France and India co-chaired the Artificial Intelligence Action Summit on 10-11 February 2025, bringing together global leaders to advance AI for public good.
About the “Inclusive and Sustainable Artificial Intelligence for People and the Planet”
|
|---|
Labour In The AI Era
|
|---|
India in The AI Summit
|
|---|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
U.S. President Trump has signed an executive order, triggering a USAid funding freeze that has disrupted global humanitarian aid efforts, with all staff put on leave and the future of the organisation unknown.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
A controversy has erupted in Parliament over the absence of 22 hand-painted illustrations in most copies of the Indian Constitution published currently.


The 22 illustrations in the Constitution serve as a visual representation of India’s cultural and historical heritage. While their omission in widely available copies has sparked debate, the original artwork remains preserved in Parliament, highlighting the rich legacy of Indian history and governance.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The Supreme Court of India has raised concerns about convicted individuals returning to Parliament and State Legislatures, questioning the potential conflict of interest.
Supreme Court Judgments on Criminalisation of Politics
|
|---|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
Recently, the government has announced plans to amend the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act (CLNDA) and the Atomic Energy Act.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has issued a warning that the Morand-Ganjal Irrigation Project in Madhya Pradesh will lead to the submergence of crucial tiger habitats in the Satpura Wildlife Sanctuary and Melghat Tiger Reserves.
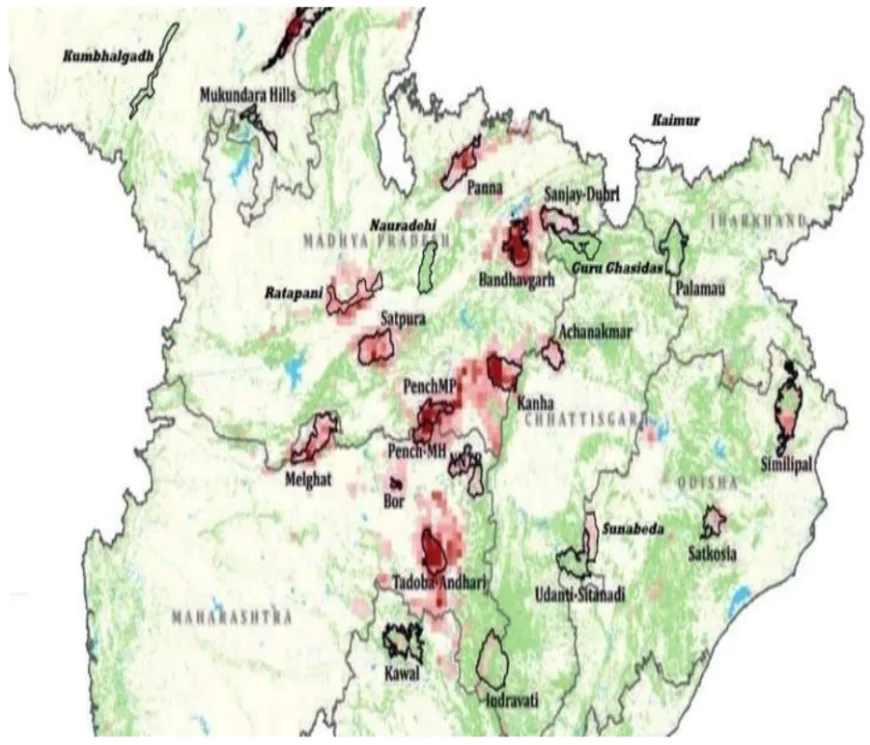
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
India has launched a nationwide Mass Drug Administration (MDA) campaign targeting 111 endemic districts across 13 states.
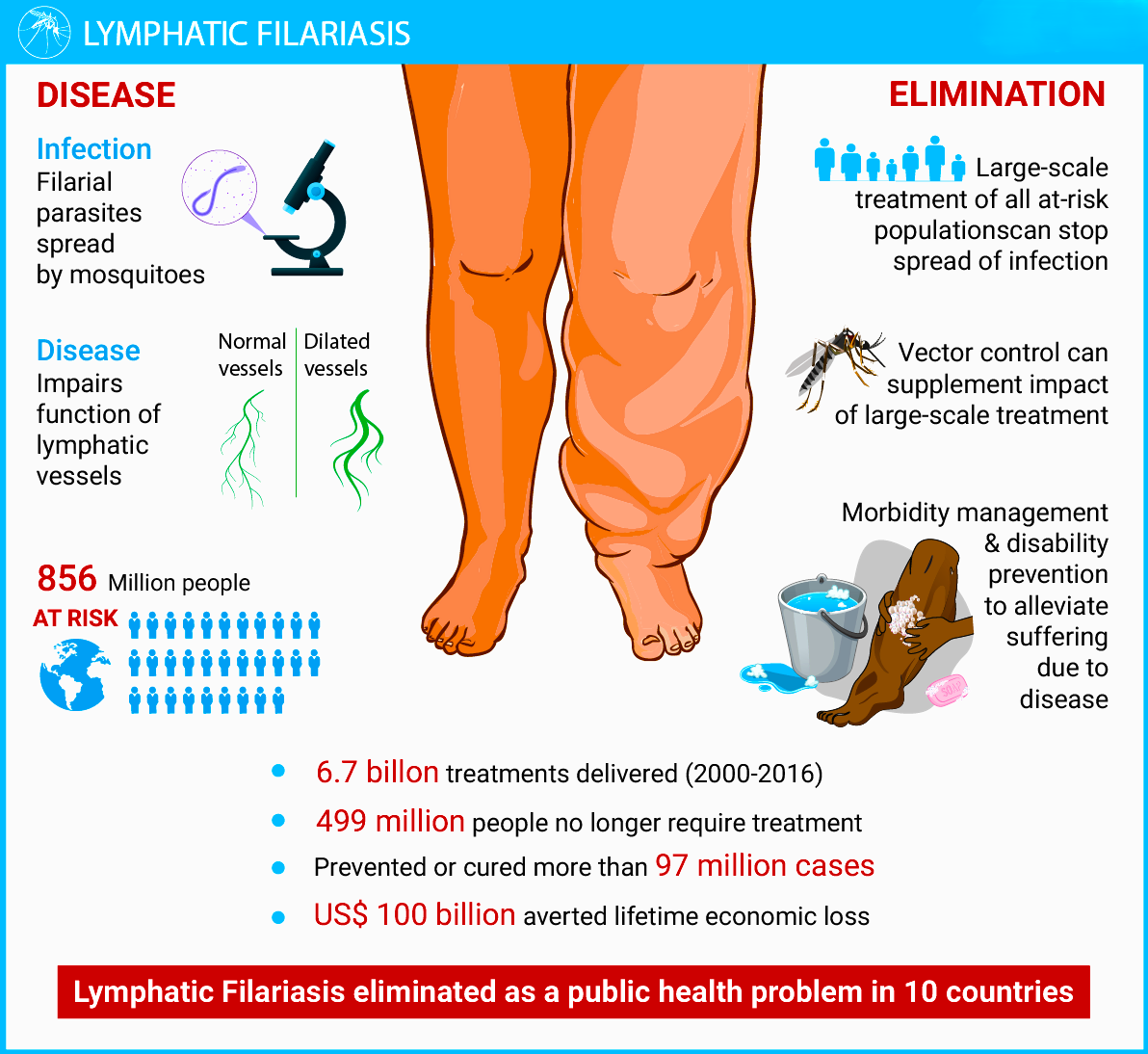
Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs)
|
|---|
National Center for Vector Borne Diseases Control
|
|---|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has decided to defer the implementation of the revised Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) norms.
Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS)
|
|---|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The Union Minister for Social Justice and Empowerment recently chaired a meeting of the Central Advisory Committee for the PM-AJAY scheme.
PM-AJAY is a merged scheme of three Centrally Sponsored Schemes:
PM-AJAY continues to play a crucial role in uplifting SC communities by ensuring better livelihood opportunities, improved education access, and enhanced infrastructure in SC-majority areas.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
Context: Recently, Union Minister launched India’s first indigenous Automated Biomedical Waste Treatment Rig, named Sṛjanam, at AIIMS New Delhi.
Context: Scientists from the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad, conducted a morphological and topographic analysis of the Chandrayaan-3 landing site
Context: India has ranked 96th out of 180 countries in the Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) 2024.
Context: Panama has officially announced its withdrawal from China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), marking a significant geopolitical realignment.
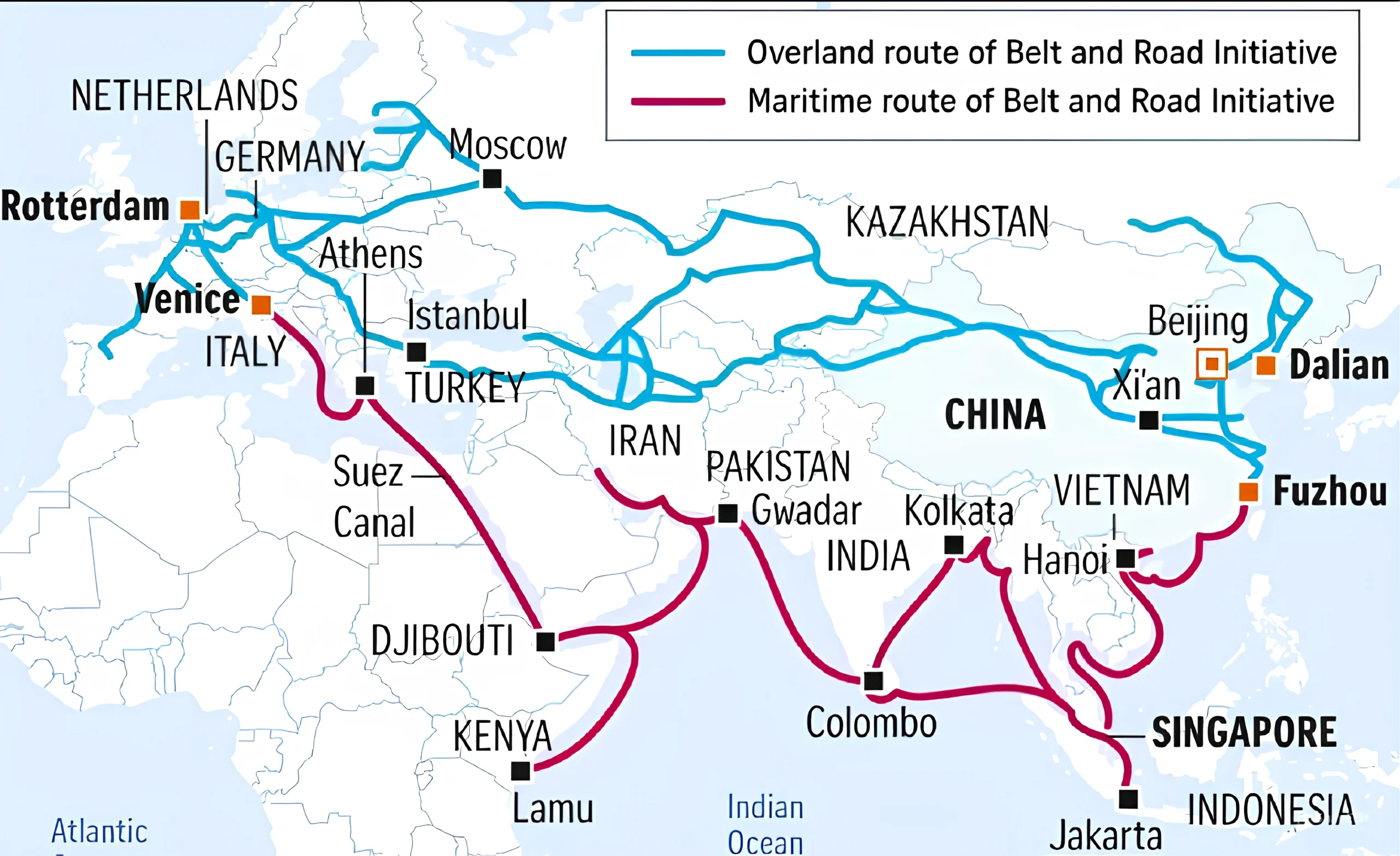
Context: India has amended the Customs Tariff Act to introduce a new HS (Harmonised System) code for exporting Geographical Indication (GI)-recognised rice that will allow the export of these special rice varieties without requiring special notifications from the Finance Ministry.
World Customs Organization (WCO)
|
|---|
Context: The 3rd edition of the Joint Special Forces Exercise CYCLONE has commenced at Mahajan Field Firing Ranges in Rajasthan, India.
Context: The Indian Prime Minister met with the President of the Republic of Estonia on the sidelines of the AI Action Summit in Paris.
Context: The ‘IRIS’ (Indigenous RISCV Controller for Space Applications) chip has been developed from the ‘SHAKTI’ processor baseline.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
