![]() April 29, 2024
April 29, 2024
![]() 7848
7848
![]() 0
0
The hot, wet equatorial climate, situated within 5° and 10° N and S of the equator, boasts uniformly high temperatures, heavy precipitation, and dense tropical rainforests. Its lush vegetation supports a diverse ecosystem and sustains economic activities such as shifting cultivation and the thriving cocoa, rubber, and oil palm industries.
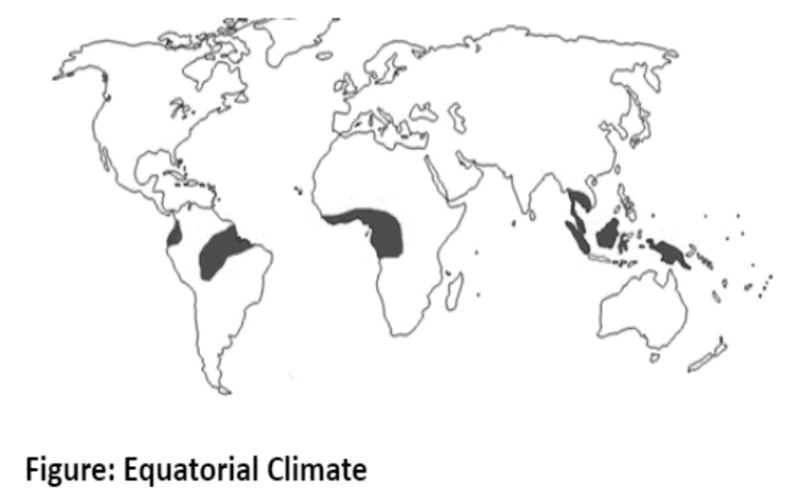 Cloudiness and heavy precipitation help to moderate the daily temperature.
Cloudiness and heavy precipitation help to moderate the daily temperature.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
The hot, wet equatorial climate fosters unique ecosystems and livelihoods, from the dense rainforests of the Amazon and Congo to the vibrant agricultural and extractive industries of Malaysia and Indonesia. Despite challenges like disease and difficult terrain, this region remains vital to global biodiversity and economic productivity.
| Related Articles | |
| TYPES OF CLIMATE | Natural Rubber Production In India |
| Forest In India | Hydrological Cycle: Clouds, Precipitation, and Rainfall Patterns |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments