A study conducted by researchers in Tanzania’s Ngorongoro Conservation Area (NCA) has offered insights into the reasons behind human-Cape buffalo conflict that occurs across sub-Saharan Africa.
Key Highlights of the Study
- Main Cause of Conflict: The study found that resource competition was the main factor that ignited human-African buffalo conflict.
- Recommendations: Involve local communities in developing and testing mitigation strategies such as chili bombs, drones, and intense light torches.
-
- Implement communal guard groups and avoid crop planting within 500-meter buffer zones near protected areas.
About Cape Buffaloes
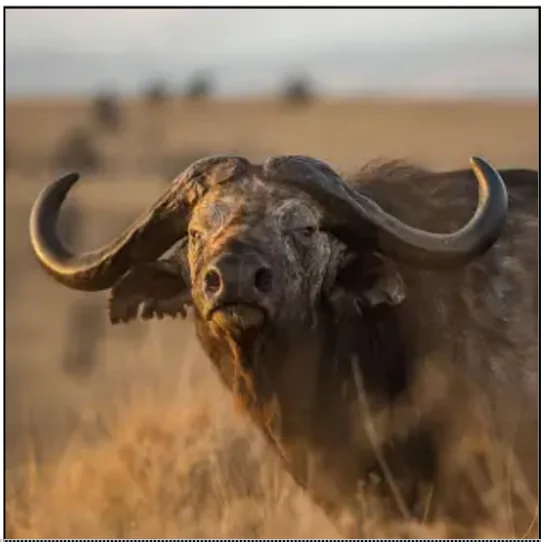

- The Cape Buffalo is one of four subspecies of African Buffalo found south of the Sahara.
- Other subspecies include the Forest Buffalo, West African Savanna Buffalo, and Central African Savanna Buffalo.
- Big Five Member: It is one of Africa’s “Big Five” species, along with the lion, leopard, elephant, and rhinoceros.
- Physical Characteristics: They have long, stocky bodies with short, thick legs.
- Adult buffalo horns have fused bases forming a continuous bone shield across the head, known as “boss”.
- Habitat: Found in swamps, floodplains, mopane grasslands, and forests of Africa’s major mountains.
- Behavior and Social Structure: Cape Buffaloes are active both day and night.
- They are social animals living in herds with related females and their offspring, maintaining a linear dominance hierarchy.
- Distribution: Found across the savannas of East and Southern Africa.
- Diet: They are strictly herbivorous, feeding on grasses and leaves.
- Special Abilities: Excellent swimmers, often crossing rivers to access better grazing areas.
- Conservation Status: Listed as “Near Threatened” by IUCN.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
About Sub-Saharan Africa
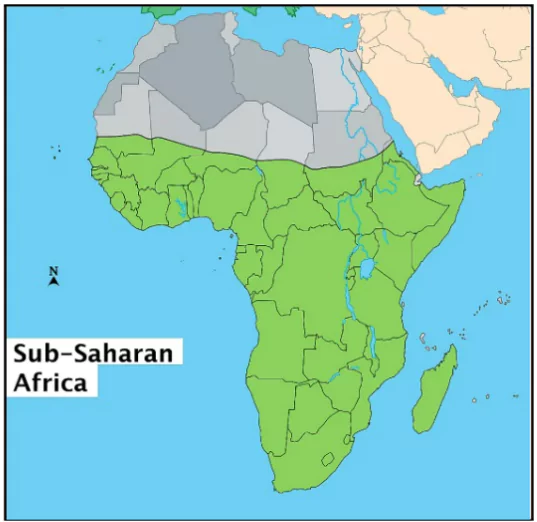
- Geographical Location: A vast region in Africa, south of the Sahara Desert.
- Diverse Landscapes: Encompasses various landscapes, including rainforests, savannas, deserts, and mountains.
- Vegetation:
- Rainforests: Lush, dense forests with diverse plant life, found in regions with high rainfall.
- Savannas: Grasslands with scattered trees, supporting a wide range of wildlife.
- Deserts: Arid regions with sparse vegetation, adapted to harsh conditions.
- Wildlife:
- Iconic Animals: lions, elephants, giraffes, zebras, and rhinoceroses.
- Diverse Ecosystems: Supports a rich biodiversity, including various bird species, reptiles, and amphibians.
- Countries: Includes nations like Nigeria, South Africa, Ethiopia, Kenya, Tanzania, Congo, Angola, and many more.
- Challenges: Faces significant challenges, including poverty, disease, conflict, and environmental degradation.
![]() 7 Dec 2024
7 Dec 2024


