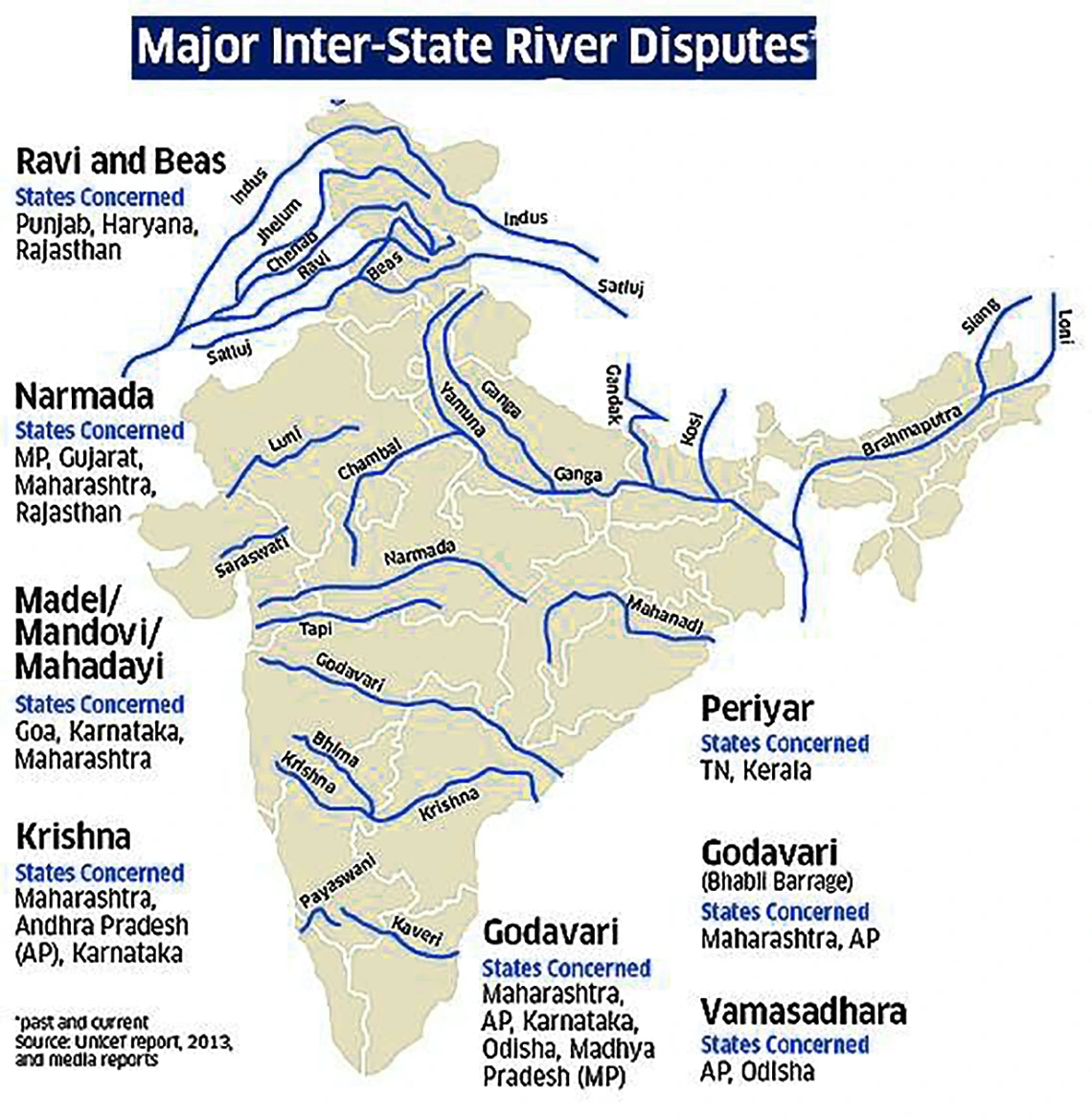
The Interstate River Water Disputes Act of 1956 was legislated under Article 262 of the Constitution of India. Its purpose is to address conflicts related to the utilization, regulation, and allocation of water in interstate rivers or river valleys.

Questionnaire:
|
|---|
Context: The Interstate River Water Disputes between the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu have been simmering for many decades without reaching a mutually acceptable conclusion.
Inter-State River Water Disputes (Amendment) Bill, 2019
|
|---|
| Yes | No |
|
|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>