![]() 20 Jun 2024
20 Jun 2024
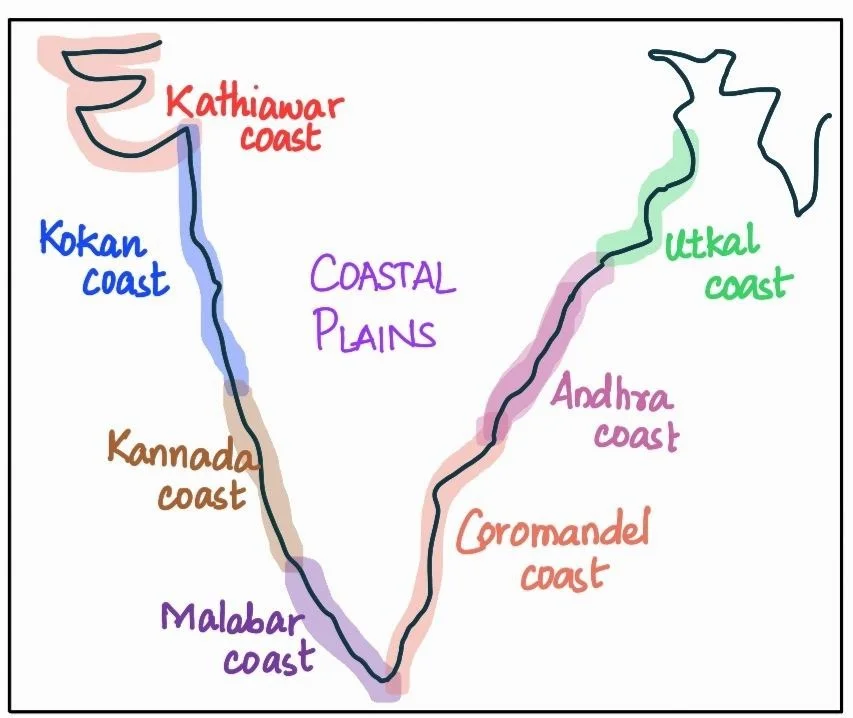
The Peninsular plateau is flanked by stretches of narrow coastal strips, running along the Arabian Sea on the west and the Bay of Bengal on the east.
India’s extensive coastline can be broadly divided into two main regions: the western coastal plains and the eastern coastal plains.
|
Chilika Lake is the largest salt water lake in India. It lies in the state of Odisha, to the south of the Mahanadi delta |
|---|
India’s Island Treasures: Bay of Bengal vs. Arabian Sea Coastal Plains

The Islands
|
Coral polyps are short-lived microscopic organisms, which live in colonies. They flourish in shallow, mud-free and warm waters. They secrete calcium carbonate and their skeletons form coral deposits in the form of reefs. They are mainly of three kinds: barrier reefs, fringing reefs and atolls. The Great Barrier Reef of Australia is a good example of the first kind of coral reef. Atolls are circular or horseshoe-shaped coral reefs. |
|---|
Significance of India’s Physical Features, from Natural Wealth to Coastal Plains
|
Glossary
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>