Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented her seventh straight Budget on July 23 for the fiscal 2024-25, surpassing the record of former Prime Minister Morarji Desai.
- The presentation on July 23 is the first Budget by the BJP-led NDA government since it was re-elected in June.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Union Budget 2024-25, Economic Survey 2024, Nine key priorities, Skilling Program, New Employment-Linked Incentive Schemes, Purvodaya Scheme, Credit Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs, Mudra Loans, PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana etc.
Relevancy for Mains: Productivity and Resilience in Agriculture, Productivity and Resilience in Agriculture, Employment & Skilling, Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice, Manufacturing & Services, Urban Development, Energy Security, Infrastructure , Innovation, Research & Development & Next Generation Reforms etc. |
Union Budget 2024-25, Nine Key Priorities
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Priority 1: Productivity and Resilience in Agriculture:
- AIM: Government will undertake a comprehensive review of the agriculture research setup to bring the focus on raising productivity.
Productivity in agriculture:
- It refers to the efficiency with which agricultural inputs (such as land, labor, fertilizers, seeds, and water) are converted into outputs (such as crops, livestock, and other agricultural products).
- Higher productivity means more output is produced from the same amount of inputs, indicating a more efficient use of resources
- China’s yield of grain production is higher than that of India’s
Resilience in agriculture:
- It refers to the capacity of agricultural systems to absorb shocks and stresses, adapt to changing conditions, and recover from adverse events such as extreme weather, pest infestations, economic fluctuations, and market volatility.
|
Challenge mode Funding
- It involves setting up a competitive process where participants (such as startups, researchers, or companies) are invited to propose solutions to predefined challenges.
- The best proposals receive funding and support to develop and implement their ideas.
|
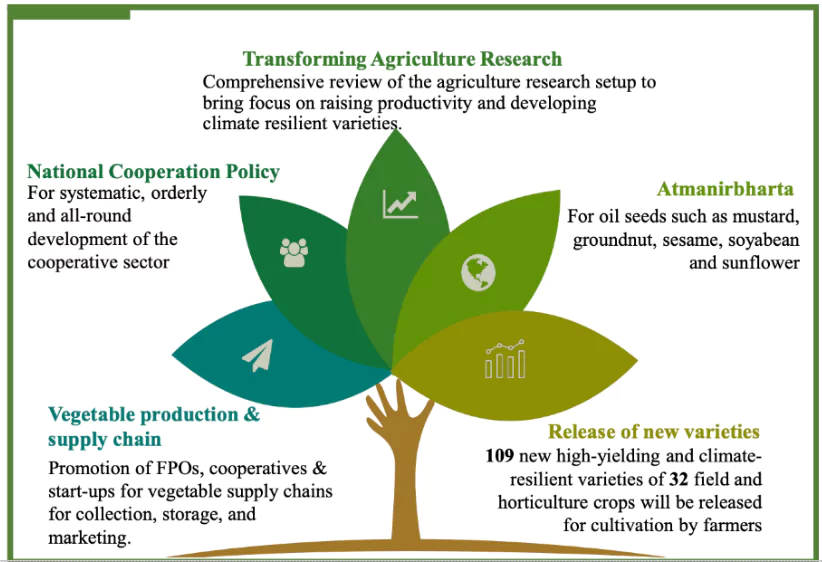
- Transforming Agriculture Research: By implementing comprehensive review of the agriculture research setup to bring focus on raising productivity and developing climate resilient varieties.
- Funding: It will be provided in challenge mode, including to the private sector. Domain experts both from the government and outside will oversee the conduct of such research.
- Release of new varieties: New 109 high-yielding and climate-resilient varieties of 32 field and horticulture crops will be released for cultivation by farmers.
- National Cooperation Policy: The government will bring out a National Cooperation Policy for systematic, orderly and all-round development of the cooperative sector.
- Policy Goal:
- Fast-tracking growth of rural economy and
- generation of employment opportunities on a large scale
- 1.52 lakh crore has been allocated for agriculture and allied sectors this year.
- Atmanirbharta: For oil seeds such as mustard, groundnut, sesame, soyabean and sunflower
- Vegetable production & supply chain: Promotion of FPOs, cooperatives & start-ups for vegetable supply chains for collection, storage, and marketing.
- Initiatives: Large scale clusters for vegetable production will be developed closer to major consumption centres.
- It will promote Farmer-Producer Organizations, cooperatives and start-ups for vegetable supply chains including for collection, storage, and marketing.
- Natural Farming:
- In the next two years, 1 crore farmers across the country will be initiated into natural farming.
- Certification and branding: One crore farmers across the country will be initiated into natural farming supported by certification and branding.
- 10,000 need-based bio-input resource centers will be established.
- Digital Public Infrastructure for Agriculture
- Central government, in partnership with the states, will facilitate the implementation of the Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in agriculture for coverage of farmers and their lands in 3 years.
- Key Initiatives:
- Digital Crop Survey: Conducted for Kharif in 400 districts this year.
- Farmer and Land Registries: The details of 6 crore farmers and their lands will be brought into the farmer and land registries.
- Kisan Credit Cards: Jan Samarth based Kisan Credit Cards will be enabled in 5 states.
- Shrimp Production & Export
- Breeding Centres for Shrimp: The Union Finance Minister said Financial support for setting up a network of Nucleus Breeding Centres for Shrimp Broodstocks will be provided.
- NABARD: Financing for Shrimp farming, processing and export will be facilitated through NABARD.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Priority 2: Employment and Skilling:
- 5 schemes aimed at skilling and employment will target 4.1 crore youth over the next 5 years with a budgetary allocation of Rs 2 lakh crore.
- New Employment-Linked Incentive Schemes Announced in Union Budget 2024-25: Finance Minister announced three employment-linked incentive schemes to boost employment in manufacturing and other formal sectors:
- Scheme A: First-Timers:
- Benefit: Provides a month’s wage (up to ₹15,000) in three installments to new employees registered with EPFO.
- Eligibility: The eligibility limit will be Rs 1 lakh per month
- Impact: Expected to benefit 210 lakh youths.
- Scheme B: Job Creation in Manufacturing
- Focus: Incentivizes additional employment in manufacturing for first-time employees.
- Benefit: Incentive provided to both employees and employers for EPFO contributions during the first four years of employment.
- Impact: Expected to benefit 30 lakh youths and their employers.
- Scheme C: Support to Employers
- Focus: Covers additional employment in all sectors.
- Benefit: Government will reimburse employers up to ₹3,000 per month for two years towards EPFO contributions for each additional employee.
- Eligibility: Employees earning up to ₹1 lakh per month.
- Impact: Expected to incentivize additional employment of 50 lakh persons.
- Skilling Program
- 4th New Scheme: A centrally sponsored scheme for skilling 20 lakh youth over five years.
- Industrial Training Institutes: 1,000 ITIs to be upgraded with hub-and-spoke arrangements.
- Course content and design: It will be aligned to the skill needs of industry, and new courses will be introduced for emerging needs.
- Skilling Loans
- Model Skill Loan Scheme: Revised to facilitate loans up to ₹7.5 lakh with a government guarantee.
- Impact: Expected to help 25,000 students annually.
- Education Loans
- Financial Support: Loans up to ₹10 lakh for higher education in domestic institutions.
- E-Vouchers: Direct interest subvention of 3% for 1 lakh students each year.
Participation Of Women In The Workforce:
- It will facilitate higher participation of women in the workforce through setting up of working women hostels in collaboration with industry, and establishing creches.
- In addition, the partnership will seek to organize women-specific skilling programmes, and promotion of market access for women SHG enterprises.
|
Priority 3: Inclusive HR Development and Social Justice:
- Purvodaya: for all round development of Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha and Andhra Pradesh.
- Andhra Pradesh:
- Rs 15,000 crore to be allocated for development of Amravati as AP’s capital.
- Money to be raised from multilateral funding agencies and routed through the Centre, announced Sitharaman.
- Bihar:
- The government also proposes Rs 26,000 crore for various road projects in Bihar.
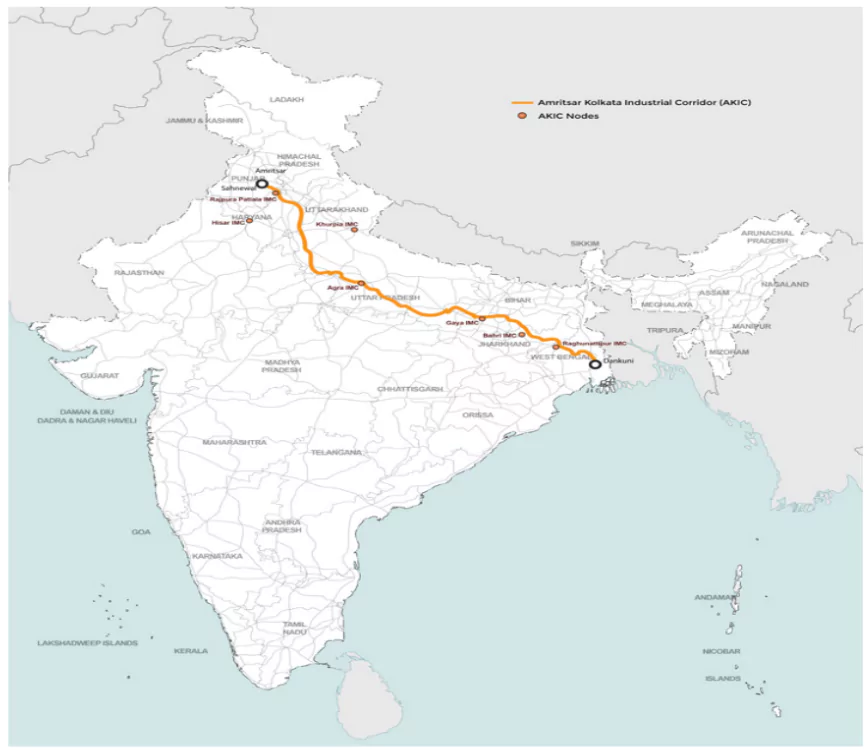 Key Infrastructure Project
Key Infrastructure Project
- Amritsar Kolkata Industrial Corridor
- Industrial Node at Gaya: Supports industrial development and integrates cultural heritage with modern economic centers (“Vikas bhi Virasat bhi”).
- Expressways: Patna-Purnia, Buxar-Bhagalpur, Bodhgaya, Rajgir, Vaishali, and Darbhanga spurs.
- Bridge: Additional 2-lane bridge over the Ganga at Buxar.
- Power Plant: New 2400 MW plant at Pirpainti.
- Cost: Total ₹26,000 crore for connectivity projects and ₹21,400 crore for power projects.
- PM Awas Yojana: Three crore additional houses under the PM Awas Yojana in rural and urban areas in the country have been announced.
- Women-Led Development: Allocation of more than ` 3 lakh crore for schemes benefitting women and girls.
- North East region: More than 100 branches of India Post Payment Bank will be set up in the NorthEast region.
- Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan: The Government will launch the Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan by adopting saturation coverage for tribal families in tribal-majority villages and aspirational districts.
- This will cover 63,000 villages benefitting 5 crore tribal people.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Priority 4: Manufacturing & Services:
- Support for Promotion of MSMEs: The budget provides special attention to MSMEs and manufacturing, particularly labour-intensive manufacturing.
Pooling of credit risk
- It refers to the process where multiple loans or financial assets are combined into a single portfolio to diversify and manage the risk associated with lending or investing.
- This technique is commonly used in finance to reduce the impact of any single loan’s default on the overall portfolio.
|
-
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs in the Manufacturing Sector
- A new credit guarantee scheme for term loans to MSMEs for machinery and equipment purchase without collateral.
- Pooling of Credit Risk: scheme will operate on pooling of credit risks of such MSMEs
- A separately constituted self-financing guarantee fund will provide, to each applicant, guarantee cover up to ` 100 crore, while the loan amount may be larger.
- New assessment model for MSME Credit
- Public sector banks will build their in-house capability to assess MSMEs for credit, instead of relying on external assessment.
- It will be developing or developing a new credit assessment model, based on the scoring of digital footprints of MSMEs in the economy.
- Credit Support During Stress: New mechanism for facilitating continuation of bank credit to MSMEs during their stress period.
- While being in the ‘Special mention account’ (SMA) stage for reasons beyond their control, MSMEs need credit to continue their business and to avoid getting into the NPA stage.
- Credit availability will be supported through a guarantee from a government promoted fund.
 Mudra Loans: The limit of Mudra loans will be enhanced to ₹ 20 lakh from the current ₹ 10 lakh for those entrepreneurs who have availed and successfully repaid previous loans under the ‘Tarun’ category.
Mudra Loans: The limit of Mudra loans will be enhanced to ₹ 20 lakh from the current ₹ 10 lakh for those entrepreneurs who have availed and successfully repaid previous loans under the ‘Tarun’ category. - SIDBI branches in MSME clusters: SIDBI will open 24 new branches this year, expanding to 168 out of 242 major MSME clusters within 3 years.
- MSME Units for Food Irradiation, Quality & Safety Testing:
- Financial support for setting up of 50 multi-product food irradiation units in the MSME sector will be provided.
- Setting up of 100 food quality and safety testing labs with NABL accreditation will be facilitated.
- Measures for promotion of Manufacturing & Services
- Internship in Top Companies:
- A new scheme (5th scheme under the Prime Minister’s package) for internships in 500 top companies for 1 crore youth over 5 years, with an allowance and one-time assistance.
- An internship allowance of ` 5,000 per month along with a one-time assistance of ` 6,000 will be provided.
- Industrial Parks:
- Offshore Mining of Minerals: The government will launch the auction of the first tranche of offshore blocks for mining, building on the exploration already carried out.
Priority 5: Urban Development
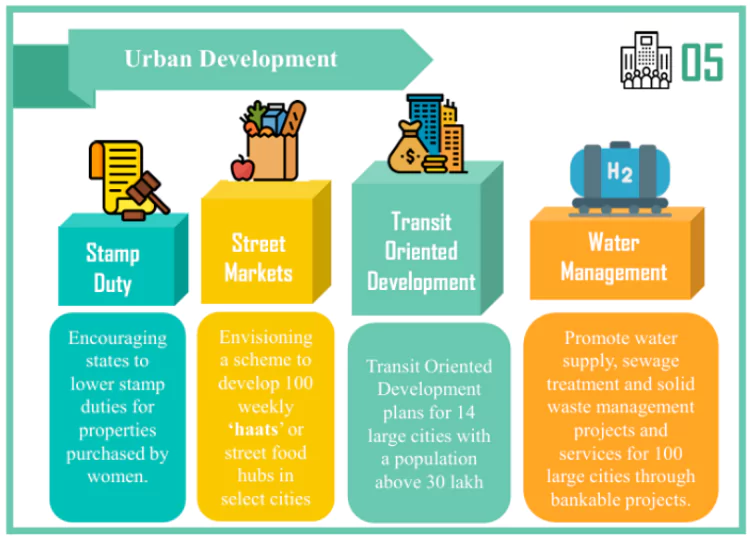
- Stamp Duty: Those states will be encouraged by the Union Government which continue to charge high stamp duty to moderate the rates for all, and also consider further lowering duties for properties purchased by women.
- This reform will be made an essential component of urban development schemes.
- Street Markets: Building on the success of PM SVANidhi Scheme in transforming the lives of street vendors, the Government envisions a scheme to support each year, over the next five years, the development of 100 weekly ‘haats’ or street food hubs in select cities.
- Cities as Growth Hubs: In collaboration with states, the Union Government will facilitate development of ‘Cities as Growth Hubs’.
- Achievement Strategy: The development of ‘Cities as Growth Hubs’ will be achieved through economic and transit planning, and orderly development of peri-urban areas utilising town planning schemes.
- Creative Redevelopment of Cities: For creative brownfield redevelopment of existing cities with a transformative impact, the government will formulate a framework for enabling policies, market-based mechanisms and regulation.
- Transit Oriented Development: This Development plans for 14 large cities with a population above 30 lakh will be formulated, along with an implementation and financing strategy.
 Urban Housing: Under the PM Awas Yojana Urban 2.0, housing needs of 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families will be addressed with an investment of ₹ 10 lakh crore.
Urban Housing: Under the PM Awas Yojana Urban 2.0, housing needs of 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families will be addressed with an investment of ₹ 10 lakh crore. -
- Implementation Strategy: This will include:
- Central Assistance: ₹ 2.2 lakh crore in the next 5 years
- Interest Subsidy: To facilitate loans at affordable rates
- Enabling Policies and Regulations: For efficient and transparent rental housing markets with enhanced availability
- Water Supply and Sanitation: The Union Government will promote water supply, sewage treatment and solid waste management projects and services for 100 large cities through bankable projects.
-
- These projects will also envisage use of treated water for irrigation and filling up of tanks in nearby areas.
- Implementation: By the Union Government in partnership with the State Governments and Multilateral Development Banks.
Priority 6: Energy Security
- Research and Development of Small and Modular Nuclear Reactors: Nuclear energy is expected to form a very significant part of the energy mix for Viksit Bharat. Towards that pursuit, the government will partner with the private sector for:
-
- Setting up Bharat Small Reactors
- Research & development of Bharat Small Modular Reactor
- Research & development of newer technologies for nuclear energy
- The R&D funding announced in the interim budget will be made available.
- Pumped Storage Policy: A policy for promoting pumped storage projects will be brought out for electricity storage and facilitating smooth integration of the growing share of renewable energy with its variable & intermittent nature in the overall energy mix.
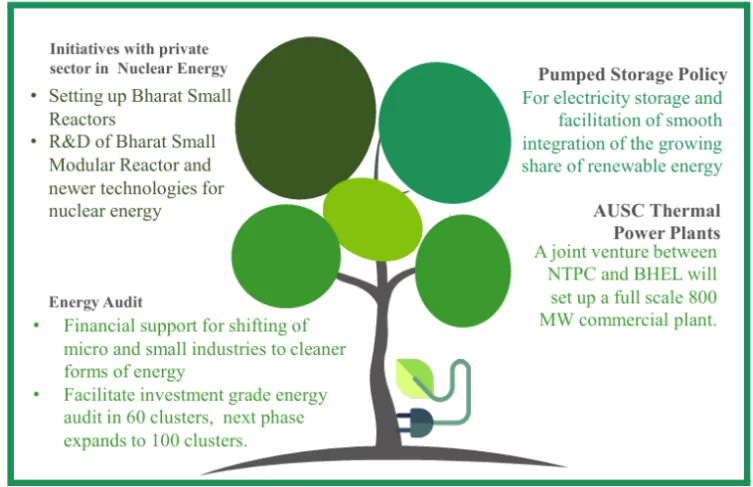 Advanced Ultra SuperCritical (AUSC) Thermal Power Plants: The development of indigenous technology for AUSC thermal power plants with much higher efficiency has been completed.
Advanced Ultra SuperCritical (AUSC) Thermal Power Plants: The development of indigenous technology for AUSC thermal power plants with much higher efficiency has been completed.
- Setting up of Joint Venture: A joint venture between NTPC and BHEL will set up a full scale 800 MW commercial plant using AUSC technology.
- Fiscal Support: The government will provide the required fiscal support.
- Significance: The development of indigenous capacity for the production of high-grade steel and other advanced metallurgy materials for these plants will result in strong spin-off benefits for the economy.
- Energy Transition: A policy document on appropriate energy transition pathways that balances the imperatives of employment, growth and environmental sustainability will be formulated.
- Energy Audit: Financial support for shifting of micro and small industries to cleaner forms of energy
- Facilitate investment grade energy audit in 60 clusters, next phase expands to 100 clusters.
 PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana: In line with the announcement in the interim budget, PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana has been launched to install rooftop solar plants to enable 1 crore households to obtain free electricity up to 300 units every month.
PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana: In line with the announcement in the interim budget, PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana has been launched to install rooftop solar plants to enable 1 crore households to obtain free electricity up to 300 units every month.
- Achievement: The scheme has received positive response with more than 1.28 crore registrations and 14 lakh applications.
- Roadmap for ‘Hard to Abate’ Industries: A roadmap for moving the ‘hard to abate’ industries from ‘energy efficiency’ targets to ‘emission targets’ will be formulated.
- Appropriate regulations for transition of these industries from the current ‘Perform, Achieve and Trade’ mode to ‘Indian Carbon Market’ mode will be put in place.
- Support to Traditional Micro and Small Industries: An investment-grade energy audit of traditional micro and small industries in 60 clusters, including brass and ceramic, will be facilitated.
- Next Phase: The scheme will be replicated in another 100 clusters in the next phase.
- Financial Support: The financial support will be provided for shifting them to cleaner forms of energy and implementation of energy efficiency measures.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Priority 7: Infrastructure

- Tourism: Positioning India as a global tourist destination will also create jobs, stimulate investments and unlock economic opportunities for other sectors.
- In addition to the measures outlined in the interim budget, following measures has been proposed:
- Corridor Projects for Vishnupad Temple at Gaya and Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya in Bihar: Their comprehensive development will be supported, modelled on the successful Kashi Vishwanath Temple Corridor, to transform them into world class pilgrim and tourist destinations.
- Both temples are of immense spiritual significance.
- Rajgir: A comprehensive development initiative for Rajgir will be undertaken.
- It holds immense religious significance for Hindus, Buddhists and Jains.
- The 20th Tirthankara Munisuvrata temple in the Jain Temple complex is ancient.
- The Saptharishi or the 7 hotsprings form a warm water “Brahmakund” that is sacred.
- Nalanda: The government will support the development of Nalanda as a tourist centre besides reviving Nalanda University to its glorious stature.
- Odisha: Its scenic beauty, temples, monuments, craftsmanship, wildlife sanctuaries, natural landscapes and pristine beaches make it an ultimate tourism destination. The Union government will provide assistance for their development.
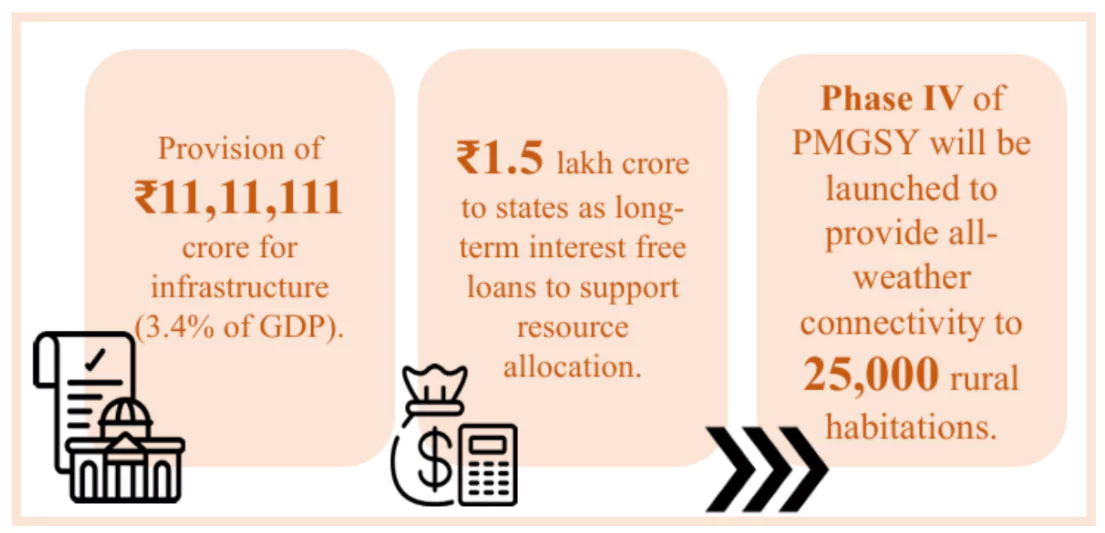 Infrastructure Investment by Central Government: The Budget has provided ₹ 11,11,111 crore for capital expenditure to maintain strong fiscal support for infrastructure over the next 5 years, in conjunction with imperatives of other priorities and fiscal consolidation.
Infrastructure Investment by Central Government: The Budget has provided ₹ 11,11,111 crore for capital expenditure to maintain strong fiscal support for infrastructure over the next 5 years, in conjunction with imperatives of other priorities and fiscal consolidation.
- This would be 3.4% of India’s GDP.
- Irrigation and Flood Mitigation:
- Bihar: This state has frequently suffered from floods, many of them originating outside India. Plans to build flood control structures in Nepal are yet to progress.
 Financial Support: Through the Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme and other sources, the Union Government will provide financial support for projects with estimated cost of ₹ 11,500 crore such as the Kosi-Mechi intra-state link and 20 other ongoing and new schemes including barrages, river pollution abatement and irrigation projects.
Financial Support: Through the Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme and other sources, the Union Government will provide financial support for projects with estimated cost of ₹ 11,500 crore such as the Kosi-Mechi intra-state link and 20 other ongoing and new schemes including barrages, river pollution abatement and irrigation projects. - Survey and investigation of Kosi related flood mitigation and irrigation projects will also be undertaken.
- Assam: It grapples with floods every year by the Brahmaputra River and its tributaries, originating outside India. The Union Government will provide assistance to Assam for flood management and related projects.
- Himachal Pradesh: Suffered extensive losses due to floods last year. The Union Government will provide assistance to the state for reconstruction and rehabilitation through multilateral development assistance.
- Others: The Union Government will provide assistance to Uttarakhand that suffered losses due to cloud bursts and massive landslides and Sikkim that witnessed devastating flash floods and landslides that wreaked havoc across the state.
Priority 8: Innovation, Research & Development

- Anusandhan National Research Fund: The Union Government will operationalize this fund for basic research and prototype development.
- Inclusion of Private Sector: The Union Government will also set up a mechanism for spurring private sector-driven research and innovation at commercial scale with a financing pool of ₹ 1 lakh crore in line with the announcement in the interim budget.
- Space Economy: With the continued emphasis on expanding the space economy by 5 times in the next 10 years, a venture capital fund of ₹ 1,000 crore will be set up.
Priority 9: Next Generation Reforms
- Rural Land Related Actions: These actions will facilitate credit flow and other agricultural services. It will include:
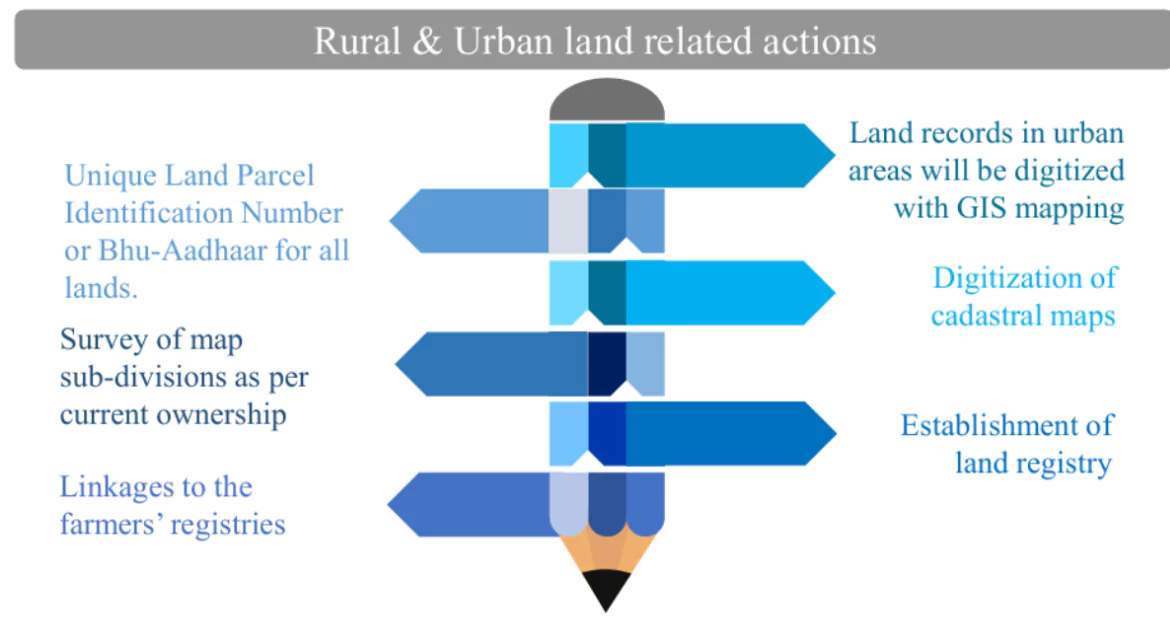 Assignment of Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN) or Bhu-Aadhaar for all lands
Assignment of Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN) or Bhu-Aadhaar for all lands - Digitization of cadastral maps
- Survey of map sub-divisions as per current ownership
- Establishment of land registry
- Linking to the farmers registry
- Urban Land Related Actions: Land records in urban areas will be digitized with GIS mapping.
- An IT based system for property record administration, updating, and tax administration will be established.
- These will also facilitate improving the financial position of urban local bodies.
- Taxonomy for Climate Finance: It will be developed for enhancing the availability of capital for climate adaptation and mitigation. This will support achievements of India’s climate commitments and green transition.
 Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Overseas Investment (OI): The rules and regulations for FDI and OIs will be simplified to:
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Overseas Investment (OI): The rules and regulations for FDI and OIs will be simplified to:
- Facilitate foreign direct investments
- Nudge prioritization
- Promote opportunities for using Indian Rupee as a currency for OIs
- NPS Vatsalya: It is a plan for contribution by parents and guardians for minors.
- On attaining the age of majority, the plan can be converted seamlessly into a normal NPS account.
- New Pension Scheme (NPS): A solution will be evolved which addresses the relevant issues while maintaining fiscal prudence to protect the common citizens.
- Labour Related Reforms:
- Services to Labour: A comprehensive integration of e-shram portals with other portals will facilitate such a one-stop solution.
- Open Architecture Databases: For the rapidly changing labour market, skill requirements and available job roles
- Connection Mechanism: A mechanism to connect job-aspirants with potential employers and skill providers will be covered in these services.
- Shram Suvidha & Samadhan Portal: These will be revamped to enhance ease of compliance for industry and trade.
- Use of Technology: The Union Government will step up adoption of technology towards digitalization of the economy.
- Achievement: Technology has been successfully used for improving productivity and bridging inequality in the Indian economy during the past 10 years.
- Public investment in digital infrastructure and innovations by the private sector have helped in improving access of all citizens, particularly the common people, to market resources, education, health and services.
- Ease of Doing Business: To enhance ‘Ease of Doing Business’, states will be incentivized for implementation of their Business Reforms Action Plans and digitalization.
- The Union Government is already working on the Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0.
- Data and Statistics: For improving data governance, collection, processing and management of data and statistics, different sectoral data bases, including those established under the Digital India mission, will be utilized with active use of technology tools.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
![]() 24 Jul 2024
24 Jul 2024


 Key Infrastructure Project
Key Infrastructure Project
 Mudra Loans: The limit of Mudra loans will be enhanced to ₹ 20 lakh from the current ₹ 10 lakh for those entrepreneurs who have availed and successfully repaid previous loans under the ‘Tarun’ category.
Mudra Loans: The limit of Mudra loans will be enhanced to ₹ 20 lakh from the current ₹ 10 lakh for those entrepreneurs who have availed and successfully repaid previous loans under the ‘Tarun’ category. 
 Urban Housing: Under the PM Awas Yojana Urban 2.0, housing needs of 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families will be addressed with an investment of ₹ 10 lakh crore.
Urban Housing: Under the PM Awas Yojana Urban 2.0, housing needs of 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families will be addressed with an investment of ₹ 10 lakh crore.  Advanced Ultra SuperCritical (AUSC) Thermal Power Plants: The development of indigenous technology for AUSC thermal power plants with much higher efficiency has been completed.
Advanced Ultra SuperCritical (AUSC) Thermal Power Plants: The development of indigenous technology for AUSC thermal power plants with much higher efficiency has been completed.
 PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana: In line with the announcement in the interim budget, PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana has been launched to install rooftop solar plants to enable 1 crore households to obtain free electricity up to 300 units every month.
PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana: In line with the announcement in the interim budget, PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana has been launched to install rooftop solar plants to enable 1 crore households to obtain free electricity up to 300 units every month.

 Infrastructure Investment by Central Government: The Budget has provided ₹ 11,11,111 crore for capital expenditure to maintain strong fiscal support for infrastructure over the next 5 years, in conjunction with imperatives of other priorities and fiscal consolidation.
Infrastructure Investment by Central Government: The Budget has provided ₹ 11,11,111 crore for capital expenditure to maintain strong fiscal support for infrastructure over the next 5 years, in conjunction with imperatives of other priorities and fiscal consolidation.
 Financial Support: Through the Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme and other sources, the Union Government will provide financial support for projects with estimated cost of ₹ 11,500 crore such as the Kosi-Mechi intra-state link and 20 other ongoing and new schemes including barrages, river pollution abatement and irrigation projects.
Financial Support: Through the Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme and other sources, the Union Government will provide financial support for projects with estimated cost of ₹ 11,500 crore such as the Kosi-Mechi intra-state link and 20 other ongoing and new schemes including barrages, river pollution abatement and irrigation projects. 
 Assignment of Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN) or Bhu-Aadhaar for all lands
Assignment of Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN) or Bhu-Aadhaar for all lands  Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Overseas Investment (OI): The rules and regulations for FDI and OIs will be simplified to:
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Overseas Investment (OI): The rules and regulations for FDI and OIs will be simplified to: