The Narmada River, a major west-flowing river of India, originates from Amarkantak in Madhya Pradesh and flows through Maharashtra and Gujarat. It spans 1,312 km, has 41 tributaries, flows in a rift valley, supports major dams like Sardar Sarovar and Indira Sagar, and holds cultural, spiritual, and economic importance.

The Narmada River is one of the most important rivers in India. It is the largest west-flowing river of the peninsular region. This river has played a vital role in the culture, economy, and environment of the regions it flows through. The river is also known for its scenic beauty and spiritual significance.
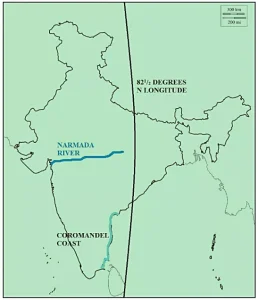
The Narmada river origin is in the Amarkantak hills, located in the Anuppur district of Madhya Pradesh. The river begins from a small reservoir called the Narmada River source Amarkantak, at an elevation of 1,057 meters. From here, it flows through Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat before emptying into the Arabian Sea.
A map shows its origin at Amarkantak, its westward course through central India, and its entry into the Arabian Sea. The map also highlights its tributaries, dams, and key towns along the river, helping in understanding its geographical and economic importance.
The River continues to be a vital waterway in India. Its natural beauty, historical significance, and the development of dams and projects make it an essential part of the country’s geography. Efforts to balance development with environmental protection remain ongoing, ensuring the river remains a lifeline for generations to come.
The Narmada river course runs between the Vindhya and Satpura ranges. The river flows westward, making it one of the few west flowing rivers of India. Along its journey, it passes through plains, uplands, and gorges, including the Hoshangabad plains, Dhar upland, and Mandhata gorges. It finally reaches the Gulf of Cambay, north of Bharuch in Gujarat.
The Narmada river length is approximately 1,312 kilometers. The river creates a natural boundary between north and south India. Its basin, known as the Narmada River basin, covers an area of about 98,796 square kilometers. The basin includes parts of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Gujarat, and a small section of Chhattisgarh.
The river has many tributaries. In total, there are 41 tributaries, with 8 joining from the right bank and 11 from the left bank. Major Narmada river tributaries include the Tawa, Banjar, Barna, and Orsang rivers. These tributaries support agriculture and water supply in the regions they pass through.
The most distinct feature of this waterway is that it is a rift valley river Narmada. Most Indian rivers flow over plains, but the Narmada occupies a structural trough. This Narmada rift valley was formed by tectonic faulting between two mountain ranges.
The Narmada valley geography is bounded by:
The river holds special significance in Madhya Pradesh, where it originates. The Narmada River in Madhya Pradesh flows through districts like Jabalpur, Hoshangabad, and Mandla, creating fertile plains. In Gujarat, the Narmada river in Gujarat provides water for irrigation, drinking, and industrial use before reaching the sea.
Several major dams and projects have been built on the Narmada to utilize its water resources. The Sardar Sarovar Dam on Narmada is one of the largest and most well-known. Another important project is the Indira Sagar Dam Narmada, which helps in power generation and irrigation. These projects aim to support agriculture, supply drinking water, and generate electricity.
The construction of large dams has led to controversies. The Narmada Bachao Andolan highlighted the social and environmental concerns caused by the dams. There have also been Narmada Dam Water Disputes between Indian States, as Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat share the river’s waters. These disputes have been resolved through tribunals and agreements, but debates continue on water sharing and displacement issues.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
The River is not only important geographically but also culturally. Many temples are situated along its banks, including Omkareshwar and Maheshwar. Legends say that bathing in the Narmada or its tributaries can cleanse sins. Historically, the river was known as Namade and has been mentioned in ancient texts like the Ramayana, Mahabharata, and Puranas.
Ready to boost your UPSC preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The Narmada River originates from the Amarkantak Plateau in the Anuppur district of Madhya Pradesh.
It flows through Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat.
The total length of the River is approximately 1312 kilometers.
It flows through a narrow depression called a rift valley, situated between the Vindhya and Satpura mountain ranges. This geological feature dictates its westward flow.
The Sardar Sarovar Dam is one of the largest and most significant dams built on the Narmada River in Gujarat.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>