AIF scheme is a Central Sector Scheme offering a medium-long term debt financing facility of Rs.1 lakh crore for funding agriculture infrastructure to support and promote agricultural development, improve productivity, and address challenges faced by farmers, agribusinesses, and the overall agricultural industry.
AIF scheme (Agriculture Investment Funds) is a Central Sector Scheme offering a medium-long term debt financing facility of Rs.1 lakh crore for funding agriculture infrastructure to support and promote agricultural development, improve productivity, and address challenges faced by farmers, agribusinesses, and the overall agricultural industry.
| Importance of AIF in UPSC Syllabus- GS Paper 1, Agricultural Resources, GS Paper 2, Government Policies & Interventions, GS Paper 3, E-Technology in the Aid of Farmers |
|---|
| AIF Full Form | Agriculture Investment Funds (AIF) |
| AIF Scheme Launch Year | July ,2020 |
| AIF Scheme Focus Area | Financial Assistance to Agricultural Infrastructure |
| Nodal Ministry | Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Govt. of India |
| AIF Scheme Time Duration | Financial Year 2020-21 to 2032-33 |
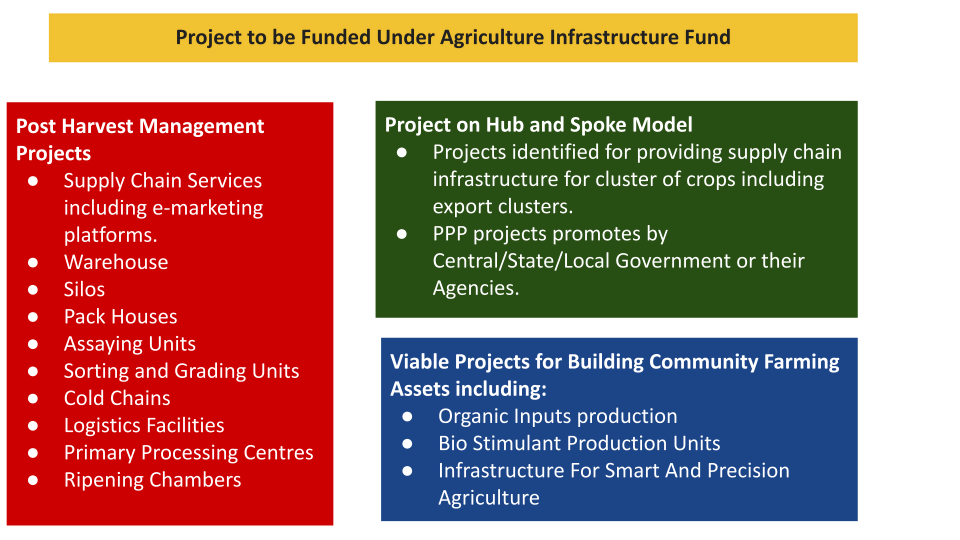
To mobilize a medium long term debt financing facility for investment in viable projects relating to post-harvest management Infrastructure and community farming assets through incentives and financial support in order to improve agriculture infrastructure in the country.
Post Harvest Management- It is a collective term of the activities and techniques used to preserve and protect crops after they have been harvested. It includes activities such as cleaning, sorting, grading, packaging, storage, and transportation.
|
|---|
AIF have multi folded objectives for every participants in agriculture
For Farmers |
|
For Government |
|
For Agri entrepreneurs and startups |
|
Banking Ecosystem |
|
Consumers |
|
| Key Features of AIF Scheme | Details |
| Fund Allocation Under AIF Scheme |
|
| Targeted Beneficiaries of AIF |
|
| Interest Subvention under AIF |
|
| Credit GuaranteeS |
|
| Duration of AIF Scheme |
|
| Hassle free process |
|
| Lending Institutions |
|
| Management |
|


| Strength |
|
| Weakness |
|
| Opportunities |
|
| Threat |
|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>