National Culture Fund
|
- The Union Minister of Culture reported to the Lok Sabha that the National Culture Fund (NCF) received ₹3.70 crore from non-government sources in the past five years.
National Culture Fund (NCF)
- About: The National Culture Fund was established by the Government of India as a Trust under the Charitable Endowment Act of 1890 and officially set up via a Gazette Notification in 1996.
- Function: To offer a new funding mechanism for arts and culture in India, separate from traditional sources.
- This enables institutions and individuals to directly support arts and culture projects in collaboration with the government.
- Aim: To gather extra resources through Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) to promote, protect, and preserve India’s cultural heritage, including both tangible (physical artifacts) and intangible (cultural practices and traditions) aspects.
- Tax Benefit: Donations to the National Culture Fund are eligible for tax benefits under the Income Tax Act.
- Management: The NCF is overseen by a Council and an Executive Committee that implement its policies.
- Administration: The Council, chaired by the Union Minister of Culture, comprises up to 24 members, including the Chairperson and Member Secretary.
- It includes representatives from the corporate sector, public sector, private foundations, and non-profit organizations to ensure diverse input in decision-making.
- The Executive Committee, led by the Secretary of the Ministry of Culture, manages the administration of the NCF.
|
Bohai Gulf
|
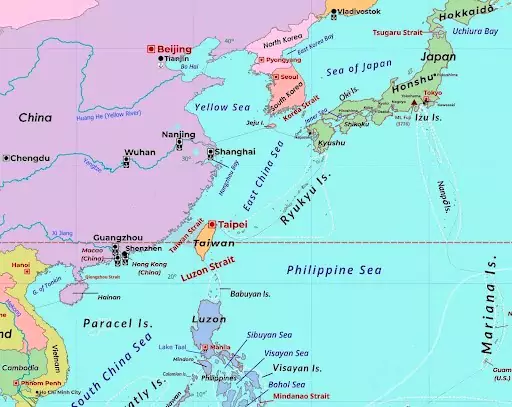
- UNESCO has recently included China’s Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf (Phase II) in its World Heritage List.
Bohai Gulf:
- Location: The Bohai Gulf, also known as the Bohai Sea or Bo Hai, is the innermost part of the Yellow Sea, located on the northeastern coast of China.
- Historically, it was referred to as the Gulf of Chili or the Gulf of Pechili.
- Coverage: It spans approximately 78,000 square kilometers and is one of the busiest seaways in the world due to its proximity to Beijing.
- Border: The gulf is bordered to the northeast by the Liaodong Peninsula and to the south by the Shandong Peninsula.
- Cities: Key cities around the Bohai Gulf include Dalian and Tianjin. Its shores feature Liaodong Bay, Bohai Bay, and Laizhou Bay.
- River: The Yellow River, China’s second-longest river, empties into the gulf.
- Resources: The area is rich in petroleum deposits and features oil refineries and various industries.
|
Pangong Lake
|
- China has completed the construction of a 400-metre bridge, connecting the northern and southern banks of the Pangong Tso.
Pangong Tso:
- Location: Pangong Tso is a landlocked lake situated partly in India’s Ladakh region and partly in Tibet. It spans over 600 square kilometers.
- Cultural Feature: The lake’s name reflects its diverse heritage: “Pangong” in Ladakhi means extensive concavity, while “Tso” is the Tibetan word for lake.
- Geological Origin: The lake is formed from the Tethys geosyncline.
- Geographical Features: The Karakoram Mountain range, which extends across Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, China, and India, with peaks over 6,000 meters including K2, the world’s second-highest peak, terminates at the lake’s northern bank.
- The southern bank is also flanked by rugged mountains that slope towards Spangur Lake.
- The lake’s water, although crystal clear, is brackish and undrinkable.
- It freezes in winter, enabling some vehicular movement on its surface.
- Control of Pangong Tso: China controls nearly two-thirds of Pangong Tso, while about 45 kilometers of the lake are under Indian control.
-
- The Line of Actual Control (LAC) runs north-south, cutting through the western part of the lake, which is aligned east-west.
- The borders between India and China are disputed, and the perception of the LAC varies in different sectors, including Pangong Tso.
|
Bagless Days
|
- The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) has launched a new initiative for students in Classes 6 to 8.
Bagless Days
- About: Bagless days are designated days when students are not required to bring their usual school bags.
- Purpose: These days are designed to provide students with a break from their regular classes and textbooks.
- Learning from Experts: Students will engage in activities conducted by local vocational experts, such as carpenters, gardeners, potters, and artists.
- Teachers will coordinate these activities to help students acquire new skills and gain insights into various professions.
- Significance: They offer students an opportunity to experience and explore the world beyond the classroom.
- Students will participate in hands-on activities, demonstrating how theoretical knowledge is applied in real life.
- These days enable students to understand their community and how various jobs contribute to it.
- Curriculum Themes: The activities during bagless days are organized into three primary themes:
- Science, Environment, and Technology – Exploring various aspects of these fields.
- Local Businesses and Public Offices – Gaining insight into their operations.
- Local Culture, Art, and Historical Practices – Learning about regional traditions and historical practices.
|
Machine Unlearning (MUL)
|
- Policymakers face challenges with the growing complexity of Machine Learning models, including LLMs and deep neural networks.
Machine Unlearning (MUL):
- About: Machine Unlearning (MUL) is a technique for AI systems to selectively forget specific types of data, such as false, discriminatory, outdated, or sensitive information.
- Origin: The concept was introduced by Cao and Yang in their work, “Towards Making Systems Forget with Machine Unlearning.”
- Purpose: MUL seeks to manage the complexities and risks associated with AI handling large volumes of data, which can result in privacy breaches, misinformation, and AI bias.
- Application Example: IBM is actively testing MUL models to enhance accuracy, clarity, and cost-efficiency in removing unnecessary or harmful data from AI systems.
Significance:
- Complexity Management: MUL aids in managing the complexity of AI systems that handle large volumes of data, which can challenge data integrity.
- Privacy and Bias Issues: It tackles issues of AI bias, misinformation, and privacy breaches, especially critical during sensitive periods such as elections.
- Cost and Efficiency: MUL can be a more cost-effective and efficient solution compared to deleting entire datasets and retraining AI models, which is expensive and can decrease accuracy, as shown by IBM’s tests on MUL models.
|
One DAE One Subscription
|
- The Department of Atomic Energy has recently launched the ‘One DAE One Subscription’ (ODOS) initiative.
One DAE One Subscription:
- Purpose: ODOS aims to provide the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and its approximately 60 units with access to national and international research papers and scientific journals through a single subscription.
- Features of ODOS: ODOS will enable DAE and its units to access and publish research papers and journals from multiple sources.
- The initiative seeks to facilitate digital sharing of resources and promote collaborative work across all units.
- Benefits of ODOS: Access to 1,353 Wiley journals (up from 166), with perpetual rights for 2024 and coverage of Article Processing Charges (APC).
- Access to 2,686 Springer Nature titles, including 553 open-access journals, perpetual rights for 2024, archives from 1997 (Springer) and 2012 (Nature), and publication of 281 open-access articles in Springer Hybrid journals without APC.
- Impact of ODOS: ODOS will expand access to a broad array of scientific publications and support research efforts.
- The initiative is anticipated to promote scientific research, drive innovation, and improve the quality of academic publications.
|
Different armed groups of Myanmar
|
- Recently Myanmar’s junta and an ethnic group both asserted control over Lashio’s military command following clashes that began on July 3.
Different armed groups of Myanmar:
- Armed Groups: The Brotherhood Alliance, which includes the Arakan Army (AA), Myanmar National Democratic Alliance Army (MNDAA), and Ta’ang National Liberation Army (TNLA), has made notable territorial advances.
- Strategic locations in Shan State and border trade routes with China have been seized by groups such as the Kachin Independence Army (KIA).
- Regional Dominance: The Arakan Army has gained control over large areas in Rakhine State, influencing local governance and resource management.
- Peace in Rakhine: Achieving peace in Rakhine is vital for infrastructure projects and addressing the Rohingya crisis.
- Southern Advances: Ethnic Armed Organizations (EAOs) like the Karen National Union (KNU) have captured key towns along the Thailand border, impacting military supply lines.
|
![]() 31 Jul 2024
31 Jul 2024