Context
Recently, a new study has shed light on the extent of microplastic pollution in Ashtamudi Lake, underscoring the need for continuous monitoring and addressing “potential public health concerns.”
- The study Microplastic contamination in Ashtamudi Lake, India: Insights from a Ramsar wetland was done by the Department of Aquatic Biology and Fisheries, University of Kerala, with support from the Ecomarine Project co-funded by the Erasmus programme of the European Union.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Microplastic Pollution in Ashtamudi Lake, Key Findings of the Study
- High Composition of Microplastics: The highest percentage composition of microplastics was found in the macrofauna, with fish accounting for 19.6% and shellfish 40.9%.
- Comprises:
- Fibers (35.6%), fragments (33.3%) and films (28%) of the microplastics found in the collected samples.
- There is presence of plastic polymers as well as hazardous heavy metals.
- Polymer composition of microplastics includes nylon, polyurethane, polypropylene, polyethylene, and polysiloxane.
- Hazardous heavy metals such as molybdenum, iron and barium.
- Source of Microplastics: Untreated municipal solid waste and plastic debris, The inadequate management of plastic solid waste and Fishing equipment.
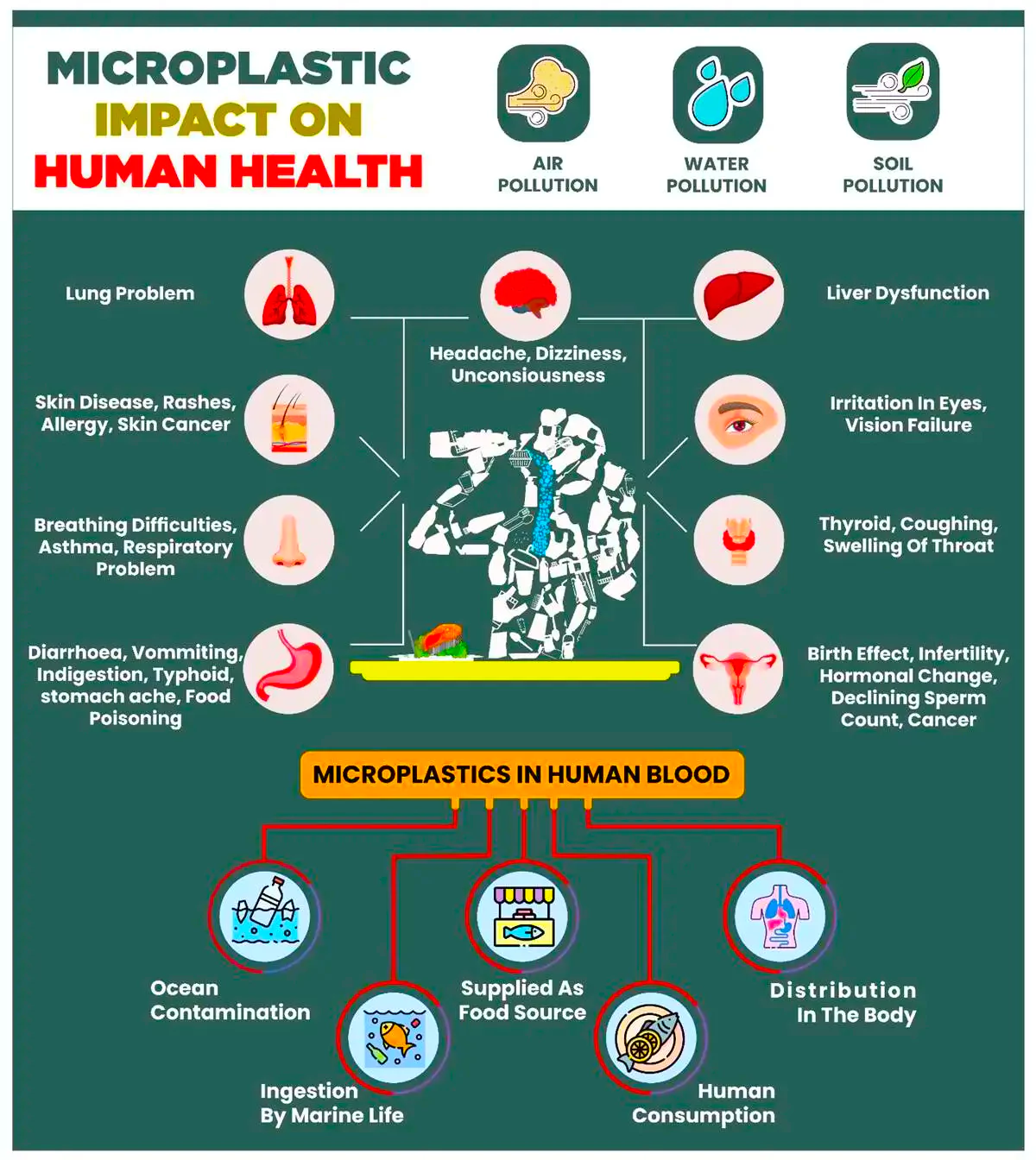 Raising Concerns: The existence of plastic polymers and heavy metals in microplastic samples poses a threat to vulnerable biota; people consume contaminated fish and shellfish.
Raising Concerns: The existence of plastic polymers and heavy metals in microplastic samples poses a threat to vulnerable biota; people consume contaminated fish and shellfish.- Actions Required: There is a need of Development of strategies and action plans to gradually reduce the entry of microplastics into estuarine systems.
About Microplastics
- Size: Microplastics are plastic fragments less than five millimeters in length.
- Formation: Microplastics are either manufactured (microbeads that are used in cosmetics and beauty products) or they are formed when larger pieces of plastic break down.
- Classifications: They are classified into following two types:
- Primary Microplastics: Tiny particles designed for commercial use and microfibers shed from clothing and other textiles.
- Secondary Microplastics: They are formed from the breakdown of larger plastics such as water bottles.
 Initiatives Taken:
Initiatives Taken:-
- Global Initiatives:
- World Environment Day (WED) 2023: It focuses on solutions to plastic pollution problem under the campaign #Beat Plastic Pollution.
- Global Partnership on Marine Litter (GPML): It was launched at the Earth Summit in 2012 in response to the Manila Declaration.
- The Manila Declaration seeks to develop policies to reduce and control wastewater, marine litter and pollution from fertilizers.
- GloLitter Partnerships Project: Launched by the IMO and FAO, with an aim to prevent and reduce marine plastic litter from shipping and fisheries.
- London Convention, 1972: To control all sources of marine pollution and prevent pollution of the sea through regulation of dumping into the sea of waste materials.
- Plastic Pacts: To transform the plastics packaging value chain for all formats and products. The first Plastics Pact was launched in the U.K. in 2018.
- India’s Initiatives:
- Elimination of Single Use Plastic, 2019: To eliminate all single-use plastic in the country by 2022, with an immediate ban in urban Delhi.
- Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016: Every local body has to be responsible for setting up infrastructure for segregation, collection, processing, and disposal of plastic waste.
About Ashtamudi Lake
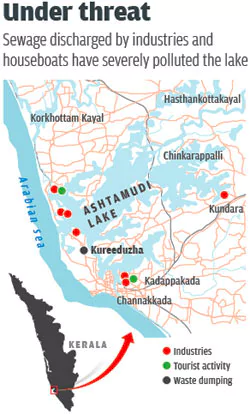
- It is a backwater lake and is also called the gateway to the backwaters of Kerala.
- Backwater is water turned back in its course by an obstruction on opposing current or the flow of tide in a river channel.
- Situated in: Kollam District, Kerala
- It is an extensive estuarine system, the second largest in Kerala State (after Vembanad).
- A Ramsar Site: The Ashtamudi wetland was designated a Ramsar site in 2002.
- Concerns: Population density and urban pressures pose threats to the site.
- Importance: Ashtamudi Kayal dates back to the times of the Romans and Phoenicians in the 14th century and was considered as one of the most important ports used for Chinese trade.
- Associated Islands: Munroe island (a group of eight small islands), Chavara south (rich in minerals) and Thekkumbhagom island.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
![]() 24 May 2024
24 May 2024
 Raising Concerns: The existence of plastic polymers and heavy metals in microplastic samples poses a threat to vulnerable biota; people consume contaminated fish and shellfish.
Raising Concerns: The existence of plastic polymers and heavy metals in microplastic samples poses a threat to vulnerable biota; people consume contaminated fish and shellfish. Initiatives Taken:
Initiatives Taken:
