The use of Meropenem drug can cause adverse reactions as per The Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC).
IPC Warns of Severe Reactions to Meropenem Drug, Calls for Regulation of Antibiotics
The Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) has found that using Meropenem can lead to adverse reactions in patients in the form of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis (AGEP), a severe drug related reaction, and can be life threatening. It is advised that doctors and patients exercise caution while using the drug.
- The IPC’s drug safety alert analyzed adverse drug reactions from Pharmacovigilance Programme of India (PvPI) database revealing that Meropenem drug causes adverse drug reaction.
- Regulation of Antibiotics: Drugs Controller General of India has directed states/UT governments to keep a close watch on the sale of inappropriate antibiotic combinations which should be banned immediately.
- Prevention: It has further instructed the officials to prevent the spread of these cocktail drugs into the market.
- The regulator has sought a detailed report of licensed antibiotics available for sale from the drug controllers in the state.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Schedule-H drugs
- Legal Provision: Schedule-H drug is a class of prescription drugs in India mentioned in Schedule-H to the Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945 as framed under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- About: These medicines contain a very high alcoholic influence and are used to treat some serious diseases like heart diseases, anxiety disorders and other diseases.
- Prescription sale: Schedule H warrants retail sale of the medicine only against a valid prescription by a Registered Medical Practitioner only.
- Schedule H list at present contains 510 drugs.
- Schedule H1: It was introduced in 2013 in the Drugs and Cosmetics Act 1940 as a new class of prescription drugs containing certain 3rd and 4th generation antibiotics, certain habit forming drugs and anti-TB drugs.
|
About Meropenem Drug
Meropenem Drug is a carbapenem antibiotic manufactured by Pfizer and is available under various brand names in India. Pfizer’s meropenem drug formulation already contains a safety alert for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) on its pack.
- Mechanism of Action: Meropenem penetrates bacterial cells and interferes with the synthesis of vital cell wall components, which leads to cell death.
- Schedule H: The medicine falls under the schedule H and H1 of the drugs and cosmetic rules, 1945 and required to be sold by retail only under the prescription by a doctor.
- Prescribed for Infections: The medication is largely prescribed for the treatment of pneumonia, UTI, intra-abdominal infection, skin infection, meningitis, septicaemia and gynecological infections etc.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC)
- Nodal Ministry: It is an Autonomous institution fully financed by the Central Government under the administrative control of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Established: The Commission has become fully operational from 1st January, 2009
- Chairman: The Secretary of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Mandate: It is to perform functions such as revision and publication of the Indian Pharmacopoeia and National formulary of India on a regular basis besides providing IP Reference Substances and training to the stakeholders on Pharmacopoeial issues.
- Functions:
- Publications: Timely publication of the Indian Pharmacopoeia, the official book of standards for drug included therein, in terms of the Second Schedule to the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940
- Establishing Standards: To specify the standards of identity, purity and strength of the drugs imported, manufactured for sale, stocked or exhibited for sale or distributed in India.
- Pharmacovigilance Programme of India: It is Government of India’s drug safety monitoring programme, which collects, collates and analyses drug-related adverse events and send recommendations to Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) for taking appropriate regulatory actions.
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis
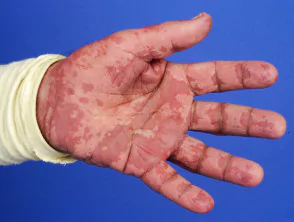
- About: AGEP is an uncommon pustular drug eruption characterized by superficial pustules and is usually classified as a severe cutaneous adverse reaction (SCAR) to a prescribed drug. It is also called toxic pustuloderma.
- Incidence Rate: It is estimated to be about 3–5 cases per million population per year.
- Causes: Close to 90% of cases of AGEP are a result of adverse reactions to a medication, most often beta-lactam antibiotics (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins).
- Other drugs: tetracyclines, sulfonamides, quinolones, oral antifungals, particularly terbinafine, calcium channel blockers such as diltiazem, hydroxychloroquine, carbamazepine, and paracetamol.
- AGEP is associated with IL36RN gene mutations.
|
![]() 6 Jun 2024
6 Jun 2024