French President Emmanuel Macron announced that France will officially recognise the State of Palestine in September 2025 at the UN General Assembly, becoming the first G7 country to do so.
- Macron called the recognition a step toward reviving the two-state solution, with Israel and Palestine coexisting in peace and security.
A state is a political entity characterized by four essential elements
- Population
- Territory
- Government,
- Sovereignty.
A nation is a group of people united by shared culture, language, history, or ethnicity.
- A state may include one or multiple nations. It is more of a socio-cultural and emotional identity.
- Nations may or may not have political sovereignty.
- Example: The Kurds are a nation without a state.
|
- He reiterated the need for:
- Immediate ceasefire in Gaza
- Demilitarisation of Hamas
- Humanitarian aid and rebuilding of Gaza
- Mutual recognition: Palestine must recognise Israel; Israel must accept Palestinian sovereignty.
Origin of Palestine
- Palestine is a historic region in the Middle East, located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River. It holds deep religious significance for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
- Over time, the region was ruled by various empires—Babylonians, Persians, Romans, Islamic Caliphates, and the Ottoman Empire (1517–1917).
- After World War I, Britain took control under a League of Nations mandate (1923), which included provisions for a Jewish homeland.
- In 1947, the United Nations proposed partitioning the land into separate Jewish and Arab states, with Jerusalem as an international city. This marked a turning point in the modern Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
- Today, the Palestinian Territories refer mainly to the West Bank and Gaza Strip, under complex and disputed governance involving Israel and Palestinian authorities.
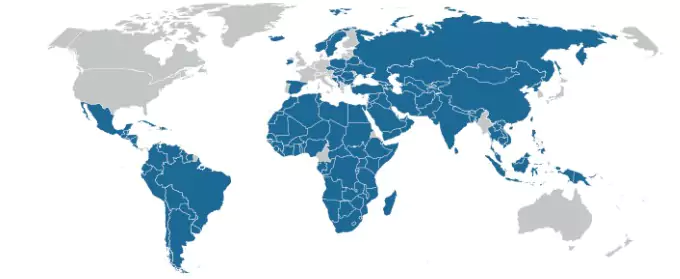
Current Recognition Status
- 146 out of 193 UN member states now recognise the State of Palestine.
- Support comes largely from: Asia, Africa, Latin America, and much of the Arab world.
- Still not recognised by: USA, Canada, most of Western Europe, Japan, South Korea, and Australia.
- Full UN membership requires Security Council approval. In April 2024, the United States vetoed Palestine’s full membership bid.
What is the Two-State Solution?
- Core idea: Partition historic Palestine into two states—one for Jews (Israel) and one for Arabs (Palestine)—as a pathway to lasting peace.
- This would mean the creation of a sovereign, independent Palestinian state, existing alongside Israel, and enjoying full rights under the UN Charter.
UN Special Commission on Palestine (UNSCOP) Plan
- UNSCOP proposed a new partition plan—UNGA Resolution 181:
- 56% of the land to Jews (who were 32% of the population)
- Remaining to Arabs
- Jerusalem to be internationally administered
- Arabs rejected; Zionists accepted and unilaterally declared Israel on May 14, 1948, leading to the first Arab-Israeli war.
|
What It Means
- Acknowledging Palestinian sovereignty within pre-1967 borders
- Full diplomatic relations, including hosting a Palestinian embassy
- Symbolic support for statehood, with little immediate legal or economic change
India’s Policy towards Palestine
- In 1974, India became the first Non-Arab State to recognize Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) as the sole and legitimate representative of the Palestinian people.
- In 1988, India became one of the first countries to recognize the Palestinian State.
- In 1996, India opened its Representative Office in Gaza, which was later shifted to Ramallah in 2003.
- In 2011, India voted in favour of Palestine becoming a full member of UNESCO.
- Voting Pattern: India has voted in favour of 54 resolutions and abstained on 8 resolution over last 5 years on resolutions related to Israel – Palestine issue in UNGA.
- De-hyphenation policy : It refers to India’s approach of engaging with Israel and Palestine separately, treating each bilateral relationship independently based on its own merits.
- Earlier, India’s foreign policy was largely pro-Palestine.
- However in recent years, India has sought to strengthen ties with Israel (especially in defence and technology) while maintaining its traditional support for the Palestinian cause thus, de-hyphenating the two relationships.
|
![]() 26 Jul 2025
26 Jul 2025

