The Prime Minister of India launched the Ken-Betwa River Link Project on the 100th birth anniversary of former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee.
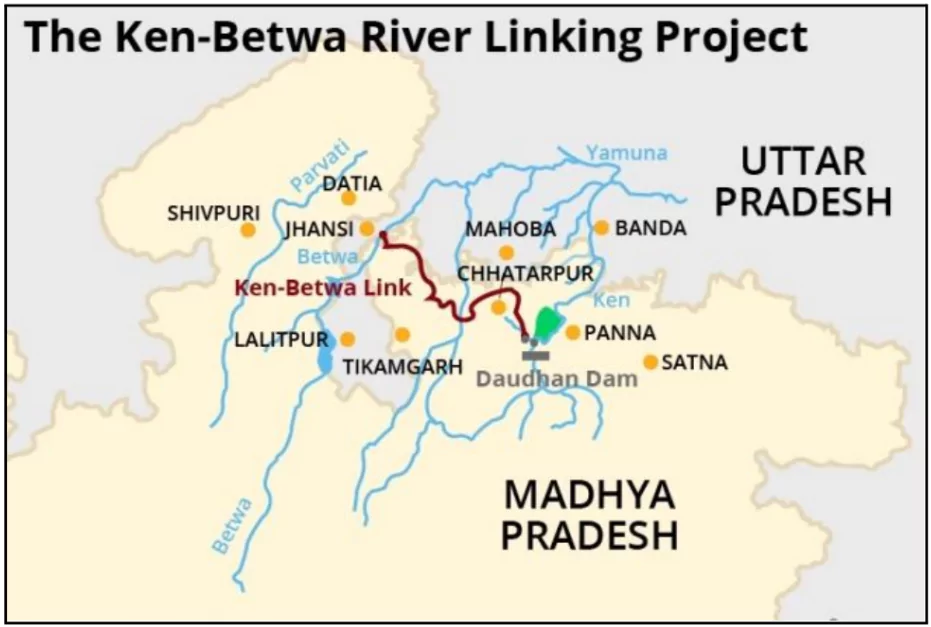
About Ken and Betwa Rivers
|
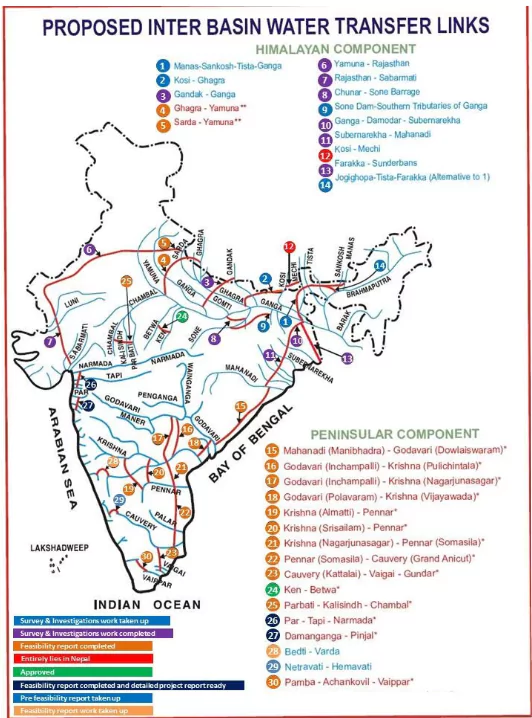
The concept of river interlinking was first proposed by Sir Arthur Cotton 130 years ago; designed irrigation dams in the Godavari and Krishna river valleys.
About National Water Development Agency (NWDA)
|
|---|
Global Examples of Water Diversion Failure:
|
|---|
Successful Case Studies of River Interlinking
|
|---|
Rivers provide critical ecosystem services, including sediment transport for delta formation, support for biodiversity, enhancement of land fertility, and groundwater recharge. Policymakers must balance technological interventions with environmental sustainability to ensure the long-term ecological and societal health of the nation. River interlinking projects must align with climate change mitigation strategies to avoid irreversible damage to natural systems.
The Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, announced major initiatives to boost the capacity at Deendayal Port worth an investment of more than ₹57,000 crores.
IndiaAI, an independent division under Digital India Corporation, has partnered with Microsoft to enhance the adoption and growth of artificial intelligence (AI) in India.
 Launch AI Catalysts as Centers of Excellence to promote AI development in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
Launch AI Catalysts as Centers of Excellence to promote AI development in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
Six people died and many were injured in a stampede at Vishnu Nivasam in Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh. The incident occurred during the token distribution for Vaikunta Dwara Sarva Darshan.
The Supreme Court noted that the Union government has not fully implemented the Dam Safety Act, 2021, which was enacted nearly five years ago.
| Dam | Location | Purpose |
| Bhakra Nangal Dam | Himachal Pradesh, Sutlej River | Power generation and irrigation |
| Hirakud Dam | Odisha, Mahanadi River | Flood control, irrigation, and power |
| Tehri Dam | Uttarakhand, Bhagirathi River | Power generation and water supply |
| Sardar Sarovar Dam | Gujarat, Narmada River | Irrigation, drinking water, and power |
| Nagarjuna Sagar Dam | Telangana/Andhra Pradesh, Krishna River | Irrigation and drinking water |
| Indira Sagar Dam | Madhya Pradesh, Narmada River | Power generation and irrigation |
| Mullaperiyar Dam | Kerala, Mullayar and Periyar Rivers | Water diversion for irrigation |
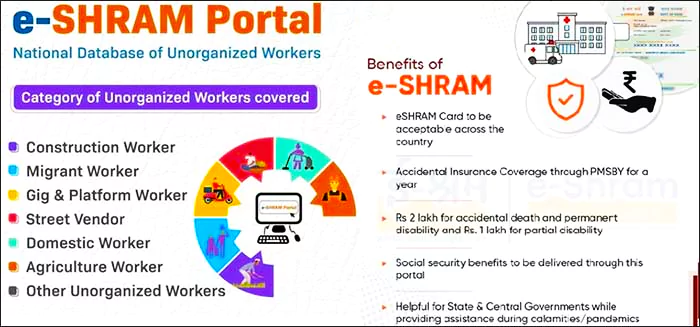
The Bhashini-enabled e-Shram Portal is now available in all 22 Scheduled Languages, enhancing accessibility for unorganized workers. Previously, the portal supported only English, Hindi, Kannada, and Marathi.
Schedules Languages
|
|---|
India and the U.S. announced a partnership for co-production of U.S. sonobuoys to enhance Undersea Domain Awareness (UDA) for the Indian Navy.
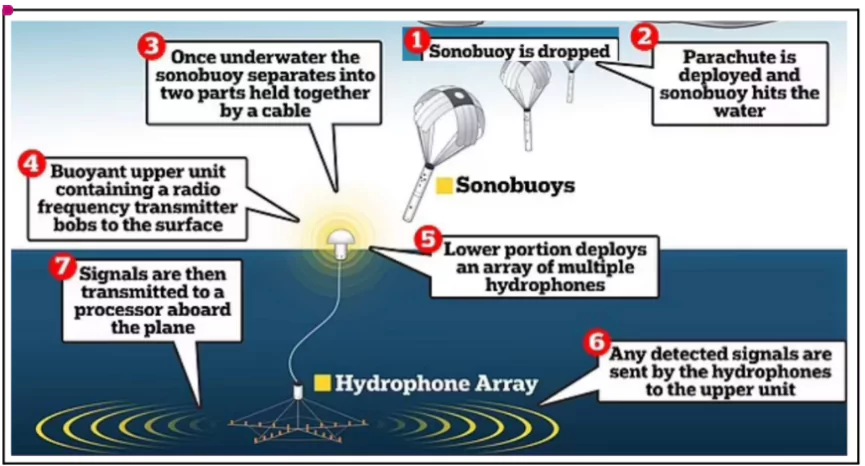
Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA)
India and UDA
|
|---|
India’s coastline has grown by 47.6%, from 7,516 km in 1970 to 11,098 km in 2023-24. The increase is due to the adoption of new methodologies for measuring coastal features.
| Aspect | Old Methodology (1970) | New Methodology (2023-24) |
| Basis of Measurement | Straight-line distances | Included complex coastal formations |
| Coastal Features Measured | Limited to general shoreline length | Incorporated bays, estuaries, inlets, and other geomorphological features |
| Technology Used | Basic tools and manual calculations | Advanced geospatial technologies and mapping tools |
| Accuracy | Relatively less precise | More precise representation of dynamic coastline |
| Reported Coastline Length | 7,516 km | 11,098 km |
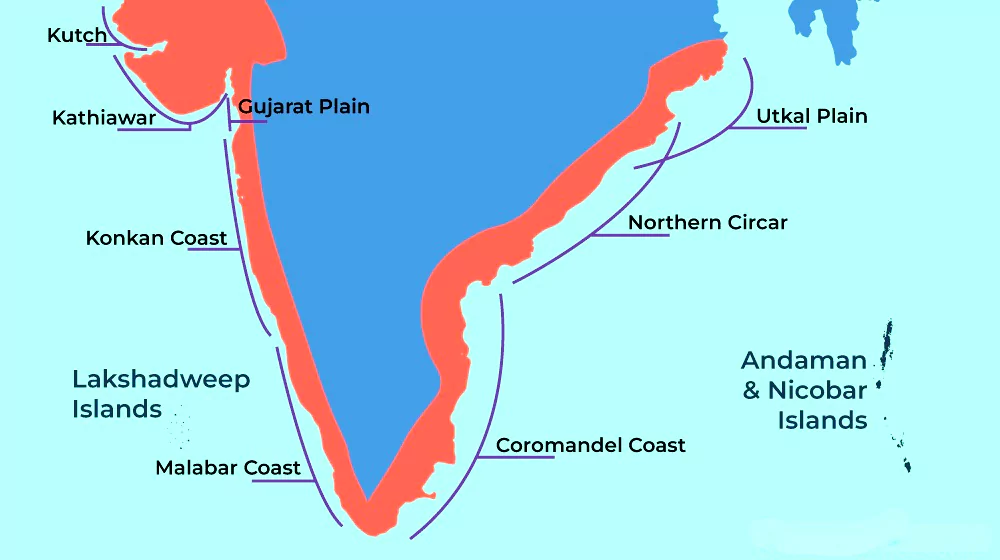
Coastlines of Emergence and Submergence
|
|---|
Researchers have demonstrated that reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants significantly improves nitrogen uptake and Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE) in rice and Arabidopsis.
Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE)
|
|---|
Context: A new ultra-diffuse galaxy forming at the end of a tidal tail associated with the galaxy NGC 3785 has been identified recently.
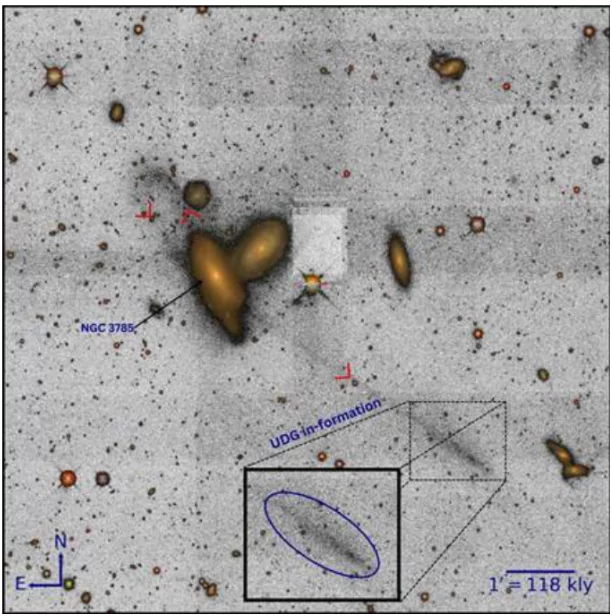 Published in: The study was published in the European journal, Astronomy & Astrophysics Letters
Published in: The study was published in the European journal, Astronomy & Astrophysics Letters
Context: Singapore has reclaimed its place at the top of the world’s most powerful passports which enjoy visa-free access to 195 out of 227 destinations worldwide, according to the Henley Passport Index.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>