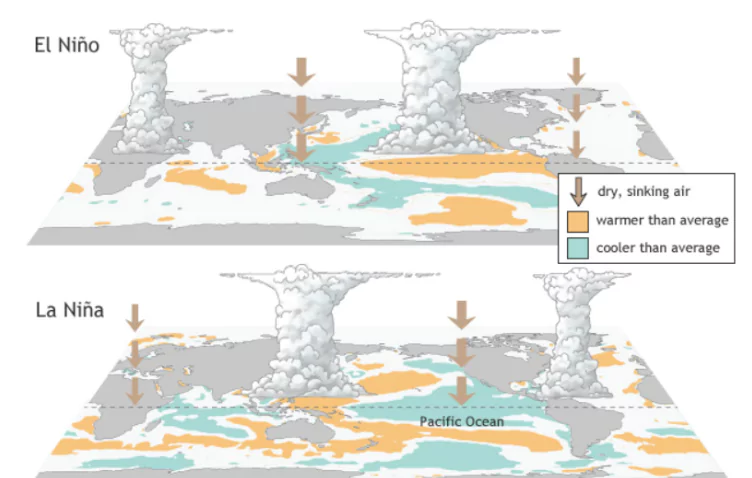
La Niña is the cooling phase of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle. During La Niña, sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific drop below normal levels. Stronger trade winds push warm water toward the western Pacific, causing cold, nutrient-rich water to rise near South America’s coast. This event leads to drier conditions in South America and heavier rains and cyclones in Australia and Southeast Asia.
La Niña is known as the “cool sister” of El Niño and typically results in cooler global temperatures. It is linked to stronger monsoons in India, increased rainfall in Southeast Asia, and hurricanes in the Atlantic. Farmers, governments, and disaster management teams closely monitor La Niña due to its profound influence on rainfall and agriculture.
El Niño refers to the warming phase of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, where sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific rise above normal levels. Weaker trade winds allow warm water to move toward South America, reducing the upwelling of cold, nutrient-rich water. This leads to a rise in ocean temperatures and shifts in global weather.
El Niño is known as the “warm brother” of La Niña and is associated with higher temperatures worldwide. It often causes droughts in Southeast Asia, India, and Australia while bringing heavy rainfall and floods to South America. Understanding what is El Niño is vital for predicting weather changes, disaster management, and agricultural planning.
The key difference between La Niña and El Niño lies in the temperature of the Pacific Ocean. While La Niña cools the sea surface, El Niño warms it. Here’s a comparison to understand what is the difference between La Niña and El Niño:
| Criteria | La Niña | El Niño |
| Sea Surface Temp | Cooler than normal | Warmer than normal |
| Trade Winds | Stronger than usual | Weaker or reversed |
| Rainfall in India | Stronger monsoon, more rain | Weaker monsoon, less rain |
| Weather Impact | Droughts in South America, heavy rain in Australia | Droughts in Australia and India, floods in South America |
| Global Effect | Cooler global temperature | Warmer global temperature |
The root cause of El Niño and La Niña lies in the Southern Oscillation, which changes atmospheric pressure in the Pacific Ocean. Here’s a brief explanation:
Both events are naturally occurring climate phenomena but are becoming more intense due to global warming.
The impacts of El Niño and La Niña are felt worldwide, affecting weather, agriculture, and economies. Here are some key effects:
These impacts explain why governments and weather agencies track what causes El Niño and La Niña and their influence on weather and climate.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
UPSC Exam 2025 Related Articles
UPSC Prelims 2025 Exam
UPSC Notification 2025
UPSC Preparation 2025
UPSC Eligibility 2025
UPSC Exam Pattern
UPSC Syllabus
El Niño is a climate phenomenon where Pacific Ocean temperatures rise, causing global weather changes like droughts and floods.
La Niña is the opposite of El Niño, where cooler Pacific Ocean temperatures lead to stronger monsoons and floods in certain regions.
El Niño causes warming of the Pacific, while La Niña causes cooling. El Niño leads to droughts in India, while La Niña strengthens monsoons.
They are caused by changes in Pacific Ocean winds and sea surface temperatures, driven by fluctuations in atmospheric pressure (Southern Oscillation).
El Niño weakens the Indian monsoon, causing droughts, while La Niña strengthens monsoons, leading to excess rainfall and floods.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>