Context:: This article is based on an Editorial “Keep calm: On solar radiation management” which was published in The Hindu. The recently released report of the Climate Overshoot Commission, calls for more research to close crucial scientific and governance gaps before any deliberations on the implementation of Solar Radiation Management (SRM) like technologies.
-
- India experienced its driest August in a century this year. It underscores the constant threat of disrupted weather, economic impact, and the importance of climate mitigation.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Temperature inversion, Heat Balance, Ozone Depletion, Air Pollution.
Relevancy for Mains: Conservation, Environmental Pollution and Degradation and Solar Radiation Management (SRM), its applications and challenges. |
About Solar Radiation Management (SRM):
- A form of climate engineering that aims to reduce global warming by reflecting some of the sun’s energy back into space.
- Cooling of Earth’s Surface: Or simply, Solar Radiation Management blocks some of the incoming solar radiation to cool the earth’s surface.
- Albedo Enhancement: One SRM approach involves increasing the Earth’s albedo, which is its reflectivity. This can be achieved by making surfaces more reflective, like painting rooftops with reflective coatings or deploying reflective materials in deserts
- Advantages of SRM:
- Rapid Cooling: SRM techniques can potentially provide rapid cooling effects, which might help counteract the immediate impacts of global warming.
- Adjustability: SRM allows for the adjustment of cooling by varying the amount of reflected sunlight, providing a degree of control over temperature.
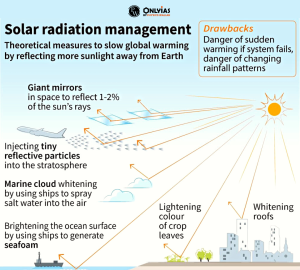
Concerns with Solar Radiation Management:
- Interference & Unavoidable Effects: Solar Radiation Management interferes with natural mechanisms with unavoidable planet-wide effects.
- For example, if an Solar Radiation Management experiment by one country leads to more rain over the Horn of Africa than expected, it could trigger a locust swarm that eventually destroys crops in Pakistan and India.
- Lack of Accountability: There is currently no mechanism that holds a geoengineering government accountable to consequences beyond its borders.
- Less Understanding & Research: There has also been little research on understanding how the world’s myriad weather systems affect each other and their relative sensitivities to interventions such as Solar Radiation Management.
- Preference of Economic growth over Climate Justice: Corporate and political actors are focusing to pursue economic growth at the expense of climate justice.
- Increase Emissions Limits: Mitigation technologies such as carbon capture take resources, focus, and political will away from the most effective strategy — cutting emissions — and increase emissions limits. SRM will only amplify this dilution.
The Way Forward for Solar Radiation Management Solutions:
- Better Understanding: The scientific community needs to understand SRM enough to attempt a deployment.
- Retain as a Solution: Focus should be on retaining Solar Radiation Management in the mix of potential climate mitigation solutions.
- Need to take Actions: The enormity of climate change requires quick and decisive action.
- Time of Implementation: Better solutions need to be implemented as well.
- International Cooperation: SRM is a global issue that requires international cooperation. Nations should work together to establish clear guidelines, governance mechanisms, and principles for responsible SRM research and deployment.
- Public Education: Invest in public education and awareness campaigns to ensure that the public understands the science, risks, and benefits of SRM, reducing misconceptions and fears.
Conclusion:
- When it comes to Solar Radiation Management (SRM), there are important concerns about its effects on our planet. It’s crucial for us to better understand SRM and its potential consequences. We should keep SRM as an option but also prioritize quick action to address climate change. It’s time to focus on implementing better solutions for a sustainable future
![]() 21 Sep 2023
21 Sep 2023
