Recently, the WEF article, “India Can Be a Global Pathfinder in Digital Health”, was released, which explores how India’s digital healthcare initiatives position the country as a leader in health technology.
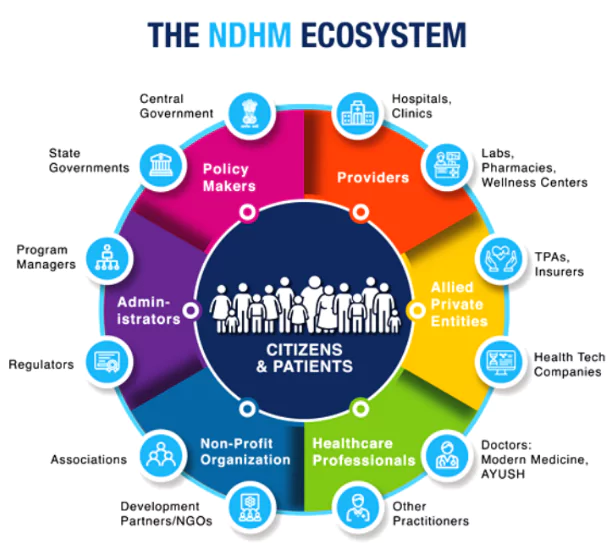 Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS): Incentivizes hospitals, clinics, and healthcare startups to embrace digital technologies, accelerating the transition to a paperless healthcare system.
Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS): Incentivizes hospitals, clinics, and healthcare startups to embrace digital technologies, accelerating the transition to a paperless healthcare system.
 Digi Doctor: A repository containing detailed information about certified doctors, including qualifications and experience.
Digi Doctor: A repository containing detailed information about certified doctors, including qualifications and experience.
| SNOMED CT (Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine- Clinical Terms) and LOINC (Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes) are two coding standards used in healthcare to reduce errors in patient data.
How they work
|
|---|
India’s digital healthcare transformation holds immense potential to enhance healthcare accessibility and efficiency. With continued policy support, infrastructure development, and public-private collaborations, the country is poised to emerge as a global leader in digital health. With growing investments in digital health and technological advancements, India’s healthcare system is expected to evolve into a globally recognized model for digital transformation, setting benchmarks for other developing nations.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA), in collaboration with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoH&FW), had organised the National Tribal Health Conclave 2025, at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.
Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan
Key Features of the Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan:
|
|---|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI) has launched its Internet Governance Internship and Capacity Building Scheme.
National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI)
|
|---|
The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In)
|
|---|
The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI):
|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
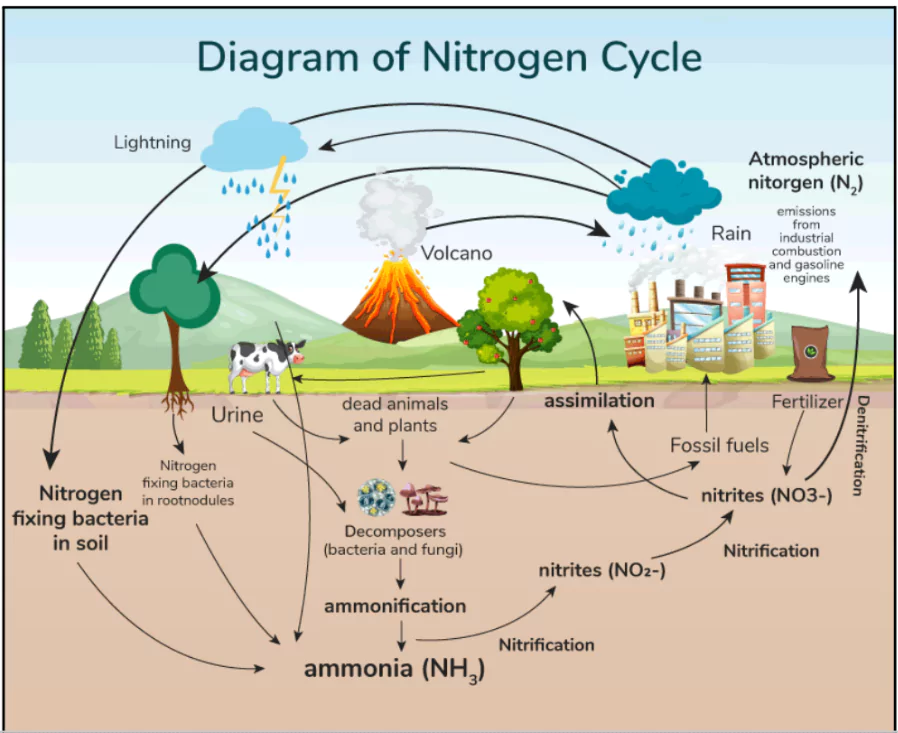
A recent report by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) highlights the alarming rise in nitrogen pollution.
Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE)
|
|---|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) has issued fresh guidelines for applying the Principal Purpose Test (PPT) provisions under Double Tax Avoidance Agreements or DTAAs.
Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) Framework
|
|---|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL), a Hyderabad-based DRDO facility, conducted the first successful scramjet combustor ground test.
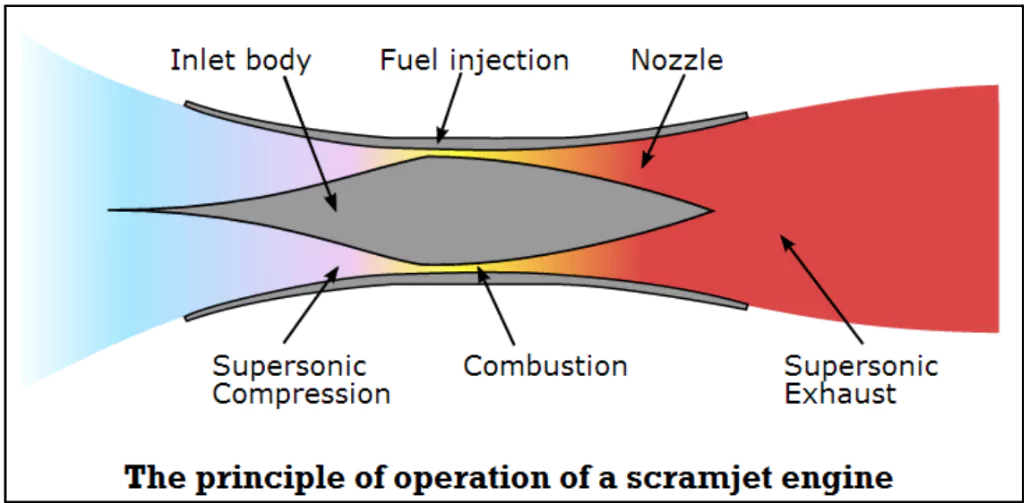
| Aspect | Turbojet | Ramjet | Scramjet |
| Operation | Compresses air using a turbine; burns fuel in the combustion chamber | Uses forward motion to compress incoming air; no external compressor or turbine | Advanced ramjet with combustion occurring in supersonic airflow |
| Speed Efficiency | Subsonic to low supersonic speeds | Supersonic speeds (Mach 3 to 6) | Hypersonic speeds (greater than Mach 5) |
| Combustion Process | Combustion occurs at subsonic airflow inside the engine | Combustion occurs at subsonic airflow using high-speed air compression | Combustion occurs at supersonic airflow inside the engine |
| Fuel Type | Aviation fuel (kerosene or similar hydrocarbons) | Aviation fuel or hydrocarbon-based fuels | Liquid hydrogen (fuel) and liquid oxygen (oxidizer) |
| Moving Parts | Includes turbines and compressors | No moving parts; depends on air compression from forward motion | No moving parts; uses advanced flame stabilization techniques |
| Operational Capability | Suitable for slower speeds and takeoff | Requires external assistance to reach supersonic speeds | Requires external assistance to achieve hypersonic speeds |
| Efficiency | Less efficient at high speeds | Efficient at sustained supersonic speeds | Extremely efficient at hypersonic speeds |
| Applications | Commercial aircraft, military fighter jets | Supersonic missiles, supersonic flight systems | Hypersonic missiles, space vehicles, advanced weapon systems |
| Examples | Subsonic cruise missile Nirbhay. | BrahMos Supersonic Cruise Missile | Hypersonic Glide Vehicles (HGVs) and Hypersonic Cruise Missiles (HCMs) |
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) directed the Uttar Pradesh (UP) government to explain the delay in notifying the Dhanauri water body near Jewar airport as a wetland.
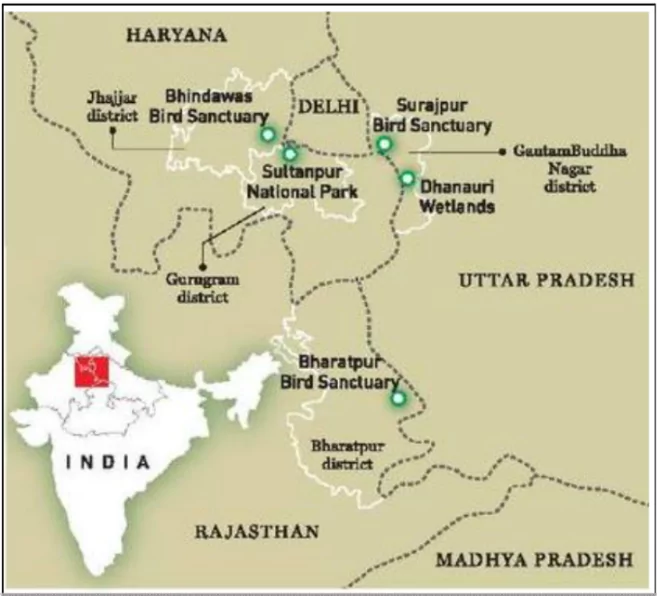
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
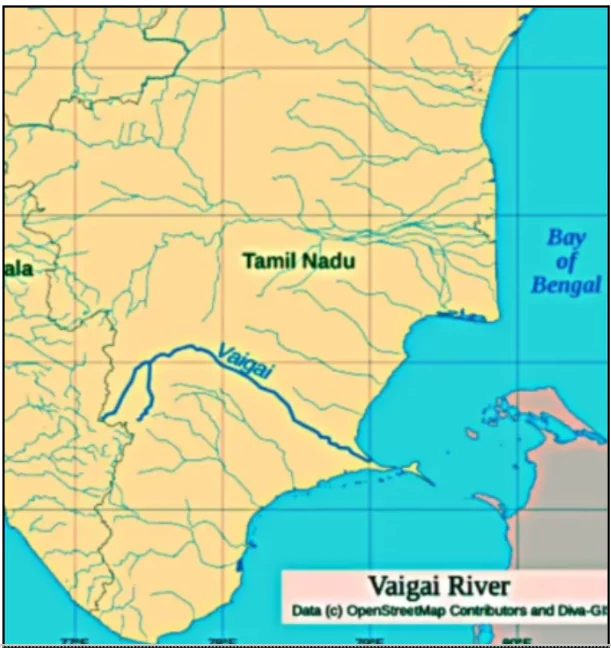
The Madurai Bench of the Madras High Court has directed local bodies in five districts of Tamil Nadu to develop an action plan to rejuvenate the polluted Vaigai River.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
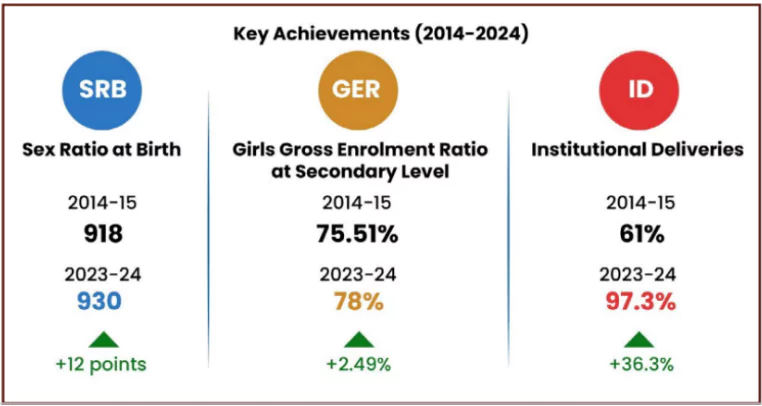
Celebrations marking 10 years of the BBBP will continue from January 22 to March 8, International Women’s Day.

Key Terms Related to BBBP Scheme
|
|---|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The U.S. Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) has recently introduced the tiered framework for licensing and exporting Artificial Intelligence chips.
Impact on India
|
|---|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
A Black Hole named ‘LID-568’ has been found feeding on a surrounding cloud of matter at almost 40-times faster showing Super -Eddington Accretion properties.
About Black Holes
|
|---|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
Context: Recently, the 85th All India Presiding Officers’ Conference (AIPOC) was held in Patna.
About All India Presiding Officers’ Conference (AIPOC)
|
|---|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
<div class="new-fform">
</div>