The Prime Minister inaugurated the 18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas convention at Bhubaneswar, Odisha on January 9, 2025. The theme for this year was the “Diaspora’s contribution to a Viksit Bharat”.
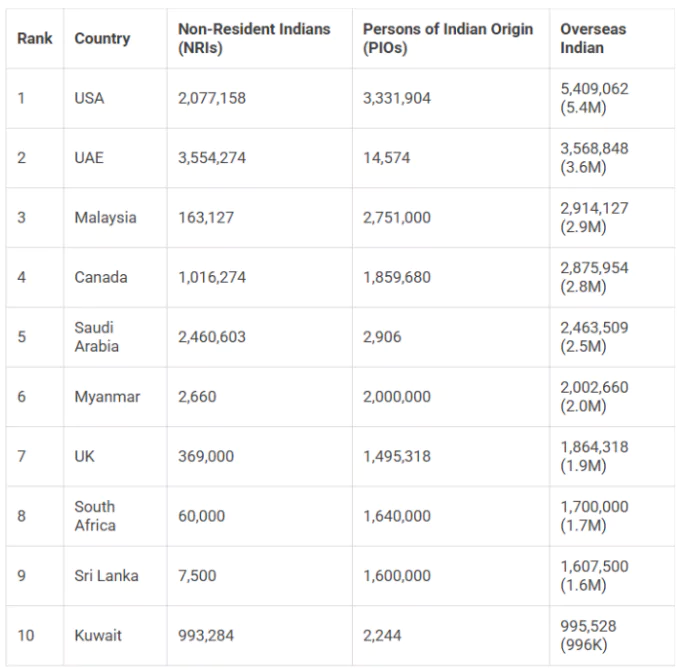
The Indian diaspora can also be categorized based on legal definitions and their connection to India, such as Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs), and Overseas Citizens of India (OCIs).
| Feature | NRI | PIO (Merged into OCI) | OCI |
| Definition | Indian citizens residing abroad. | Foreign citizen of Indian origin. | Foreign nationals registered as OCI. |
| Citizenship | Indian passport holder. | Held foreign citizenship and PIO card. | Foreign citizenship; OCI cardholder. |
| Voting Rights | Yes | No | No |
| Government Jobs | Yes | No | No |
| Visa Requirement | Not required | Required earlier; now merged into OCI. | Visa-free lifelong entry to India. |
| Eligibility for Citizenship | Already an Indian citizen. | 7 years’ residence in India. | 5 years as OCI and 1 year residence. |
The Indian diaspora, with over 35 million individuals spread across 125 countries, plays a crucial role in shaping India’s global influence, economy, and cultural heritage.
The Indian diaspora is a vital bridge between India and the world, contributing to economic growth, cultural preservation, and global influence. In the context of Pravasi Bharatiya Diwas 2025, celebrating the diaspora’s role in shaping a “Viksit Bharat” reinforces India’s commitment to engaging with its global community while acknowledging their invaluable contributions.
The much-awaited Flamingo Festival 2025′ will be conducted at Sullurpeta in Tirupati district of Andhra Pradesh from January 18 to 20.
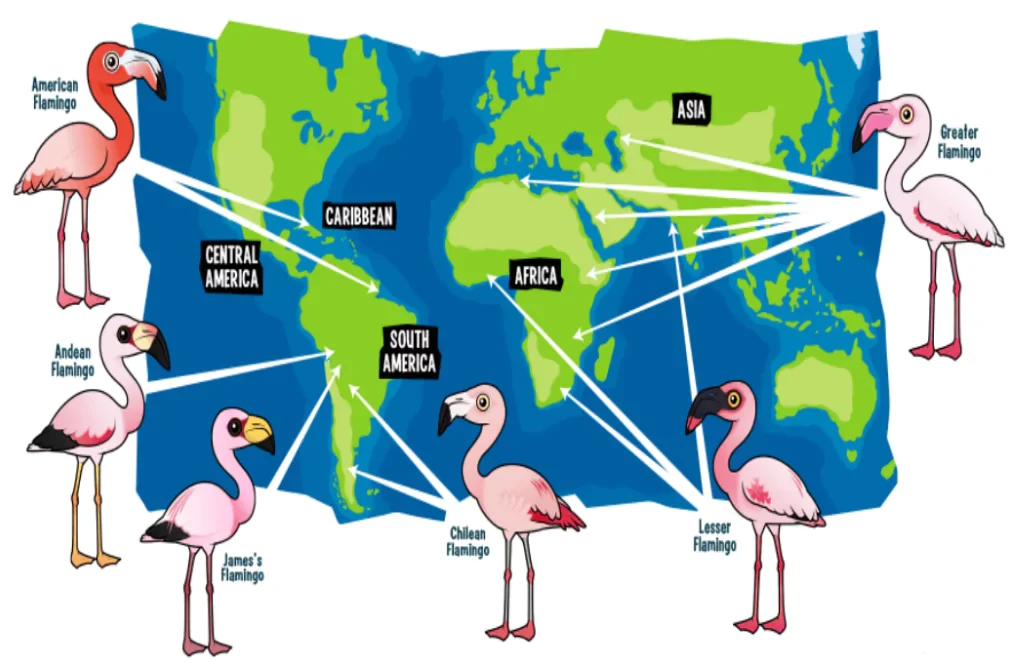
Details about different Flamingo species, their conservation status and features
| Species | Distribution | IUCN Status | Distinctive Features |
| Greater Flamingo (Phoenicopterus roseus) | Africa, Europe, and Asia (India) | Least Concern
CITES → Appendix II |
Largest flamingo species, pale pink plumage |
| Chilean Flamingo (Phoenicopterus chilensis) | South America | Near Threatened | Similar to Greater Flamingo but with a darker pink hue |
| American or Caribbean Flamingo (Phoenicopterus ruber) | Caribbean, South America, and Florida | Near Threatened | Bright pink plumage, long, slender neck |
| Lesser Flamingo (Phoeniconaias minor) | Africa and India | Near Threatened
CITES → Appendix II |
Smallest flamingo species, bright pink plumage |
| Andean Flamingo (Phoenicoparrus andinus) | Andes Mountains in South America | Vulnerable | Yellow legs and feet, red spot between nostrils |
| James’s or Puna Flamingo (Phoenicoparrus jamesi) | Andes Mountains in South America | Near Threatened | All-black flight feathers, unique bill shape |
Nelapattu Bird SanctuaryIntroduction
Uniqueness
Forest Type
Flora
Fauna
|
|---|
External Affairs Minister of India acknowledged the challenges of granting dual citizenship to Indians abroad.
| Benefits of Dual Citizenship | Cons of Dual Citizenship |
|
|
Non-Resident Indians (NRIs)
People of Indian Origin (PIOs)
Difference
|
The World Economic Forum’s bi-annual Future of Jobs Report 2025 edition has been released recently.
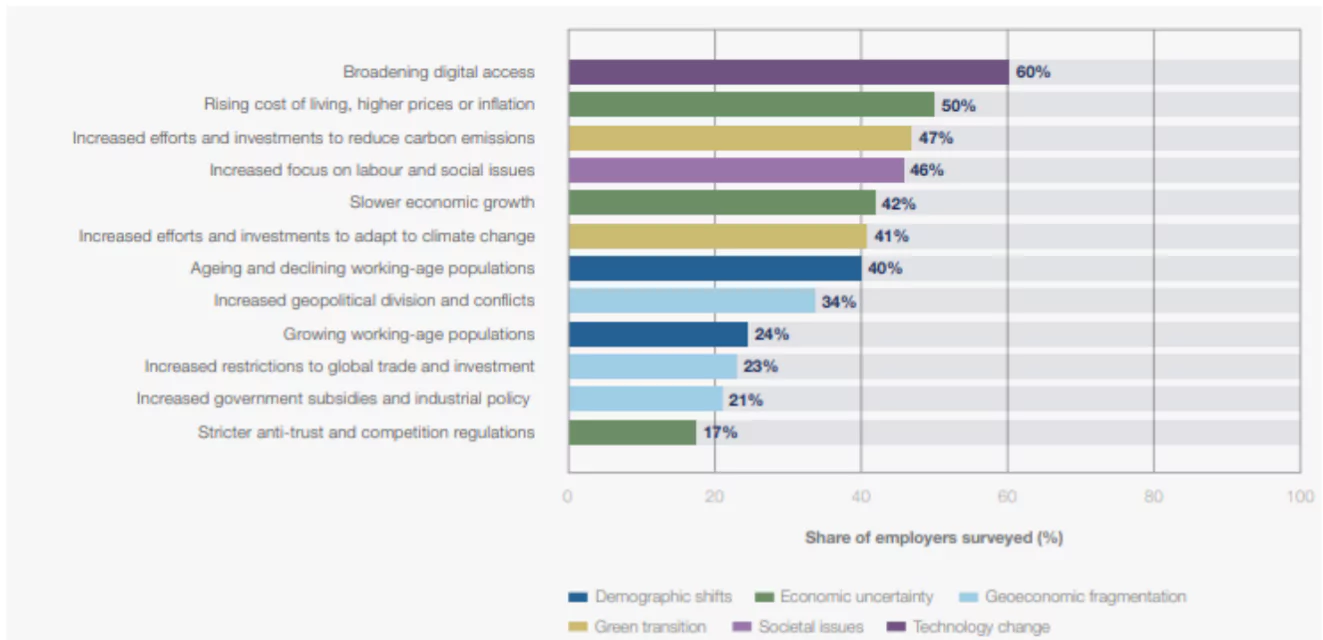 Dataset: The Report is a result of an unique dataset derived from an extensive survey of 1,000 leading global employers, across 22 industry clusters and 55 economies
Dataset: The Report is a result of an unique dataset derived from an extensive survey of 1,000 leading global employers, across 22 industry clusters and 55 economies
Top 10 Fastest Growing Jobs By 2030
|
|---|
The World Economic Forum
|
|---|
The Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP) of NITI Aayog, launched EmpowHER Biz – Sapno Ki Udaan in partnership with New Shop. This is India’s convenience retail chain under its Award to Reward (ATR) program.
Since 2023, the ‘Award to Reward’ initiative under WEP also offers a plug and play framework for stakeholders to develop impactful programs.
The upcoming Maha Kumbh Mela in Prayagraj, scheduled from January 13 to February 26, 2025, is set to be one of the largest human gatherings on Earth, with an estimated 400 million participants.
| Type of Kumbh Mela | Frequency | Locations | Significance |
| Maha Kumbh Mela | It comes every 144 years or after 12 Purna (Complete) Kumbh Mela. | Prayagraj | Largest and most significant of all. |
| Ardh Kumbh Mela | Every 6 years | Prayagraj & Haridwar | Midpoint gathering between Maha Kumbhs. |
| Magh Mela | Annually | Prayagraj | Smaller version of Maha Kumbh, celebrated annually. |
Context: The Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways has announced the launch of a nationwide scheme for ‘Cashless Treatment’ to provide financial aid to road accident victims
Context: The United Nations (UN) released its flagship report, World Economic Situation and Prospects 2025.
Context: The Global Energy Alliance for People and Planet (GEAPP) and the International Solar Alliance (ISA) have strengthened their collaboration by signing ISA’s Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF).
Context: The DRDO Chief in a speech, stressed upon the needs for India to pursue the development of Sixth Generation Aero Engines through co-development with a foreign manufacturer.
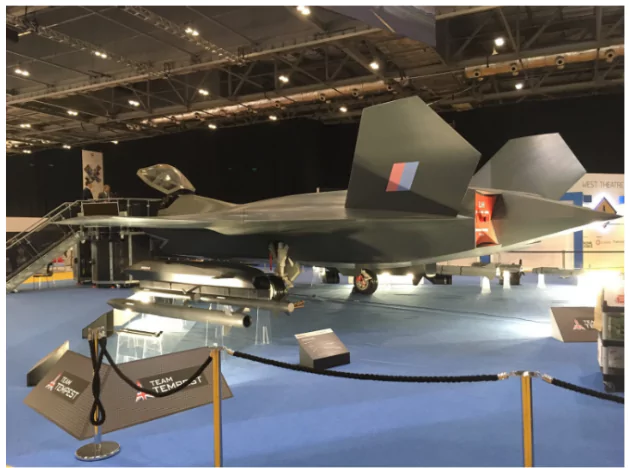 Example:
Example:
Context: Months after granting classical language status to Marathi, the Union government issued an official notification to this effect.
Criteria For Classical Language Status: The Ministry of Culture has rules that must be followed in order to be classified as a classical language in India:
<div class="new-fform">
</div>