Recently, a winter storm hit the United States, leading to mass school closures, dangerous road conditions and power cuts.
About Polar vortex
- Definition: It is a large low-pressure and cold air system that surrounds the Earth’s poles.
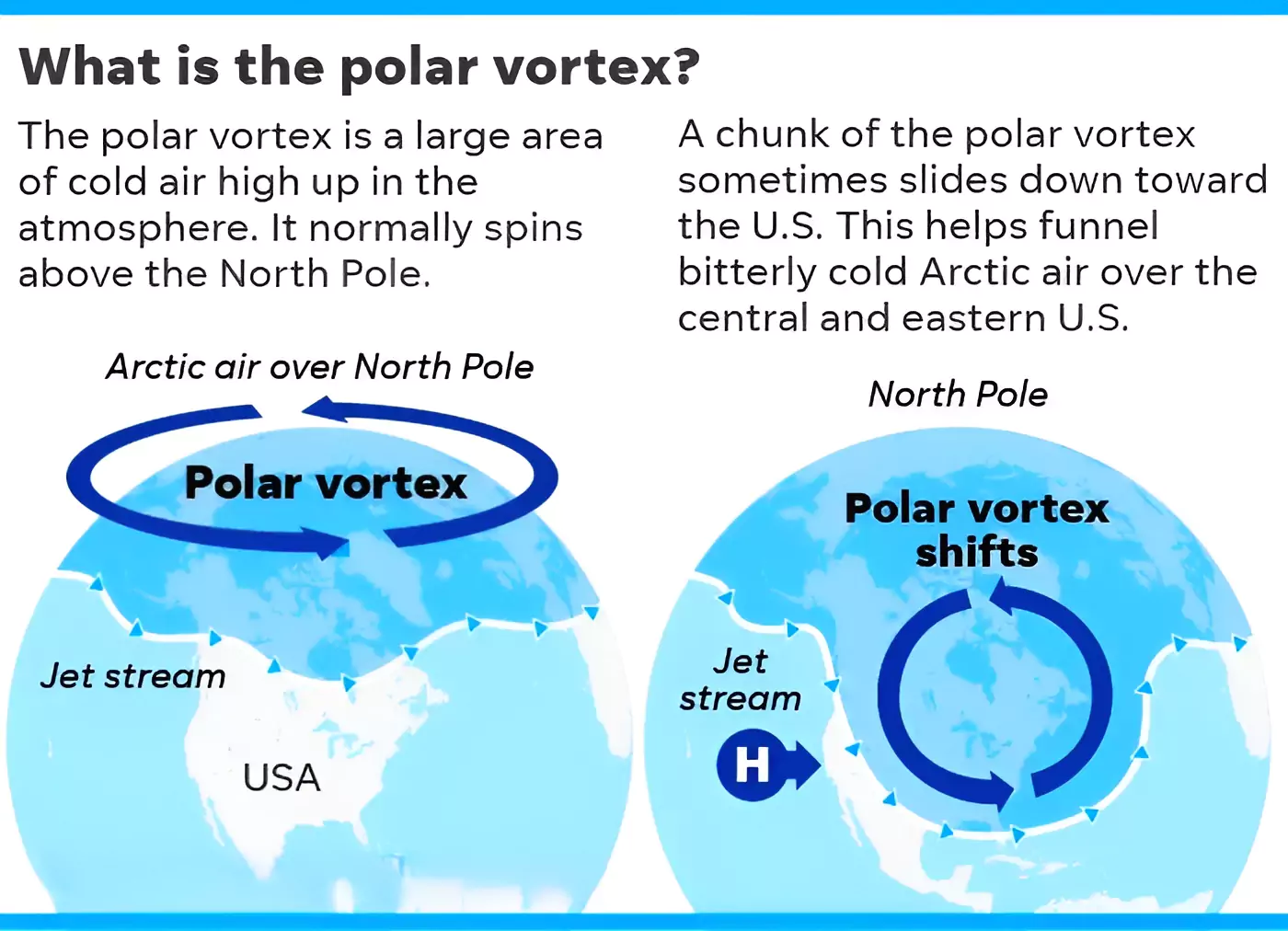 It always exists near the poles but becomes stronger in winter and weaker in summer.
It always exists near the poles but becomes stronger in winter and weaker in summer.- The term “vortex” refers to the counter-clockwise flow of air, which keeps cold air confined near the poles.
- Types of Polar Vortex:
- Tropospheric Polar Vortex: Found in the lowest atmospheric layer (up to 10-15 km), where most weather events occur.
- Stratospheric Polar Vortex: Found at higher altitudes (15-50 km), strongest during autumn and disappears in summer.
- Key Features of the Polar Vortex
- Northern Hemisphere Vortex
- Has two main centers:
- Near Baffin Island, Canada.
- In northeastern Siberia.
- Southern Hemisphere Vortex
- Typically located around the South Pole.
- Stronger and more stable compared to the northern vortex, making it less likely to wobble.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
How Does the Polar Vortex Work?
- Constant Spin: The vortex spins counter-clockwise around the North Pole throughout the year.
- Seasonal Shifts
- In summer months, the vortex sits at higher latitudes.
- In winter months, it shifts southward.
How Does the Polar Vortex Cause Extreme Cold?
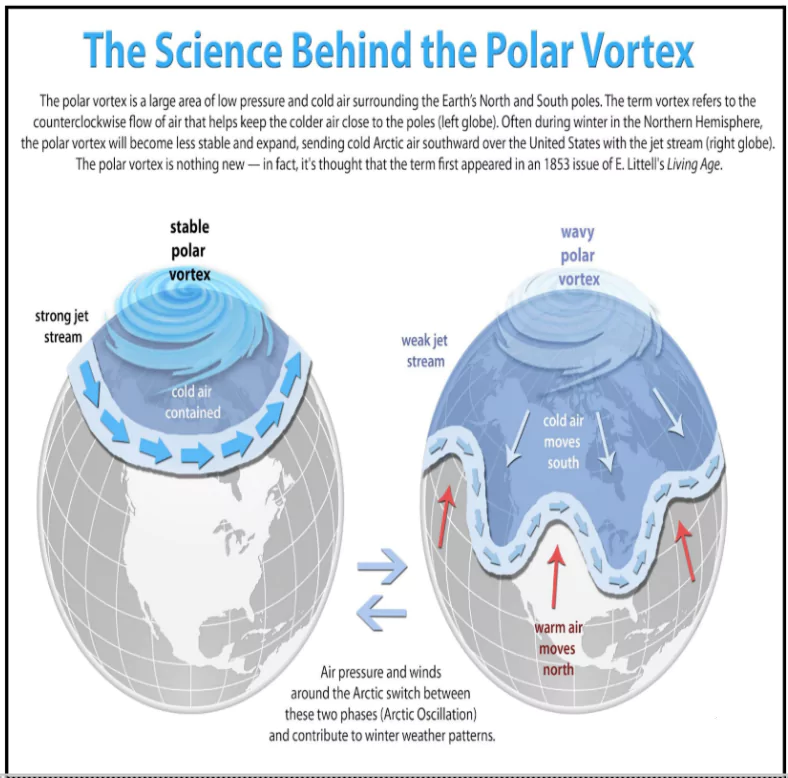
- When the polar vortex weakens, cold Arctic air moves south, bringing freezing temperatures to regions like the US, Europe, and Asia.
- Role of the Jet Stream
- A strong polar vortex keeps the jet stream stable, trapping cold air in the north and keeping warm air in the south.
- When the polar vortex is strong, the polar jet stream locks bitterly cold, dry air in place over the Arctic. When strong, these winds essentially act as an unscalable wall that frigid air cannot breach.
- However, parts of this “wall of wind” can become vulnerable when certain atmospheric conditions build into place.
- A weakened polar vortex makes the jet stream wavy, allowing cold Arctic air to move south, sometimes as far as Florida (U.S).
- Impact of High-Pressure Systems: A strong area of high pressure near the Arctic disturbs the polar vortex.
-
- Strong high pressure that develops in the atmosphere surrounding the North Pole can “squish” the polar vortex farther south, into places like North America or Europe and Asia.
- High-pressure systems can disrupt the jet stream, pushing the cold air even farther south, leading to extreme cold in unusual areas.
Image of Global Warming on the Polar Vortex
- Global warming impacts the polar vortex, causing changes in weather patterns and leading to extreme cold events.
- More Extreme Cold Spells
- Even though global temperatures are rising, warming in the Arctic can lead to more cold weather in some regions.
- This happens because warmer temperatures in the Arctic make the polar vortex more unstable, allowing cold air to move south.
- Faster Arctic Warming
- The Arctic is warming faster than the rest of the world, a phenomenon called Arctic amplification.
- This makes the polar vortex more likely to cause cold air outbreaks in lower latitudes.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Famous Polar Vortex Events
- 2013- 2014 Event: This event caused low temperature and heavy snowfall across Canada and eastern US.
- 2021 Texas event: This polar vortex caused freezing temperatures in Texas in February.
-
- The low temperature remained for 9 days.
![]() 8 Jan 2025
8 Jan 2025

 It always exists near the poles but becomes stronger in winter and weaker in summer.
It always exists near the poles but becomes stronger in winter and weaker in summer.