Context: Ethiopia has signed a deal granting it naval and commercial access to ports along Somaliland’s coast, in exchange for recognition for the breakaway republic’s independence.
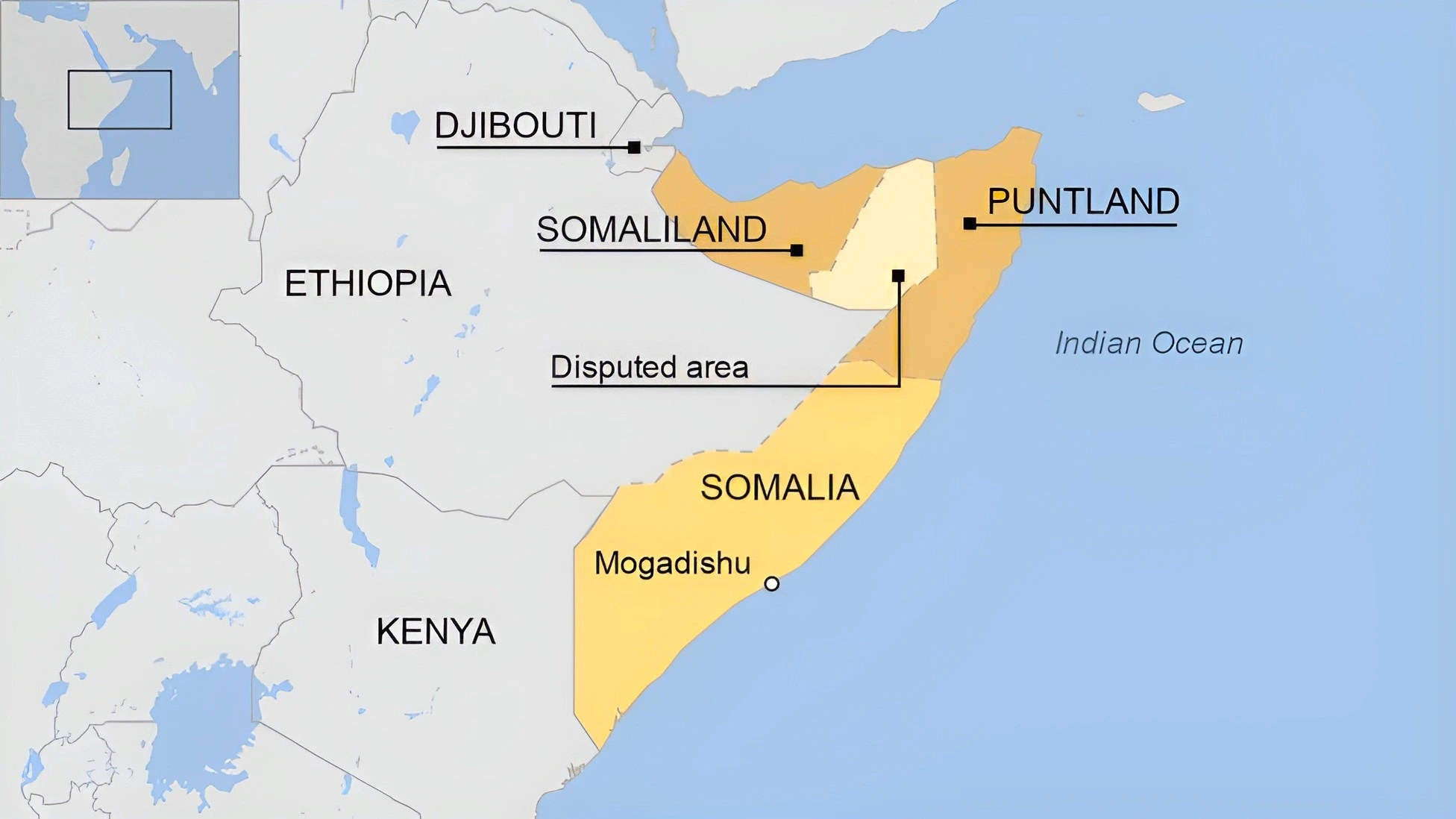 Hargeisa, Somaliland’s capital, has sought international recognition for over three decades.
Hargeisa, Somaliland’s capital, has sought international recognition for over three decades.News Source: TH
Context: Muhammad Yunus was convicted of violating Bangladesh’s labour laws and sentenced to 6 months in jail.
Muhammad Yunus, also known as ‘Banker to the Poor’ is a prominent figure known for his contributions to ‘Social Entrepreneurship and Microfinancing.’

| Social Entrepreneurship is a for-profit business model that strives to make a positive impact on social issues or the environment. |
|---|
What is Microfinance?
|
|---|
News Source: IE
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Sadyr Zhaparov, the president of Kyrgyzstan signed a decree to declare the snow leopard as the national symbol of Kyrgyzstan.
Global Snow Leopard and Ecosystem Protection (GSLEP) Programme
|
|---|
About KyrgyzstanKyrgyzstan is a landlocked country in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and China to the east and southeast.
|
Must Read: Snow Leopard Population Assessment
News Source: DTE
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: The Prime Minister inaugurated the Kochi-Lakshadweep Islands Submarine Optical Fiber Connection (KLI – SOFC) project to resolve the slow internet speed problem in Lakshadweep.

Must Read: What Are Optical Fibre Cables And How Do They Works?
Source: The Economic Times
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
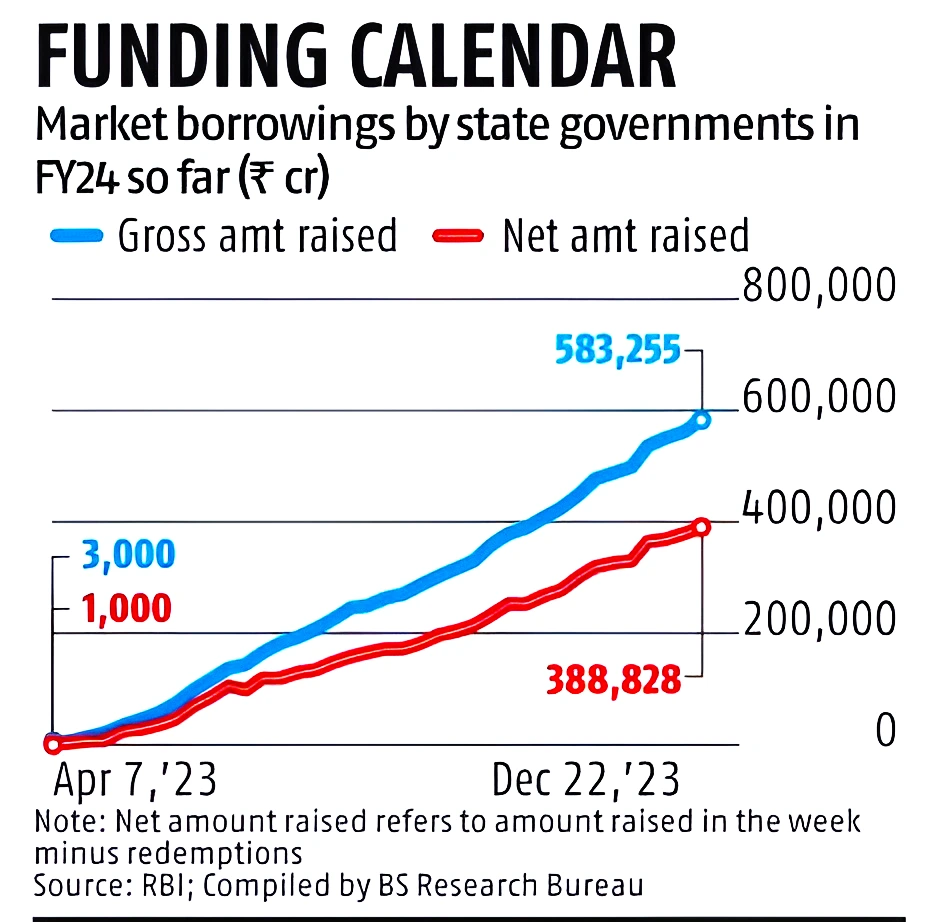
Context: The spread between yields on the 10-year state development loans (SDL) and the Centre’s G-sec (government securities) widened to a two-year high.
About Bonds
|
|---|
Source: Indian Express
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: The Appellate Tribunal on Disputes in Benami Matters has ruled that “Held” used in the Benami Act 2016 also covers the proceeds of crime committed before 2016, and is currently being held or possessed by the beneficiary.
Source: The Economic Times
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: The recent visit of Indian Army Chief General Manoj Pande to the Republic of Korea, marked a crucial moment in the course of India-South Korea defence relations.
What is Korean War (1950-1953)?It was a conflict between North and South Korea which resulted in at least 2.5 million casualties. Initiated in June 1950 with North Korea invading the South, it escalated into an international conflict involving the United Nations, the U.S., and China. The war concluded in July 1953, leaving Korea divided. |
|---|
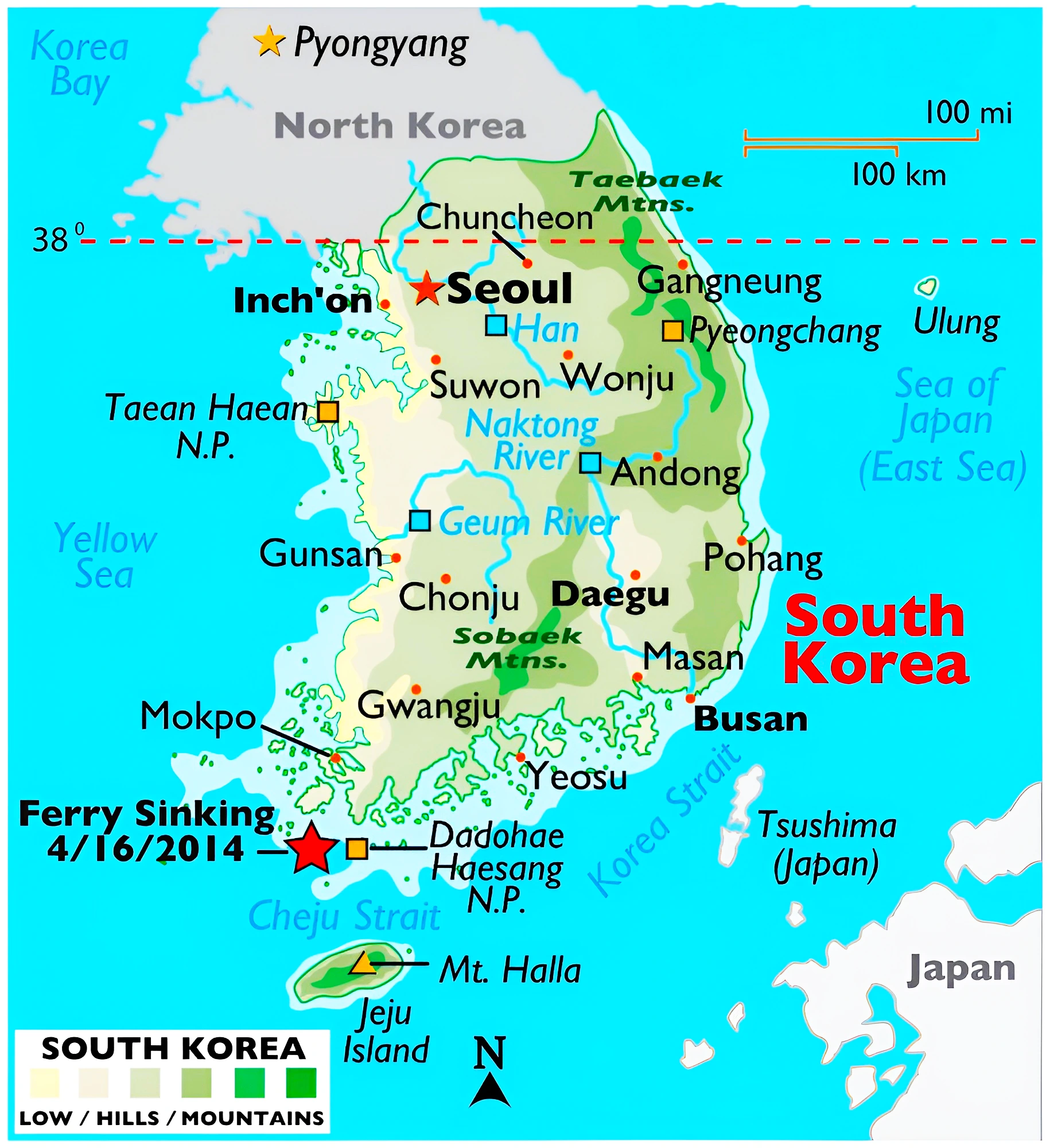
Continue Reading: India-Korea Defence Cooperation
News Source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: The SKAO or Square Kilometer Array Observatory is an international mega-science project that will serve as the largest radio telescope in the world, will now include scientists from India.
What are radio telescopes?
|
|---|
About Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT):
|
|---|
News Source: Indian Express
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Every year on 3rd January, India celebrates Rani Velu Nachiyar Jayanti.

News Source: PIB
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Every year on 3rd January, India celebrates Savitribai Phule Jayanti.

News Source: PIB
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: The government is set to issue orders for smart fencing for an additional 300 kilometres out of the 1,643 km of India-Myanmar border, running along Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur and Mizoram.
| Relevancy for Prelims: India-Myanmar Border, Smart Fence Project, Free Movement Regime (FMR), and United Nations High Commission for Refugees (UNHCR).
Relevancy for Mains: India-Myanmar Border: Challenges, Issues and Way Forward to the Indo-Myanmar Border Management. |
|---|
About Smart Fence Project
|
|---|
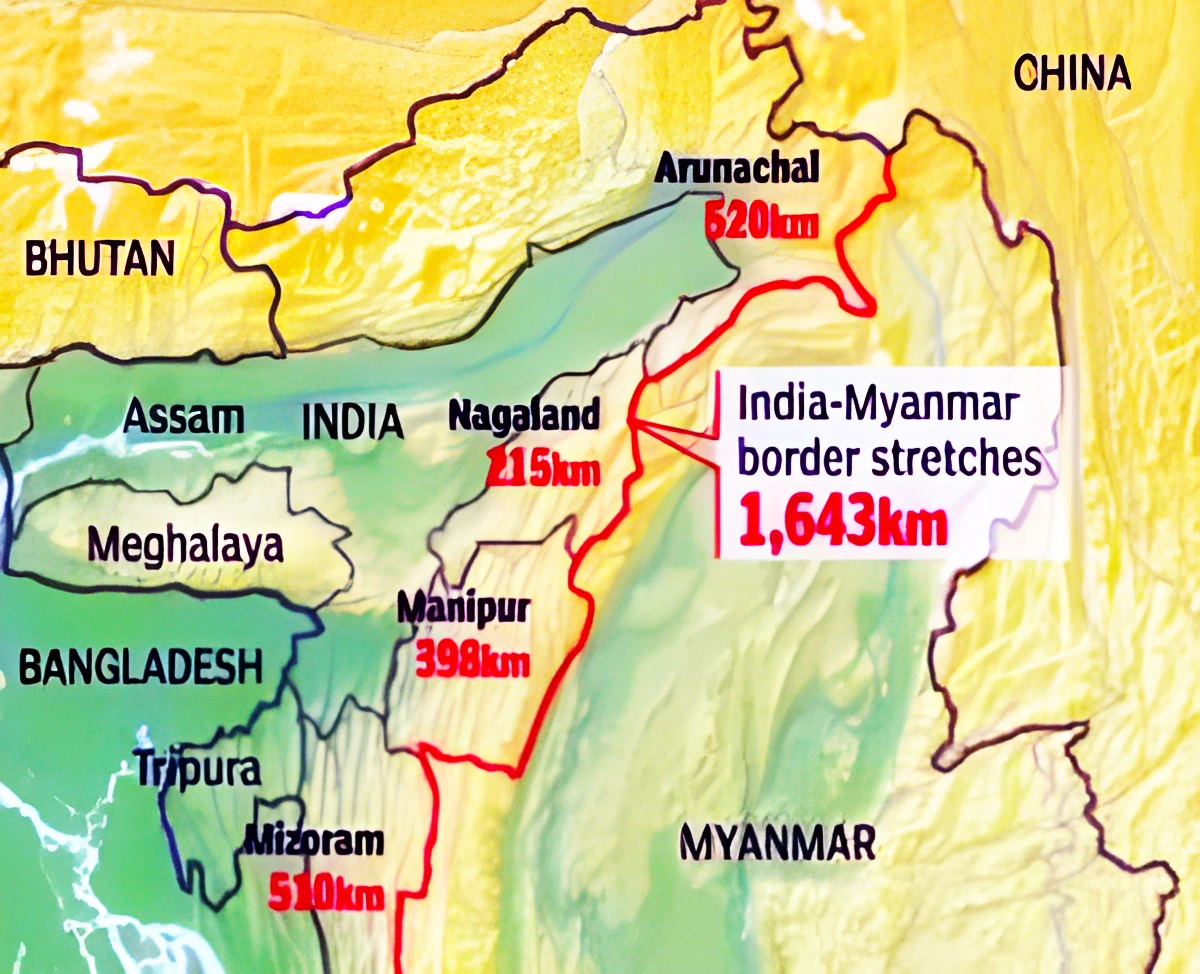
About Free Movement Regime (FMR)
|
|---|
Also Read: Centre Signs Peace Pact With ULFA Faction
The implementation of smart fencing technology along the India-Myanmar border reflects a strategic response to address security challenges, ethnic conflicts, and illicit activities.
| Mains Question: How does the ‘Free Movement Regime’ along the India-Myanmar border contribute to the internal security challenge of ethnic violence in Manipur? (15 marks, 250 words) |
|---|
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: This article is based on the news “Truckers strike: Home Ministry seeks to pacify truckers protesting new hit and run law” which was published in the Hindu. Transporters are protesting against the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), as per which, a driver may face up to 10 years’ imprisonment related to road accidents in India.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Road Accidents In India, Road Safety, Three New Criminal Law Reform Bills, National Highways Authority of India, Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, 2019, and Brasilia Declaration on Road Safety (2015).
Relevancy for Mains: Road Accidents in India: Data, Causes, Government Initiatives for Road Safety and Legislation Regarding Hit and Run Cases. |
|---|
Legislation Regarding Hit and Run Cases
Concerns of Transporters
To read more about New Hit and Run Law Backlash, refer:, New Hit and Run Law Backlash |
|---|
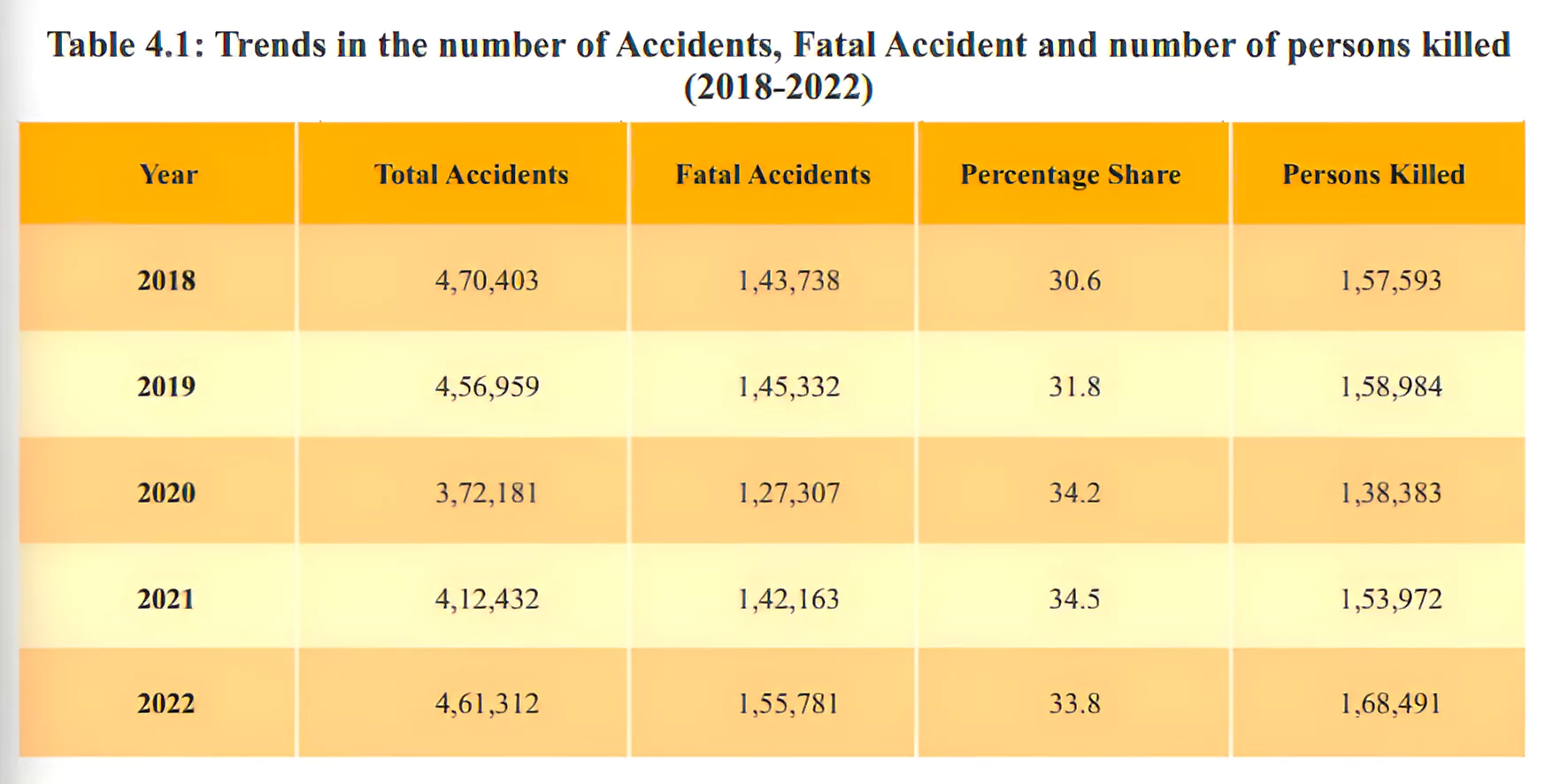
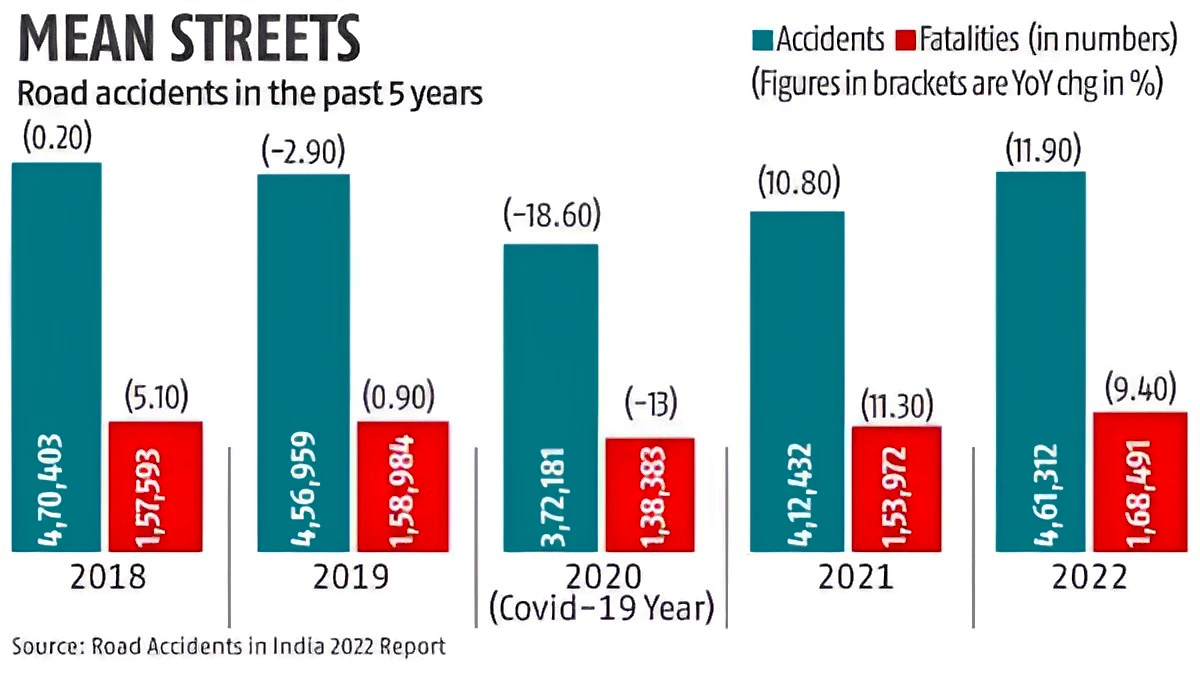 For instance, during 2022, over speeding accounted for 72.3 percent of the total road accidents, 71.2 percent of total deaths and 72.8 percent of total injuries.
For instance, during 2022, over speeding accounted for 72.3 percent of the total road accidents, 71.2 percent of total deaths and 72.8 percent of total injuries. 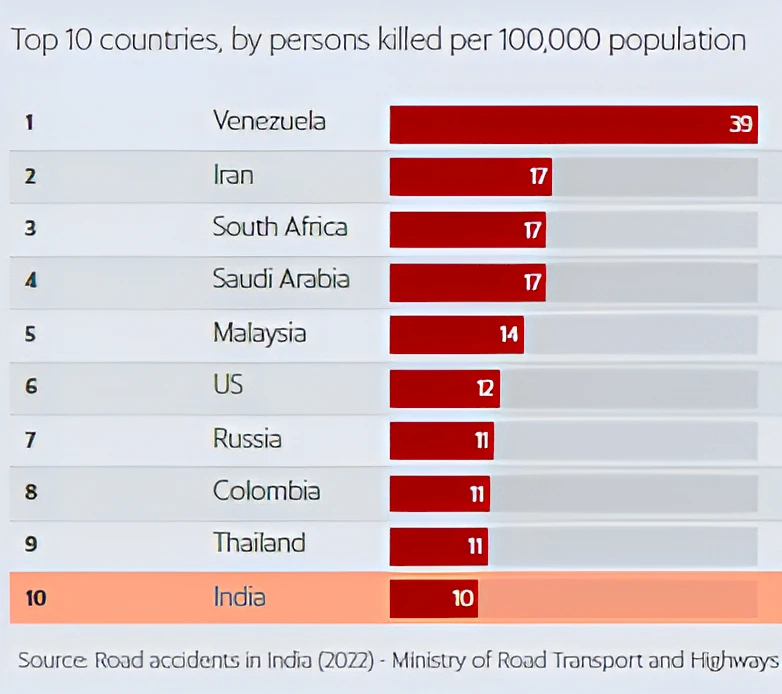
Global Initiatives Related to Road Safety
|
|---|
Addressing road accidents in India necessitates a comprehensive strategy involving better enforcement, improved infrastructure, and increased public awareness for safer roads and reduced fatalities.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>