Belgium has become the first European Union country to recognise ‘ecocide’ as a national as well as an international crime.
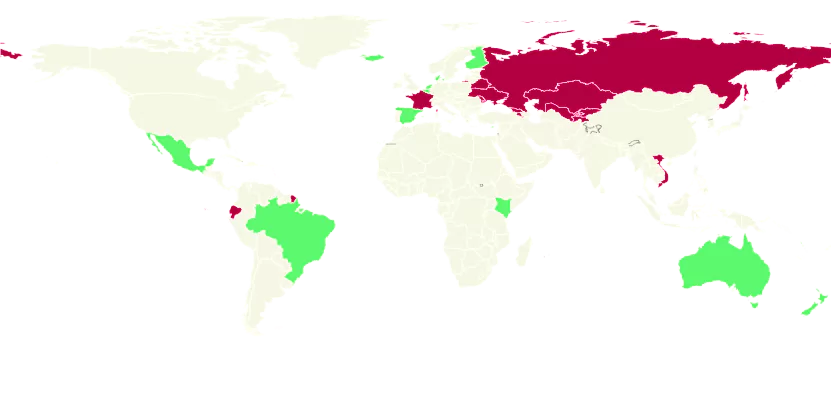
Ecuador; Vietnam; Uzbekistan; Russia; Kazakhstan; Kyrgyz Republic; Tajikistan; Georgia; Belarus; Ukraine; Moldova; Armenia.
News Source: DTE
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |

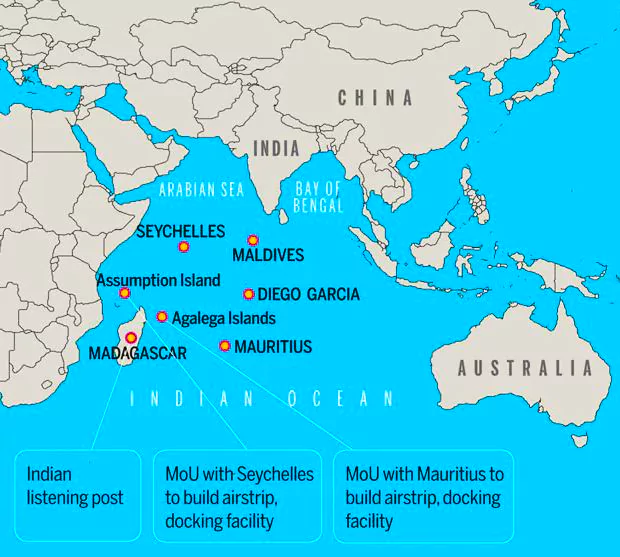
Prime Minister Narendra Modi, alongside his Mauritian counterpart Pravind Jugnauth, is set to inaugurate a new airstrip and jetty, alongside six developmental projects on Mauritius’ Agalega Island.
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, India announced the names of the four astronaut designates for the Gaganyaan human spaceflight mission, planned for launch in 2025.
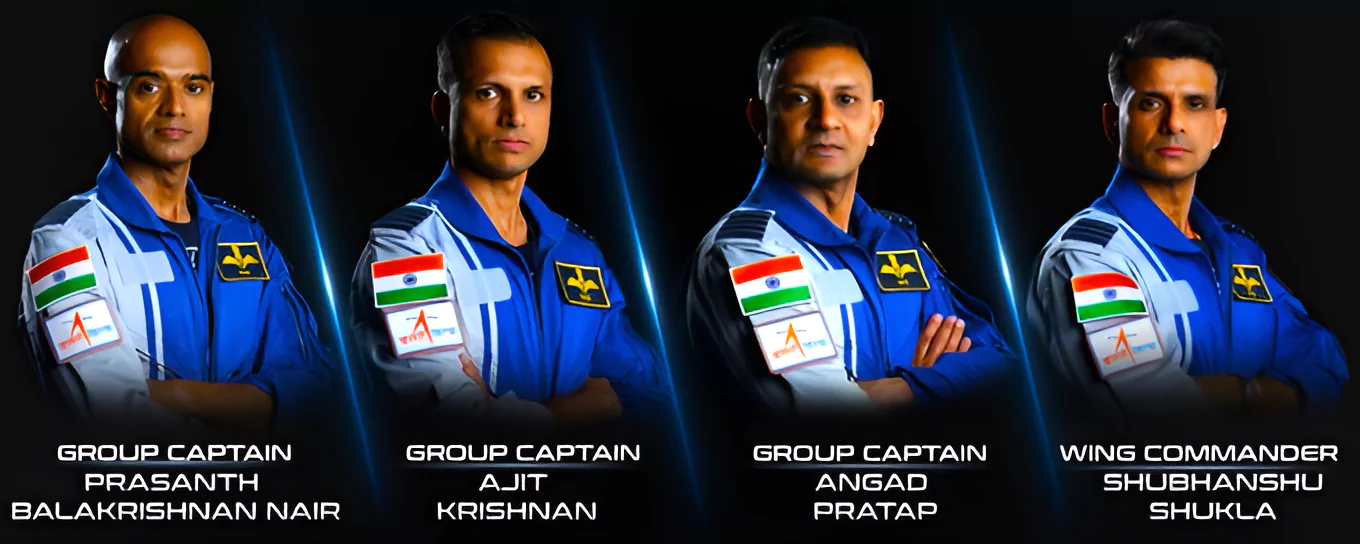

It is a space mission to demonstrate ISRO’s human spaceflight capability by launching a human crew to an orbit of 400 km and bringing them safely back to Earth.
News Source: TH
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |

The 37th African Union Summit was convened in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Agenda 2063: The Africa We Want.
|
|---|
Africa Club:
|
|---|
African Union
|
|---|
News Source: DTE
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
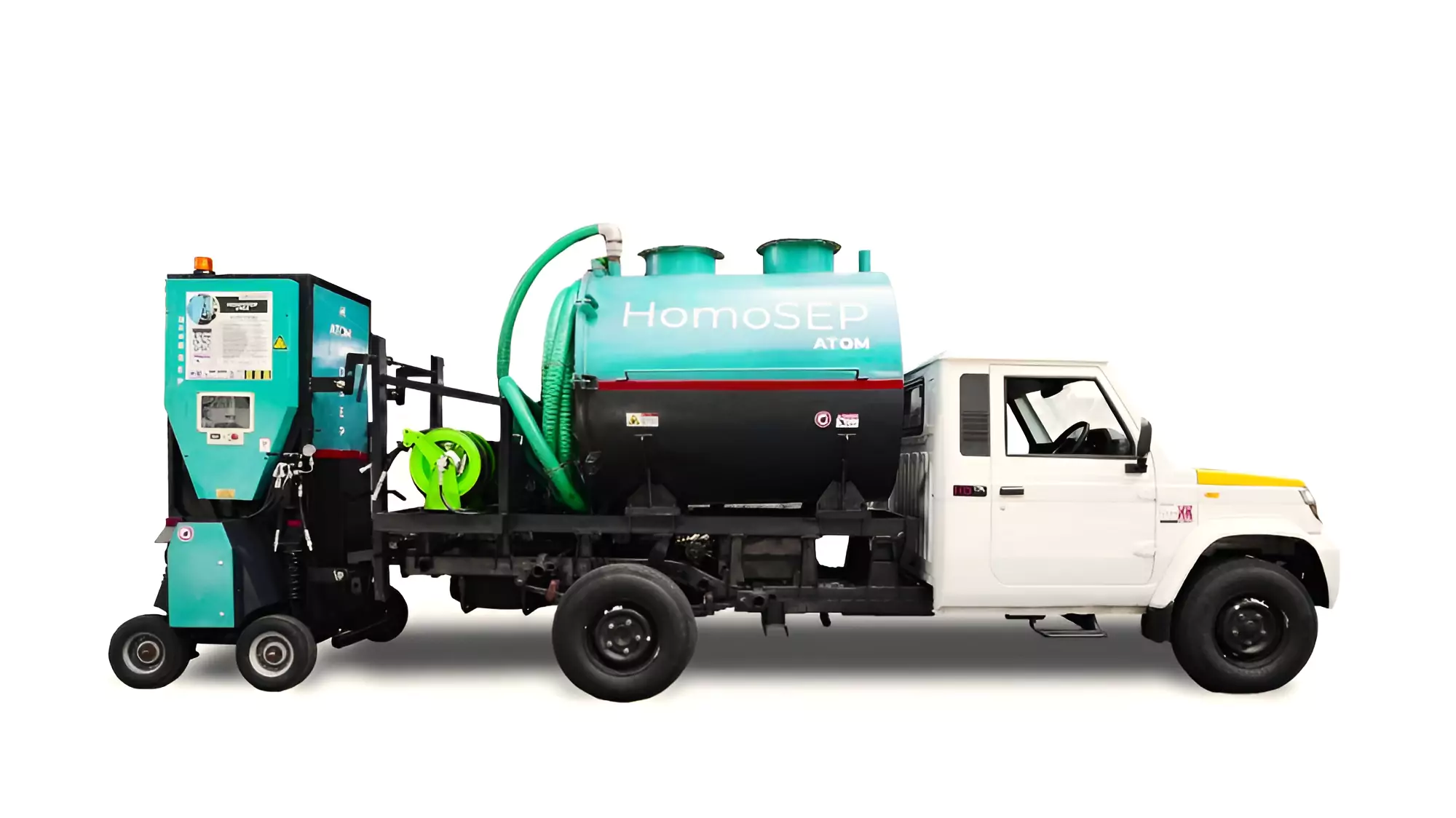

Recently, India’s first septic tank/manhole cleaning robot- Homosep Atom has been developed which helps to eliminate manual scavenging.
About Solinas:
|
|---|
News Source: AIR
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
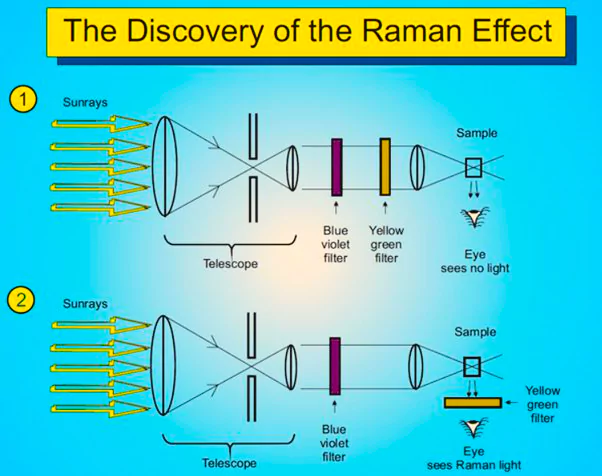
National Science Day is observed on February 28 to commemorate the discovery of the Raman Effect by Indian Scientist CV Raman.

News Source: AIR
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Union Minister of Education and Skill Development & Entrepreneurship recently launched the SWAYAM Plus Platform in New Delhi.
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, Scientists at Stanford University identified a new form of life ‘obelisks’ lying between viruses and viroids from bacteria present in the human gut.
What is Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)?
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news ‘‘10,000 genome’ project completed, says the government” which was published in the Hindu. The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) officially announced the completion of the “10000 Genome project”.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Biotechnology, Genome Sequencing, SWAYAM Plus Platform, Bio Manufacturing And Biofoundry.
Relevancy for Mains: Genome India Project (GIB): Background, Objectives, Application and Significance. |
|---|
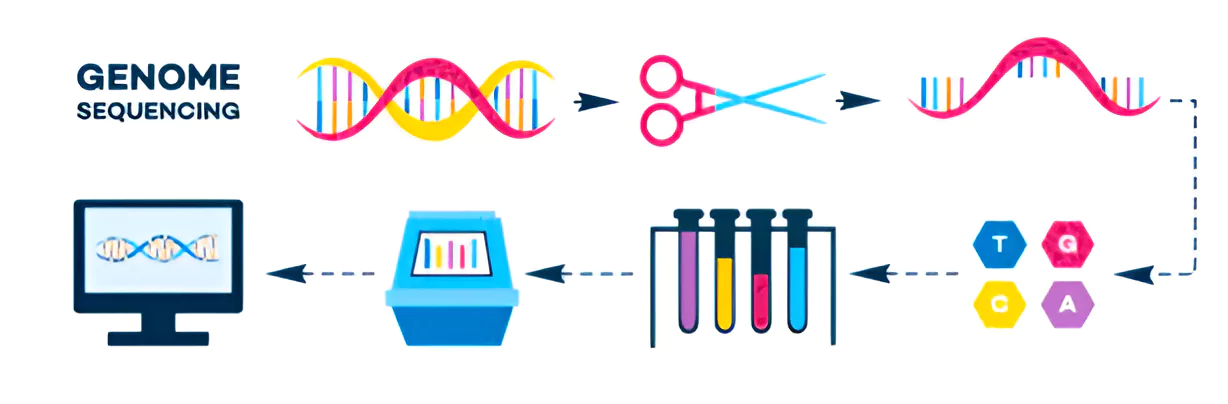
News Source: The Hindu and CDC
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Express View on government’s new grain storage plan: More in store” which was published in the Indian Express. Recently, the President of India appointed former Supreme Court Judge Justice AM Khanwilkar as the Chairperson of the Lokpal.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Lokpal And Lokayuktas In India, Corruption Perceptions Index 2023, Supreme Court, Money Laundering, and Enforcement Directorate (ED).
Relevancy for Mains: Lokpal: Compositions, Chairperson, Members, Appointments Procedure, Tenure, Mandate, Powers, Functions, Criticisms and Way Forward. |
|---|
Corruption: A Serious Concern
India is a signatory to the United Nations Convention against Corruption
|
|---|
First Lokpal Chairperson:
|
|---|
 In 2002: The Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution headed by M.N. Venkatachaliah recommended the appointment of the Lokpal and Lokayuktas, also recommended that the PM be kept out of the ambit of the authority.
In 2002: The Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution headed by M.N. Venkatachaliah recommended the appointment of the Lokpal and Lokayuktas, also recommended that the PM be kept out of the ambit of the authority.
About Lokayukta
|
|---|
About Lokpal Search Committee:
|
|---|
| Prelims PYQ (2018):
Consider the following statements: 1. In the first Lok Sabha, the single largest party in the opposition was the SwatantraParty 2. In the Lok Sabha, a “Leader of the Opposition” was recognised for the first time in 1969. 3. In the Lok Sabha, if a party does not have a minimum of 75 members, its leader cannot be recognised as the Leader of the Opposition. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 3 only (b) 2 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (b) |
|---|
| Mains Question: A national Lokpal, however strong it may be, cannot resolve the problems of immorality in public affairs’. Discuss. (200 words, 10 marks) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Union Cabinet Approves National Sports Policy 2025...
What are Altermagnets? A Breakthrough in Magnetism...
India’s 7-Point Strategy for Sustainable Gro...
Cabinet Approves Employment Linked Incentive Schem...
INS Udaygiri Delivered Under Project 17A to Indian...
SC Issues Implemented Reservation Roster for SC/ST...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>