The recent train tragedy in Jalgaon, Maharashtra has brought to light critical issues surrounding passenger safety and negligence in Indian Railways.
Organizational Structure of Indian Railways
|
Steps taken to improve Low Average Speed of Freight Trains
|
|---|
Steps Taken by the Government to Enhance Passenger Safety in Railways
Committees made to Enhance Railway Safety
|
|---|
While Indian Railways remains a vital part of India’s economy, addressing these challenges through modernization, financial restructuring, and technological advancements is crucial for its long-term sustainability and efficiency.
Kavach: India’s Automatic Train Protection System
|
|---|
| Privatisation of Indian Railways | |
| Pros | Cons |
| Increased Efficiency: Privatization can lead to better management, improved services, and operational efficiency due to competition. | Loss of Accessibility: Private players may focus on profitable routes, neglecting less profitable, remote, or rural areas. |
| Better Infrastructure: Private companies may invest in modern technology and upgrade facilities, leading to improved infrastructure and passenger experience. | Higher Fares: Privatization could lead to fare increases, making travel less affordable for certain sections of society. |
| Innovation & Technology: Private operators may introduce innovative technologies, like high-speed trains, modern ticketing systems, and better maintenance protocols. | Job Losses: There could be job cuts or changes in labor conditions, affecting the livelihood of current railway employees. |
| Boost to Economic Growth: Enhanced efficiency and infrastructure could result in increased trade, tourism, and economic activity. | Profit Motive Over Public Good: Private operators may prioritize profits over passenger welfare, compromising service quality and safety. |
| Reduced Government Burden: The government may be able to reduce the financial burden by transferring the responsibility of maintenance and development to private entities. | Safety Concerns: Privatization could lead to safety risks if cost-cutting measures are taken at the expense of proper maintenance and regulations. |
| Current Scenario:
The Indian government has taken steps towards partial privatization and corporatization of certain services within Indian Railways. For example:
|
|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The Supreme Court has recently delivered a split verdict in the Chhattisgarh burial case.
Division Bench
Constitution Bench
|
|---|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
Recently, Uttarakhand Chief Minister officially rolled out the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) for all residents of the State, except the Scheduled Tribes and natives who have migrated out of the State.
Status of UCC in the World
|
|---|
Notable Supreme Court cases related to UCC
|
|---|
The Uniform Civil Code (UCC) is a complex but crucial step toward ensuring gender justice, national unity, and legal uniformity in India. However, its implementation must be gradual, consultative, and inclusive, respecting India’s cultural and religious diversity. A balanced approach—harmonizing existing personal laws, securing constitutional safeguards for minorities, and promoting legal awareness—will be key to achieving social cohesion and legal equality without triggering unnecessary conflicts.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
Recently the rare corpse flower bloomed simultaneously in Sydney, Australia, and New York, U.S., marking its first bloom in Sydney in over a decade.
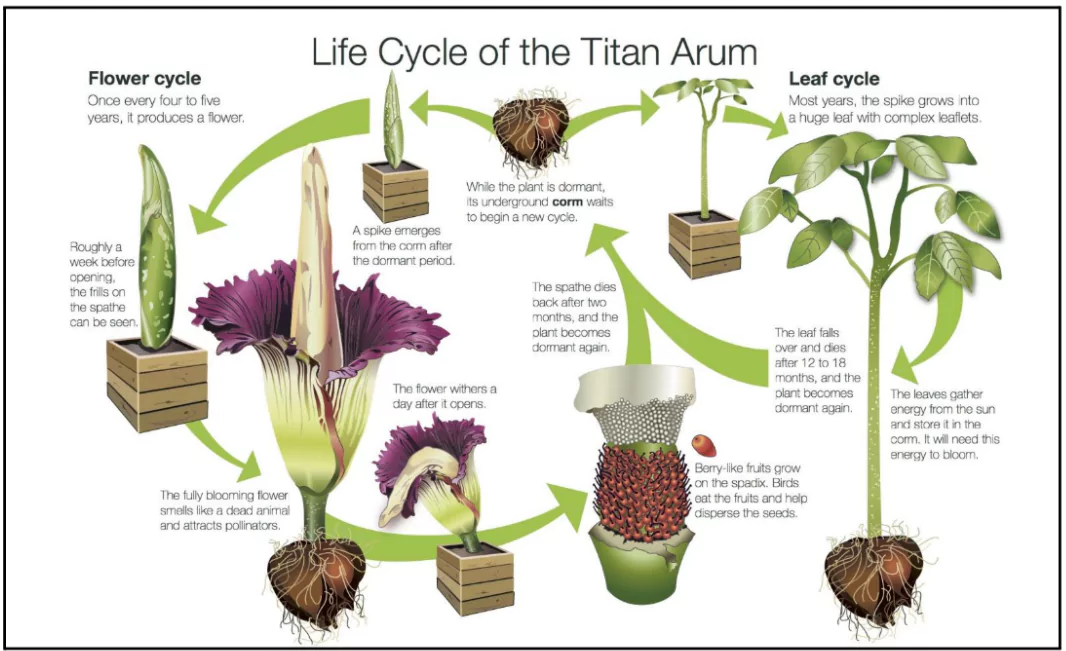 The bloom lasts for only a single day.
The bloom lasts for only a single day.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
Recently , Rwanda-backed M23 rebels claimed to have captured Goma, a strategic city in eastern Congo.
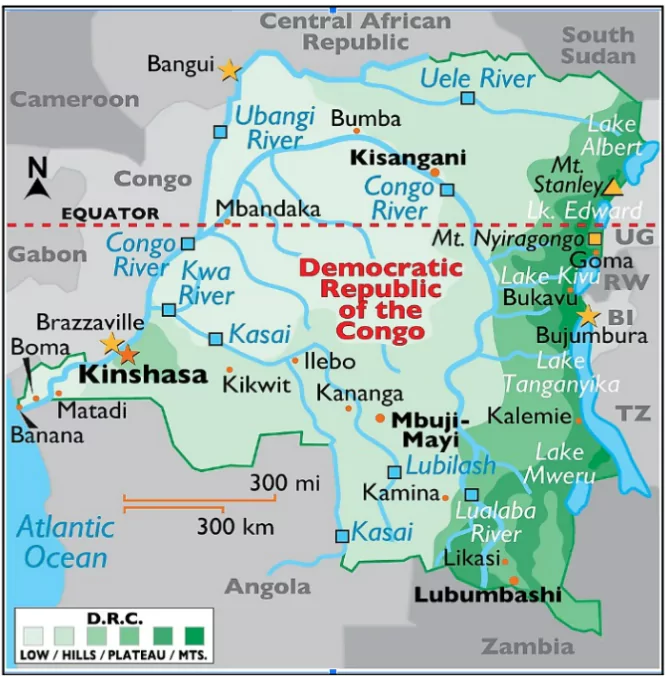 As the Equator passes through it , it lies in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
As the Equator passes through it , it lies in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
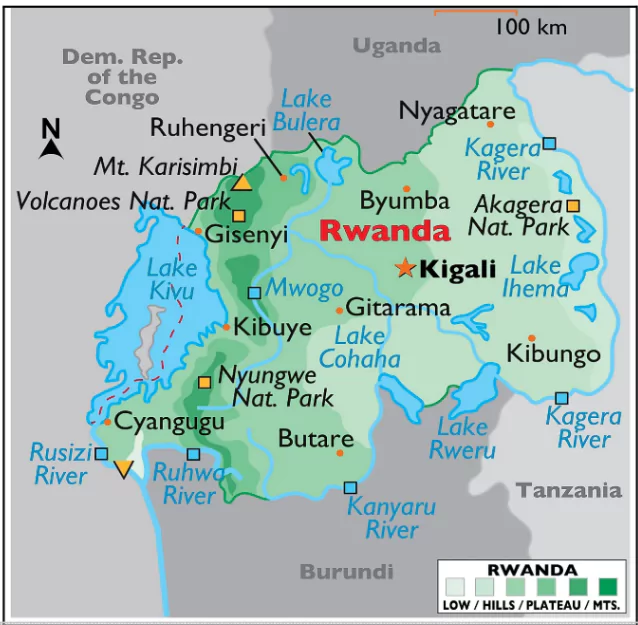 It is located in the African Great Lakes region with the capital at Kigali.
It is located in the African Great Lakes region with the capital at Kigali.Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
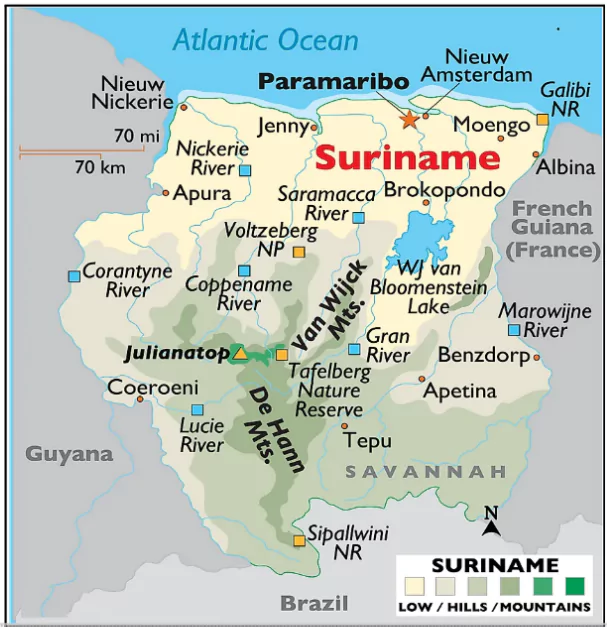
The Ordnance Clothing Factory (OCF), Avadi, a unit of Defence PSU Troop Comforts Limited, under the Ministry of Defence, executed India’s first defence export order to the Republic of Suriname.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
Recently a male elephant was camera-trapped in Namdapha National Park and Tiger Reserve , Changlang district, Arunachal Pradesh
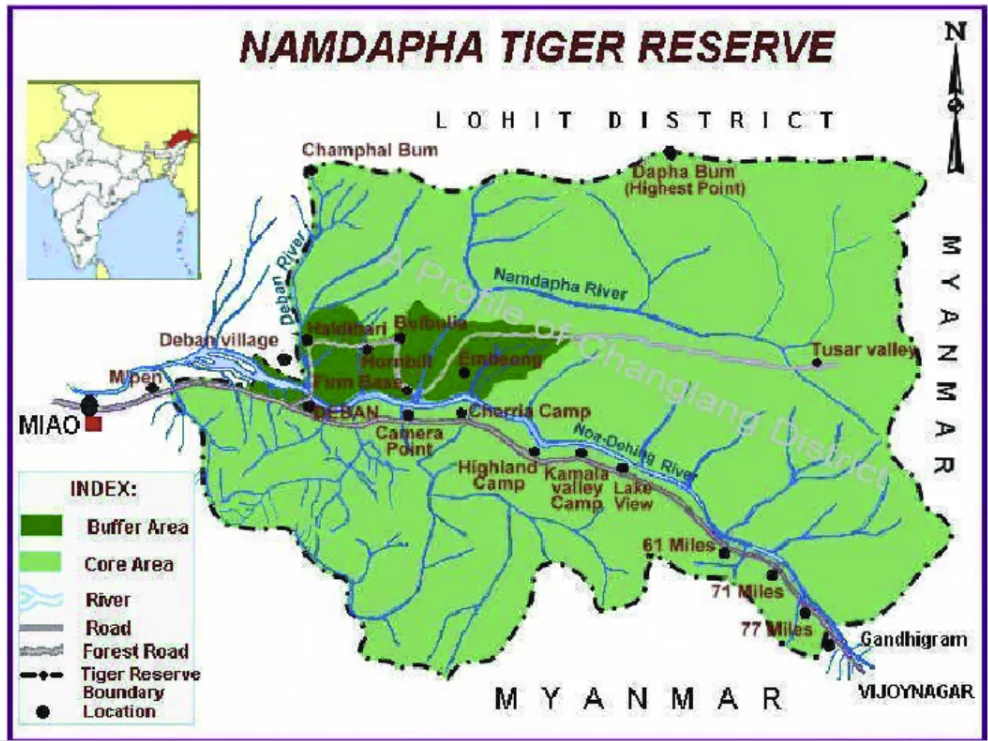
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The Draft Legal Metrology (Indian Standard Time) Rules, 2025 were published by the Legal Metrology Division, Department of Consumer Affairs recently.
About Legal Metrology
|
|---|
About Indian Standard Time (IST)
|
|---|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) 2024 has been released recently.
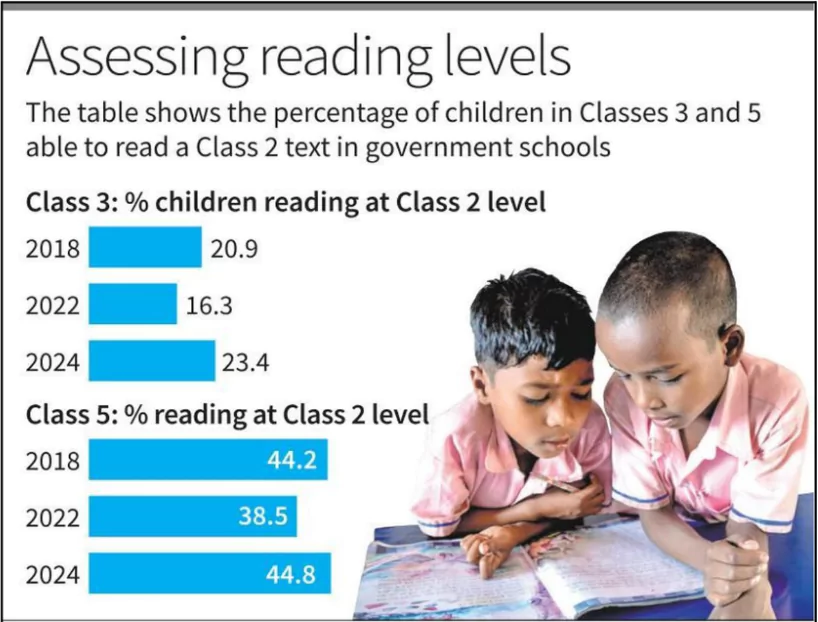 Basic Numeracy Skills: Children showed substantial improvement in both government and private schools in basic arithmetic (recognizing numbers, subtracting double-digit numbers with borrowing, and dividing three-digit numbers by one digit).
Basic Numeracy Skills: Children showed substantial improvement in both government and private schools in basic arithmetic (recognizing numbers, subtracting double-digit numbers with borrowing, and dividing three-digit numbers by one digit).Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
Every year, Punjab Kesari Lala Lajpat Rai’s birth anniversary is celebrated on 28th January.
![]()
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
Context: “On November 18, 2023, the Food Safety and Drug Administration in Uttar Pradesh banned the production, storage, sale, and distribution of food products with halal certification in the state, except for export items.”
Context: Recently, a series of deaths in Jammu and Kashmir has raised suspicions of organophosphate poisoning, a chemical commonly used in pesticides and insecticides.”
Context: DeepSeek is a Chinese-made artificial intelligence (AI) model that has the tech world buzzing as it has occupied the top spot for free Apple Store’s downloads.
Context: The Paris AI Action Summit, scheduled for February 10-11, 2025, is a key global event on AI governance and regulation.
Significance of the summit: It comes as the US launches a $500 billion AI project, and China makes significant AI breakthroughs by launching Deepseek .
Context: Georgia has been certified malaria-free by the World Health Organization (WHO) joining 45 countries and 1 territory underscoring the global progress towards malaria elimination.
WHO Certification Process: WHO grants malaria-free certification when a country proves that indigenous transmission has been interrupted nationwide for at least three consecutive years.
Context: Meteorologists are comparing Storm Éowyn to a bomb Cyclone due to its intensification.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
What National Sports Policy can do for India’s A...
Ukraine-Russia: A War turned into a Costly Test of...
China, India and the Conflict over Buddhism
At FTA’s Heart, the Promise of Global Capacity C...
Student Suicides in Universities are often a Produ...
Milk that has its Source in Soil: The Growing Popu...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>