Context:
Scientists are finding that ‘Gut Microbiota may be linked to heart health, some cancers, and even the color of urine.
- In 2012, an international consortium of scientists launched the Human Microbiome Project that provided the first glimpses into the human body’s complex microbial makeup using genome sequencing.
About Human Microbiome Project (HMP)
- Aim: To generate the baseline microbiome data of Indians.
- It will enable tracing trillions of microbes found in Indians, particularly on their skin.
- Initiated by: This Union government-funded, ₹150 crore project was initiated in 2019 by the Department of Biotechnology.
- This study is being led by Pune’s National Centre for Microbial Resource (NCMR), which is a part of the National Centre for Cell Science.
|
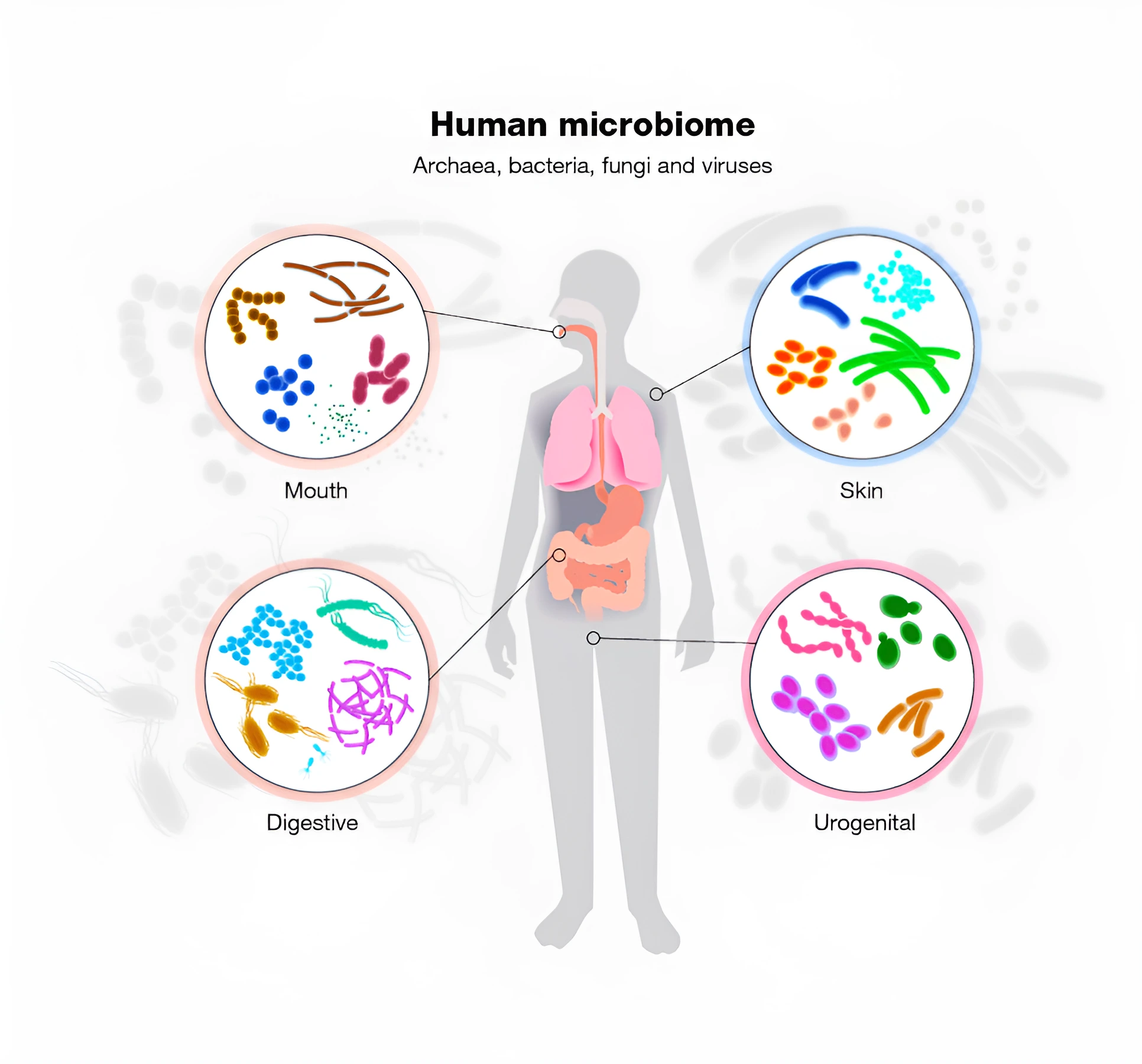
About Human Microbiomes
- The human microbiome is a community of trillions of microorganisms (bacteria, fungi archaea, protists and viruses) that live in our body, especially in the digestive tract.
- These microbes change in response to the environment, diseases and human diets.
- It is a dynamic community that plays a pivotal role in regulating our health and diseases.
Importance of Human Microbiomes
- These microorganisms are dynamic and play a pivotal role in regulating human health and diseases including the way humans digest food, absorb nutrients, develop immunity, etc.
- For example: Autoimmune diseases such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, muscular dystrophy, multiple sclerosis, and fibromyalgia are associated with dysfunction in the microbiome.
- Microbiota stimulate the immune system, break down potentially toxic food compounds, and synthesize certain vitamins and amino acids, including the B vitamins and vitamin K.
- For example, the key enzymes needed to form vitamin B12 are only found in bacteria, not in plants and animals.
About Probiotics
- Probiotics are foods or supplements that contain live microorganisms intended to maintain or improve the “good” bacteria (normal microflora) in the body.
- These are foods (typically high-fiber foods) that act as food for human microflora. Prebiotics are used with the intention of improving the balance of these microorganisms.
Gut Microbes & Diseases
- Cardiometabolic Traits: Researchers identified a link between genetic variants in the ABO blood group and microbial genes involved in metabolizing N-acetylgalactosamine (an amino-sugar).
- This link provides a significance in identification of cardiometabolic traits, including lipid levels and blocks in blood vessels and risk of severe COVID-19 infections.
- Colorectal Cancer: Recently, researchers found that the development of colorectal cancer could be mediated by administering a molecule called trans-3-indoleacrylic acid (IDA) or implanting the microbe Peptostreptococcus anaerobius.
- The effects of IDA could be abolished by deleting two human genes – AHR or ALDH1A3.
- Neuronal Signaling: Gut microbes produce vitamin B12, which could influence neuronal signaling by influencing the availability of free choline.
- Choline is a molecule that neurons use to make a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine.
- Jaundice: The human microbiome could be involved in the metabolism of urobilinogen. A bacterial enzyme, bilirubin reductase (BilR), is responsible for reducing bilirubin to urobilinogen.
- The yellow color of urine comes from a pigment called urobilinogen.
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 18 Jan 2024
18 Jan 2024

