Context: This article is based on an Editorial “Natural farming needs better prices, markets” which was published in the Hindu. This article is discussing the challenges faced by natural farming (NF) and the steps need to be taken to promote natural farming.
- NF is ‘agriculture as per local ecology and hence also called as agroecology’.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Agroecology and Zero Budget Natural Farming, Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), and Public Distribution System (PDS).
Relevancy for Mains: Agroecology- Its Need, Associated Challenges and the Way Forward |
What are the Challenges Faced by Natural Farming?
- Lack Premium Prices & Protocols: Natural farming practicing farmers do not get premium prices for their products, as differentiated markets, standards and protocols do not exist sufficiently.
- Self Consumption: For many farmers NF products are largely for home consumption.
Steps taken by the Government to Promote Natural Farming
- Participatory Guarantee System (PGS-India): It was launched by the Indian Government in 2011.
- This is a quality assurance initiative that emphasizes active participation of producers and consumers, and operates outside of third-party certification processes.
- Self-Certification Tool (CETARA-NF) for Natural Farming: It was developed by Himachal Pradesh.
- Draft of Differentiation by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS): The BIS has recently released a draft for public comments, on the requirements for NF and labeling NF produce.
- This draft differentiates between NF and organic farming.
- Its aim is to foster common understanding amongst stakeholders, farmers, market players and consumers.
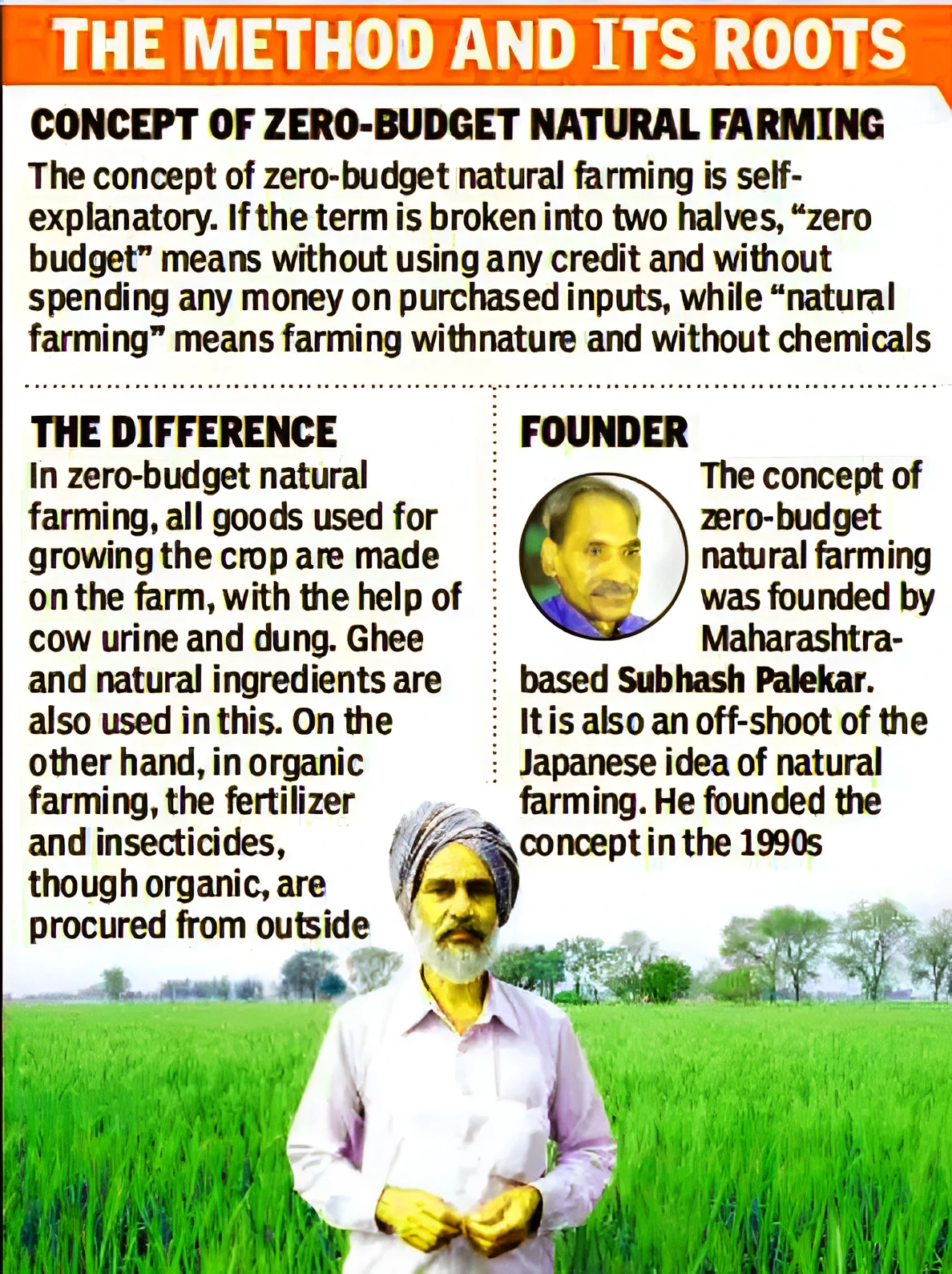
About Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF)
- It is a type of chemical-free farming where the total cost of growing and harvesting plants comes out to be zero. Mr Suresh Palekar coordinated with the Karnataka Rajya Raitha Sangha (KRRS) to form the practices of ZBNF.
- Four Wheels of Zero Budget Natural Farming, are
- Bijamrit: The microbial coating of seeds with formulations of cow urine and cow dung.
- Jivamrit: The enhancement of soil microbes using an inoculum of cow dung, cow urine, and jaggery.
- Mulching: The covering of soil with crops or crop residues.
- Waaphasa: The building up of soil humus to increase soil aeration.
- ZBNF Methods of Insect and Pest Management: Agniastra, Brahmastra and Neemastra
Advantages of Zero Budget Natural Farming
- Beneficial to farmers as it reduces production cost, Increases soil fertility, Biodiversity Conservation, Resources (water and electricity) efficient utilization, Food Produced does not contain harmful chemicals, Climate Resilience, Women’s Empowerment, etc.
Challenges with Zero Budget Natural Farming
- Costly Practice: Many ingredients have to be purchased, imputed value of family labour, rent over owned land, costs of maintaining cows and paid-out costs on electricity and pump sets.
- No Independent Proof of Higher Yield: There are no independent studies to validate the claims that ZBNF plots have a higher yield than non-ZBNF plots.
- Poor Organic Matter Content of Indian Soil: About 59% of soils are low in nitrogen, about 49% are low in phosphorus and about 48% are low or medium in potassium.
- Indian soils are also varyingly deficient in micronutrients, such as zinc, iron, manganese, copper, molybdenum and boron.
- Toxicity of Soil: In certain regions, soils are toxic due to heavy metal pollution from industrial and municipal wastes or excessive application of fertilizers and pesticides.
Need To Do for Promotion of Natural Farming
- Need to develop alternative and differentiated markets.
- Need to develop awareness amongst farmers and consumers.
Expansion of Alternative Markets for the Natural Farming
Public Distribution System (PDS) is a significant market for agricultural commodities.
- The Mid-day meal programme is another market.
- A decentralized, production, procurement, storage and distribution system, focused on local crops and the inclusion of the existing networks of Primary Agricultural Cooperative Societies and Marketing Federations.
- Dedicated haats can be dedicated to certified natural farming produce and backward integration developed.
- Establishment of Consumer Cooperatives in urban/peri-urban areas of major cities.
Successful Projects
- India: In 2022, Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams (TTD), made arrangements with 5,000 Self-Help Groups to source the pesticide-free produce for making offerings to the deities.
- World: The Colombian private network and the Maputo Earth Market (MEM) in Mozambique.
Must Read: Need For Climate Smart Agriculture In India
Conclusion:
There is a need to create awareness among farmers and consumers towards natural farming products and also to motivate farmers for which stable markets and remunerative prices can help.
![]() 30 Dec 2023
30 Dec 2023

