Explore the High Seas Treaty, a game-changer for marine biodiversity. Safeguard oceans and join the mission for sustainable seas with the High Seas Treaty.

High Seas Treaty, also known as the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Agreement, represents a groundbreaking international effort intended to protect marine biodiversity and address the challenges of governance in areas beyond national jurisdiction. Recently, India signed the treaty, reaffirming its commitment to ocean conservation under the framework of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
According to the 1958 Geneva Convention on the High Seas, the high seas refer to parts of the ocean that are not included in any country’s territorial waters or internal waters. These marine regions extend beyond a country’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), which typically stretches 200 nautical miles from the coastline.
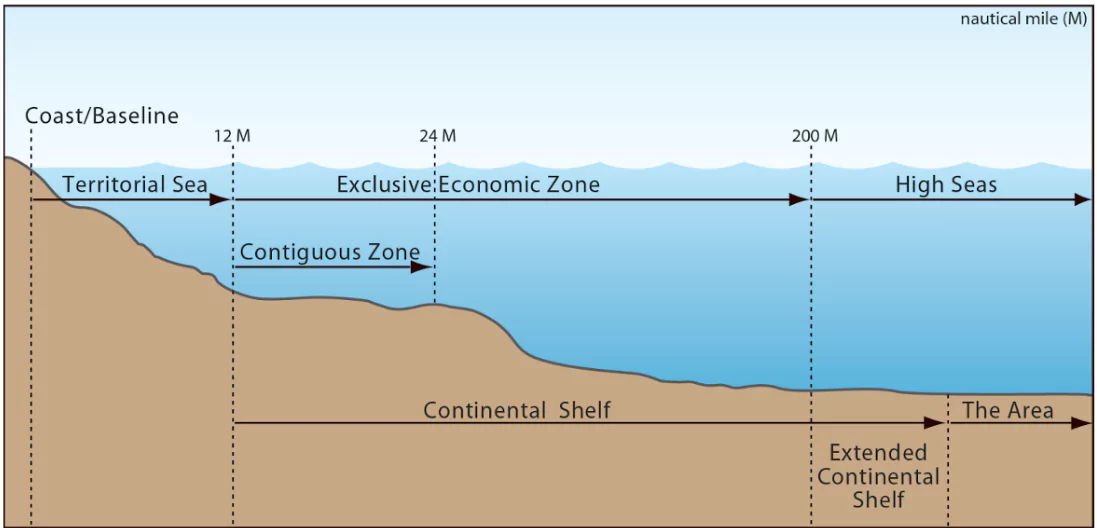
The UN High Seas Treaty is an international agreement that was finalized under the United Nations in March 2023, after almost two decades of negotiations. It aims to create a legal framework that will govern the ocean areas beyond the exclusive economic zones (EEZs) of individual countries. These areas, referred to as the “global commons,” are currently under minimal regulation, leaving them vulnerable to overfishing, climate change, and pollution.
As of 2024, 91 countries have signed the High Seas Treaty. This includes major players such as the European Union (as a Regional Economic Integration Organization) and the State of Palestine (as a non-member observer State), the United States, China, and small island nations. These signatories represent a global commitment to conserving marine biodiversity by showing concern towards marine by signing the treaty opened for signatures on September 20, 2023.
India is a significant maritime nation, and has expressed support for the treaty’s principles but has not yet ratified the agreement. India is deliberating on its domestic policies and international obligations before formalizing its position.
| Countries That Have Signed and/or Ratified the High Seas Treaty | |||||
| Serial No. | Country | Signed | Signature Date | Ratified | Ratification Date |
| 1 | Antigua and Barbuda | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 2 | Argentina | Yes | 18th Jun 2024 | No | – |
| 3 | Australia | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 4 | Austria | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 5 | Bahamas | Yes | 12th Apr 2024 | No | – |
| 6 | Bangladesh | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | Yes | 26th Sep 2024 |
| 7 | Barbados | Yes | 26th Sep 2024 | Yes | 26th Sep 2024 |
| 8 | Belgium | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 9 | Belize | Yes | 22nd Sep 2023 | Yes | 8th Apr 2024 |
| 10 | Bolivia | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 11 | Botswana | Yes | 24th Sep 2024 | No | – |
| 12 | Brazil | Yes | 21st Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 13 | Bulgaria | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 14 | Burkina Faso | Yes | 25th Sep 2024 | No | – |
| 15 | Cabo Verde | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 16 | Canada | Yes | 4th Mar 2024 | No | – |
| 17 | Chile | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | Yes | 20th Feb 2024 |
| 18 | China | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 19 | Colombia | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 20 | Congo | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 21 | Cook Islands | Yes | 22nd Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 22 | Costa Rica | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 23 | Cote d’Ivoire | Yes | 24th Sep 2024 | No | – |
| 24 | Croatia | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 25 | Cuba | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | Yes | 28th Jun 2024 |
| 26 | Cyprus | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 27 | Czechia | Yes | 29th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 28 | Denmark | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 29 | Dominica | Yes | 21st Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 30 | Dominican Republic | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 31 | Ecuador | Yes | 21st Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 32 | Egypt | Yes | 14th Oct 2024 | No | – |
| 33 | Estonia | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 34 | European Union | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 35 | Fiji | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 36 | Finland | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 37 | France | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 38 | Gabon | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 39 | Gambia | Yes | 27th Sep 2024 | No | – |
| 40 | Germany | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 41 | Ghana | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 42 | Greece | Yes | 21st Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 43 | Honduras | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 44 | Hungary | Yes | 21st Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 45 | Iceland | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 46 | India | Yes | 25th Sep 2024 | No | – |
| 47 | Indonesia | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 48 | Ireland | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 49 | Italy | Yes | 22nd Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 50 | Jamaica | Yes | 24th Sep 2024 | No | – |
| 51 | Kenya | Yes | 24th Sep 2024 | No | – |
| 52 | Lao People’s Democratic Republic | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 53 | Latvia | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 54 | Liberia | Yes | 24th Sep 2024 | No | – |
| 55 | Lithuania | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 56 | Luxembourg | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 57 | Madagascar | Yes | 25th Sep 2024 | No | – |
| 58 | Malawi | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 59 | Maldives | Yes | 3rd Sep 2024 | Yes | 24th Sep 2024 |
| 60 | Malta | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 61 | Marshall Islands | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 62 | Mauritania | Yes | 22nd Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 63 | Mauritius | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | Yes | 30th May 2024 |
| 64 | Mexico | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 65 | Micronesia (Federated States of) | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | Yes | 3rd Jun 2024 |
| 66 | Monaco | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | Yes | 9th May 2024 |
| 67 | Morocco | Yes | 21st Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 68 | Nauru | Yes | 22nd Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 69 | Nepal | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 70 | Netherlands | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 71 | New Zealand | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 72 | Nigeria | Yes | 4th May 2024 | No | – |
| 73 | Norway | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 74 | Palau | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | Yes | 22nd Jan 2024 |
| 75 | Panama | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | Yes | 23rd Oct 2024 |
| 76 | Philippines | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 77 | Poland | Yes | 21st Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 78 | Portugal | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 79 | Republic of Korea | Yes | 31st Oct 2023 | No | – |
| 80 | Romania | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 81 | Saint Lucia | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | Yes | 26th Nov 2024 |
| 82 | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 83 | Samoa | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 84 | Sao Tome and Principe | Yes | 24th Sep 2024 | No | – |
| 85 | Seychelles | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | Yes | 13th Apr 2024 |
| 86 | Sierra Leone | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 87 | Singapore | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | Yes | 24th Sep 2024 |
| 88 | Slovakia | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 89 | Slovenia | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 90 | Solomon Islands | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 91 | Spain | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 92 | State of Palestine | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 93 | Sweden | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 94 | Timor Leste | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | Yes | 26th Sep 2024 |
| 95 | Togo | Yes | 22nd Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 96 | Tonga | Yes | 26th Jan 2024 | No | – |
| 97 | Turkiye | Yes | 27th Sep 2024 | No | – |
| 98 | Tuvalu | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 99 | United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 100 | United Republic of Tanzania | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 101 | United States | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 102 | Uruguay | Yes | 29th Jan 2024 | No | – |
| 103 | Vanuatu | Yes | 30th Nov 2023 | No | – |
| 104 | Viet Nam | Yes | 20th Sep 2023 | No | – |
| 105 | Zambia | Yes | 14th Feb 2024 | No | – |
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), adopted in 1982, provides the legal framework for ocean governance. UNCLOS defines EEZs and territorial waters, but it does not adequately address the conservation and sustainable use of marine biodiversity on the high seas. The High Seas Treaty fills this gap by building on UNCLOS to ensure the protection of marine life in international waters.
The BBNJ Agreement is part of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, which is often called the “constitution of the ocean”. It addresses important issues like ocean protection, fairness, environmental damage, climate change and biodiversity loss.
The High Seas Treaty is a significant milestone, but its implementation faces several challenges:
Understanding the High Seas Treaty is essential for UPSC aspirants as it integrates many topics, such as international relations, environmental conservation, and sustainable development.
The High Seas Treaty represents a landmark in international ocean conservation efforts, addressing critical issues related to biodiversity loss, resource exploitation, and climate change impacts. With India’s endorsement, the treaty not only strengthens its environmental leadership but also contributes to a sustainable future for global marine ecosystems. As nations work together under this agreement, the vision of a healthier and more sustainable ocean becomes a promising reality.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
UPSC Exam 2025 Related Articles
UPSC Prelims 2025 Exam
UPSC Notification 2025
UPSC Preparation 2025
UPSC Eligibility 2025
UPSC Exam Pattern
UPSC Syllabus
The High Seas Treaty protects marine biodiversity beyond national waters, promoting conservation, sustainable use, and fair resource sharing.
India's commitment to the High Seas Treaty showcases its role in global ocean governance, aligning with sustainability and blue economy goals.
The EU High Seas Treaty refers to Europe's strong backing for the global agreement aimed at preserving international waters and marine ecosystems.
UNCLOS defines ocean zones and principles, while the High Seas Treaty focuses on conserving and sustainably managing resources in global waters.
The treaty mandates marine protected areas and environmental impact assessments to tackle pollution, overfishing, and climate impacts.
The treaty will be binding 120 days after 60 countries ratify it, marking a global commitment to ocean preservation.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>