The last decade has seen the emergence of numerous internet-based tech startups, often referred to as the children of the internet as these unicorns and consumer companies will not exist without the internet.
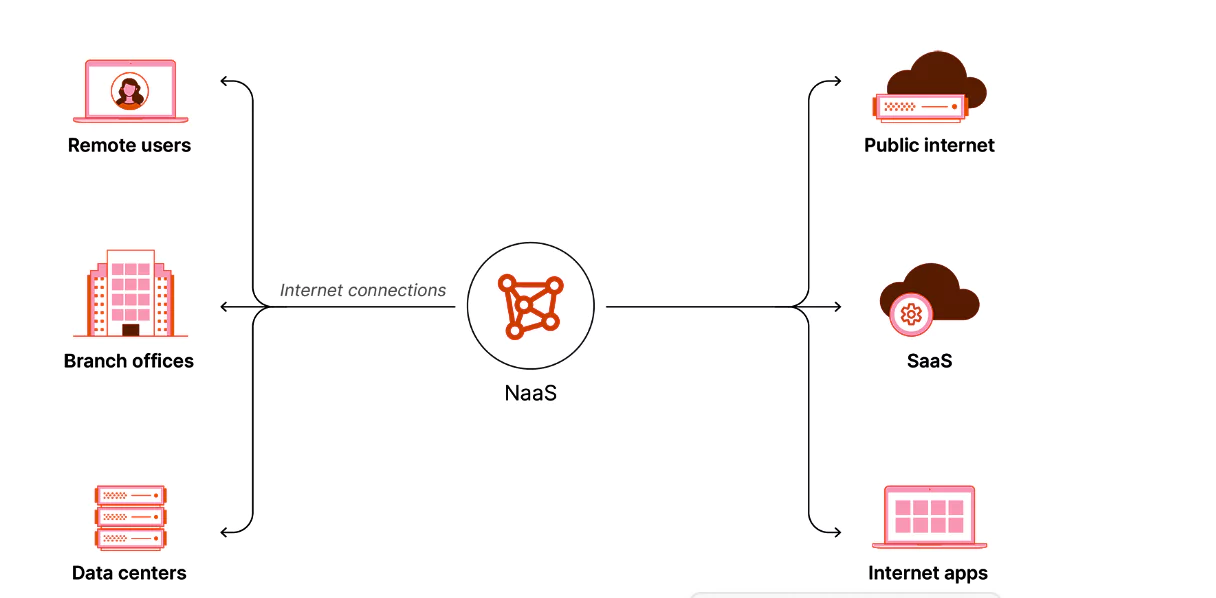
| Software as a service (SaaS) | Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) | Network as a service (NaaS) |
| Software As A Service (SaaS) applies to any software application delivered via the cloud as a subscription-based offering. | It is defined as the use of any IT hardware and software infrastructure components like compute power or storage utilized through the cloud in a flexible consumption or subscription-based model. | It is much more specific and relates directly only to networking functionality. |
| SaaS spans across a variety of online applications utilized through the internet every day. | Like SaaS, it’s an all-inclusive category that can span the entire IT infrastructure portfolio from compute to storage to networks. | It refers to only networking hardware, software, and services delivered in a “cloud-like” motion, which implies subscription-based or consumption-based billing. |
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
According to recent data from the Reserve Bank of India, India’s net household savings have reached their lowest point in 47 years.
| Gross Domestic Product(GDP): It is the market value of all the goods and services produced within the domestic territory of a country during a specified time period, usually one year. |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Ancient rocks that bear the oldest remnants of Earth’s early magnetic field were discovered in Greenland by the geologists at MIT and Oxford University.
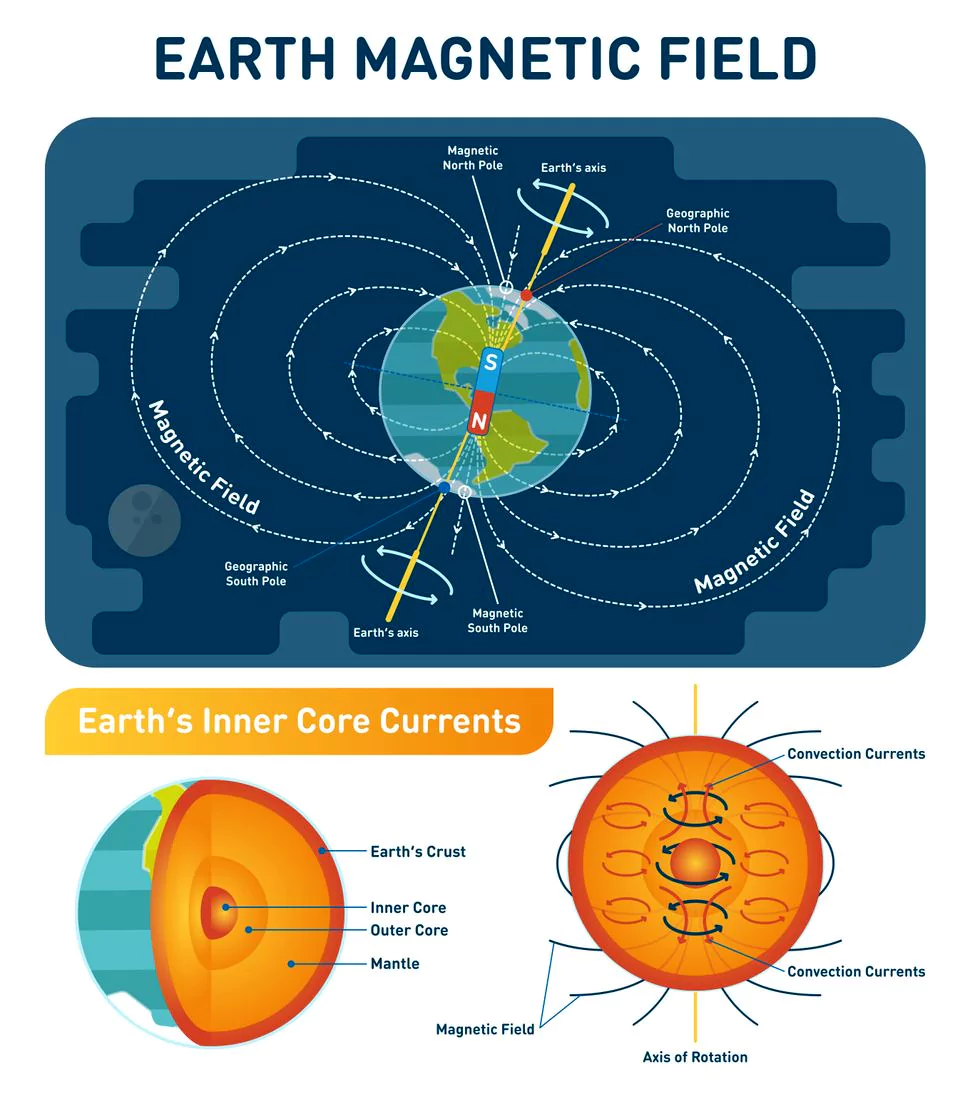 Early evidence on the habitable nature of Earth: The discovery sheds light on how the Earth was able to foster life early in its evolution ie. in part due to an early magnetic field that was strong enough to retain a life-sustaining atmosphere and simultaneously shield the planet from damaging solar radiation.
Early evidence on the habitable nature of Earth: The discovery sheds light on how the Earth was able to foster life early in its evolution ie. in part due to an early magnetic field that was strong enough to retain a life-sustaining atmosphere and simultaneously shield the planet from damaging solar radiation. The Magnetic Field is generated through a process named the geodynamo process. It has the following characteristics:
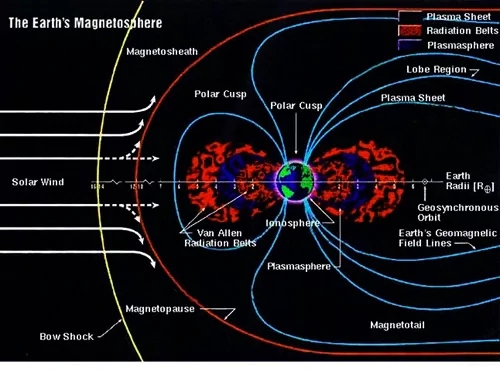
Magnetic Fields on Other Planets:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The US Secretary of State during his three-day visit to China spoke about the production and export of “synthetic opioid precursors”, specifically the drug fentanyl.
Opioid Menace in India:
|
|---|
They are a class of drugs that “derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the opium poppy plant”. Some common opioids include oxycodone, morphine, codeine, heroin, and fentanyl.
Fentanyl is a potent synthetic opioid drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use as an analgesic [for pain relief] and anesthetic.
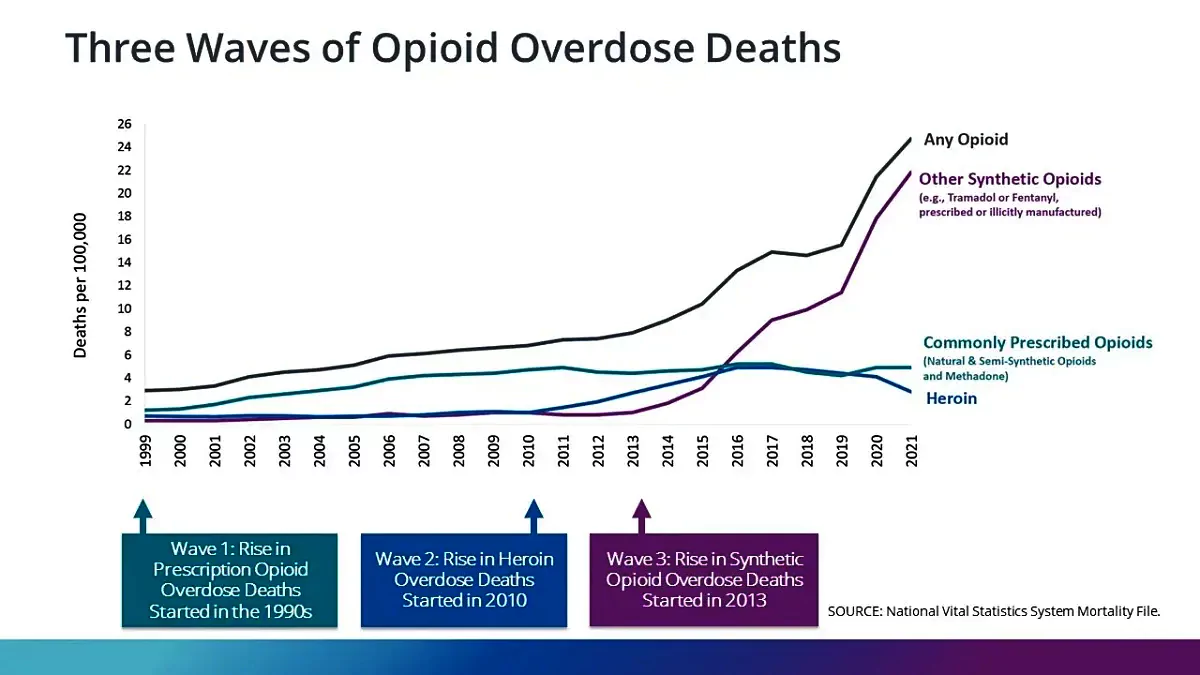 A US House Committee report found that inexpensive fentanyl is increasingly cut into other drugs, often without the buyers’ knowledge.
A US House Committee report found that inexpensive fentanyl is increasingly cut into other drugs, often without the buyers’ knowledge.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Dengue fever is spreading across regions such as southern Europe and the United States as the planet is getting warmer.

This fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease.
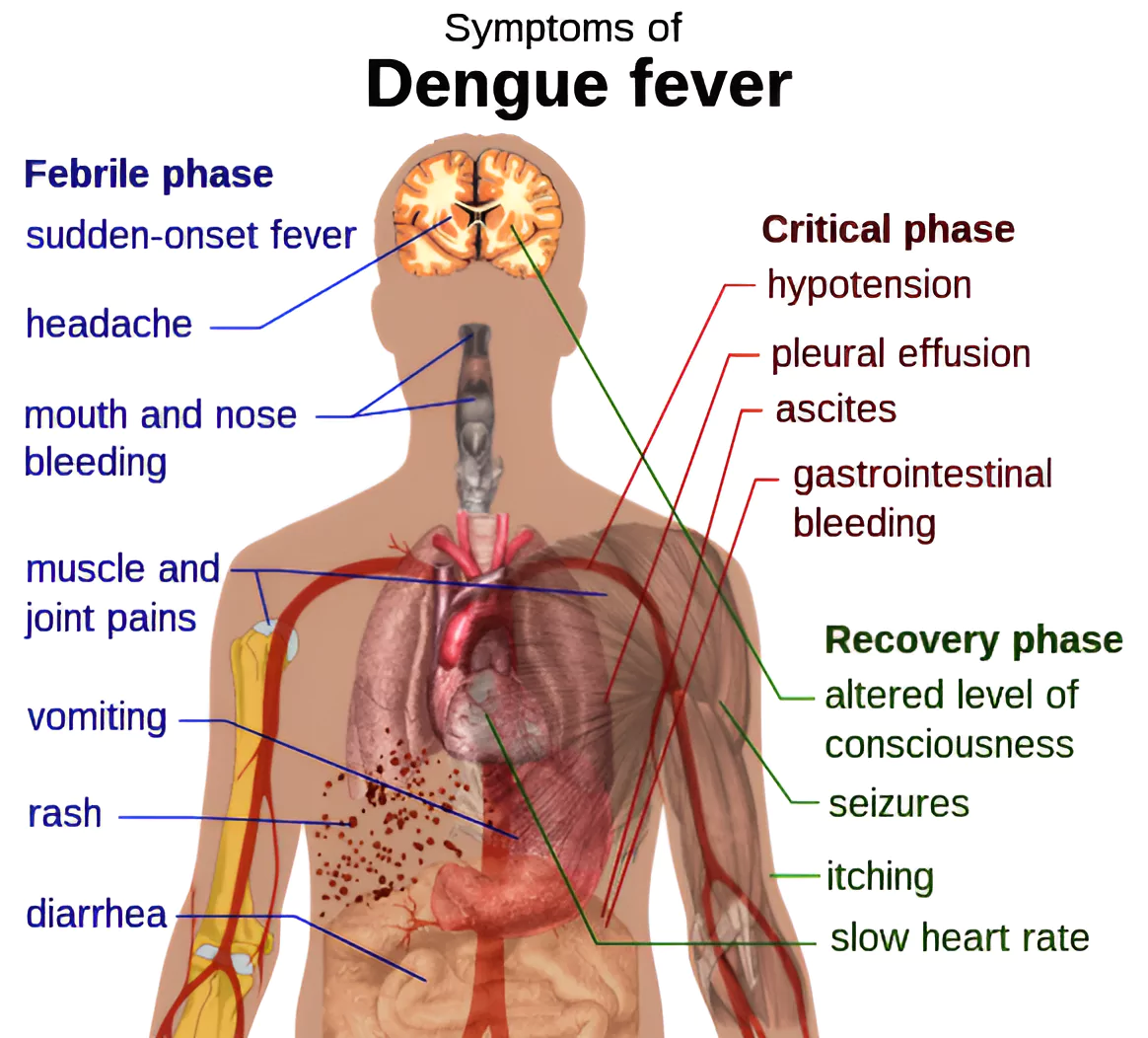
Dengue feveris common in tropical and subtropical regions due to various reasons
| Year | Dengue cases in India |
| 2017 | 188,401 |
| 2018 | 101,192 |
| 2019, | 157,315 |
| 2021. | 193,245 |
| 2022 | 110,473 |
 Vaccine in India: Currently, there is no approved vaccine in India.
Vaccine in India: Currently, there is no approved vaccine in India.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, Indian Air Force’s MI 17 V5 helicopter was deployed to extinguish the raging forest fires in Nainital district, Uttarakhand.

| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The ruling Party secured its first victory in the Lok Sabha elections as its candidate, Mukesh Dalal, was elected uncontested for the Surat constituency in Gujarat.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the US Trade Representative’s 2024 Special 301 Report has been released that has again included India in the ‘Priority Watch List’ of countries, along with China, Russia, Venezuela, Indonesia, Chile and Argentina.
About “Special 301” Report
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Election Commission of India (EC) invoked Sections 58(2) and 58A(2) of the Representation of People Act, 1951 (RPA) to annul the elections held on April 19 in 11 polling stations in Manipur and 8 polling stations in Arunachal Pradesh.
| Disruptions | Definition as per RPA | Available Choices |
| Intentional destruction, taking away of EVMs | Under Section 58 of the RPA, the EC can declare the poll at a polling station to be void if:
|
|
| Booth capturing | Booth-capturing, defined in Section135A of the RPA, includes:
Booth capturing is punishable for a term of not less than one year, which may extend to three years for lay people, and not less than three years, extending to five years for government servants. |
|
| Natural disasters, other disruptions to polling | The Presiding Officer of a polling station can adjourn the poll under section 57(1) of the RPA in case of:
|
After seeking the EC’s approval on the date and hours, the adjourned poll will recommence from the stage at which it was left immediately before the adjournment.
|
| Death of a candidate | If the candidate with a valid nomination dies at any time after 11.00 a.m. on the last date for making nominations, until the commencement of the poll. | As per Section 52 of RPA, amended in 1996, the poll shall be adjourned only in case of the death of a recognised political party’s candidate.
|
It provides for the conduct of elections to the houses of parliament and the legislatures of each state, corrupt practices, and other offenses taking place at or in connection with the elections.
| RPA, 1950 | RPA, 1951 |
| The allocation of seats in, and the delimitation of constituencies for the purpose of election to the Lok Sabha and the Legislatures of States; | Methodology for the conduct of elections of the Houses of Parliament and to the Lok Sabha and the Legislature of each State; |
| Qualification of voters at such elections. | Qualifications and disqualifications for membership of those Houses. |
| Methodology of preparation of electoral rolls | Corrupt practices and other offences at or in connection with such elections. |
| Manner of filling seats in the Council of States | Decision on doubts and disputes arising out of or in connection with elections. |
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI’s) latest Monetary Policy Report (included in its April Bulletin) has given primacy to “extreme weather events” and “climate shocks”.
| Relevance For Prelims: Reserve Bank Of India (RBI), India’s Banking Sector And Monetary Policy, Monetary Policy, Vision India@2047, and India’s Path To A Greener Future In The Globalization Age.
Relevance For Mains: Towards a Green Growth: Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI’s) Role and India’s Green Taxonomy. |
|---|
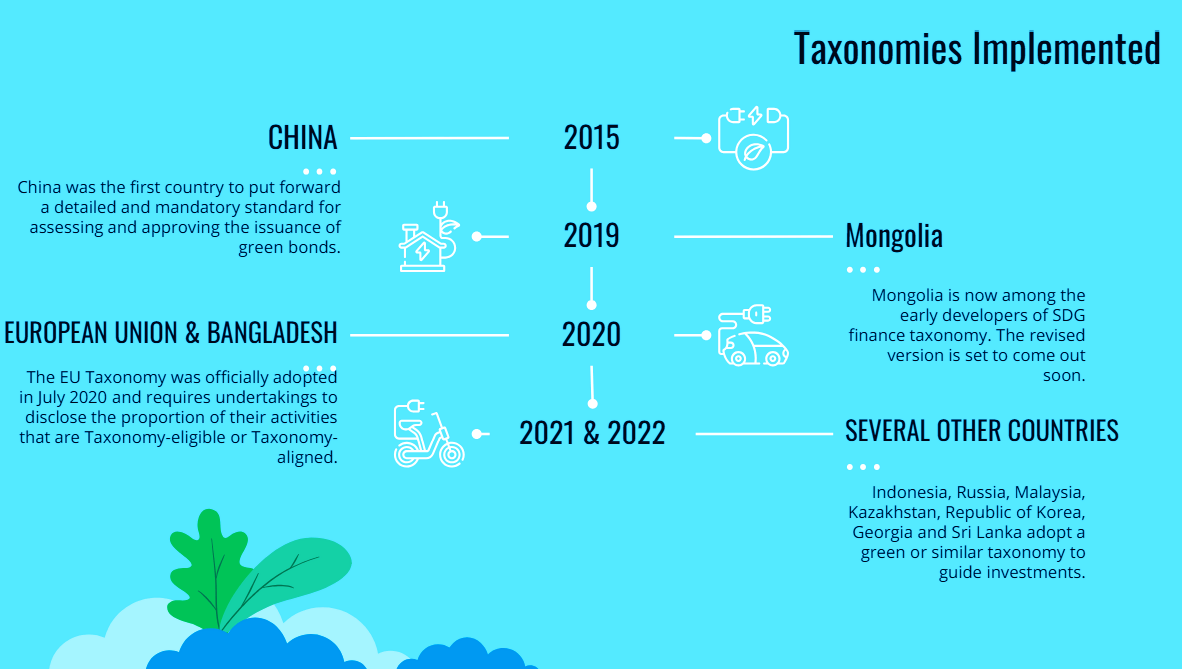
Beginning with its July 2022 discussion paper on ‘climate risk and sustainable finance’, the RBI has made incremental progress to address the transition to a green economy.
The European Central Bank has aided the formulation of a green taxonomy for the entire Eurozone’s economic value chain.
Monetary Policy:
|
|---|
| The natural rate refers to the short-term real interest rate that would prevail in the absence of business cycle shocks, with output at potential, saving equating investment and stable inflation. |
|---|
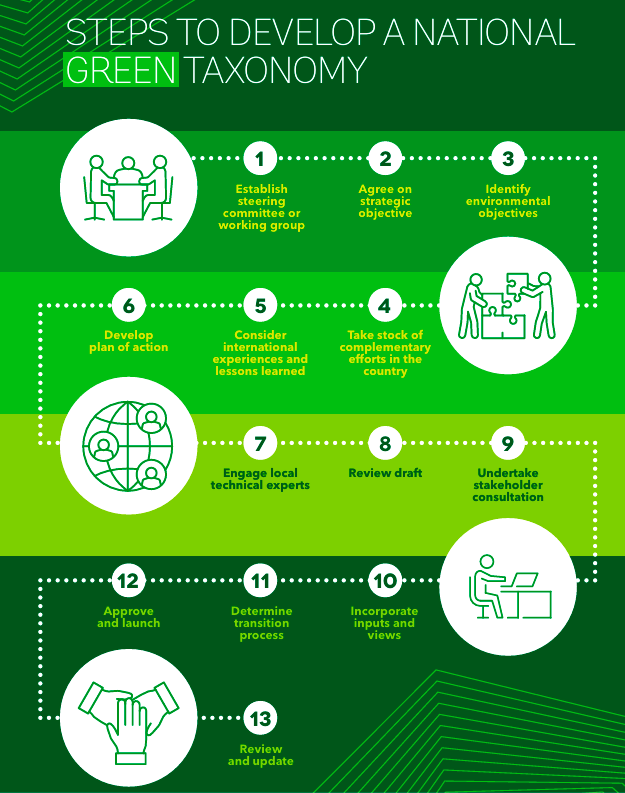
Green Taxonomy is defined as a framework to assess the sustainability credentials and possible ranking of an economic activity.
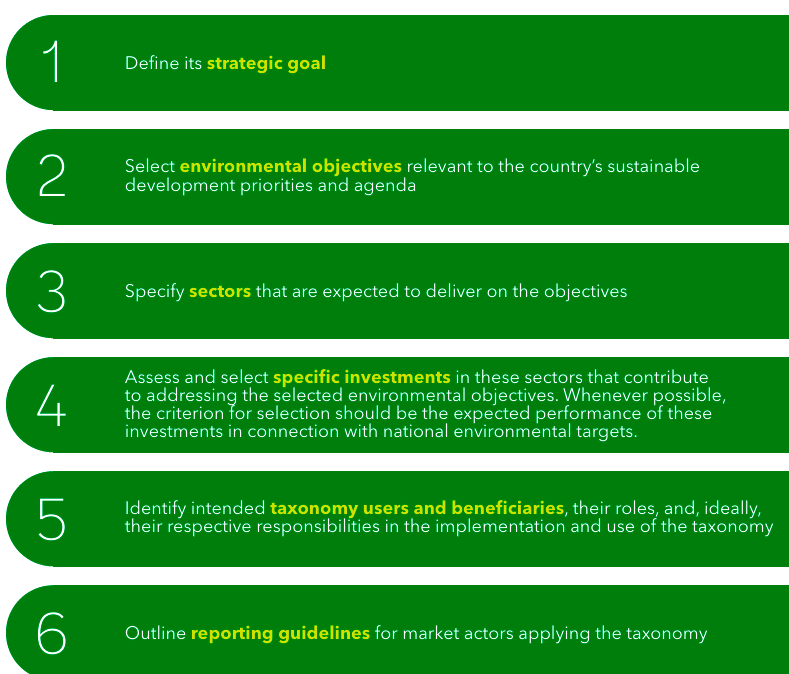
Principles of a Green Taxonomy: The World Bank Group recommends the principles and methodology for developing a taxonomy of environmentally sustainable activities.
 In Harmony with International Standards: Existing Indian standards may be revised to be at par with international benchmarks within the scope provided by domestic circumstances.
In Harmony with International Standards: Existing Indian standards may be revised to be at par with international benchmarks within the scope provided by domestic circumstances.
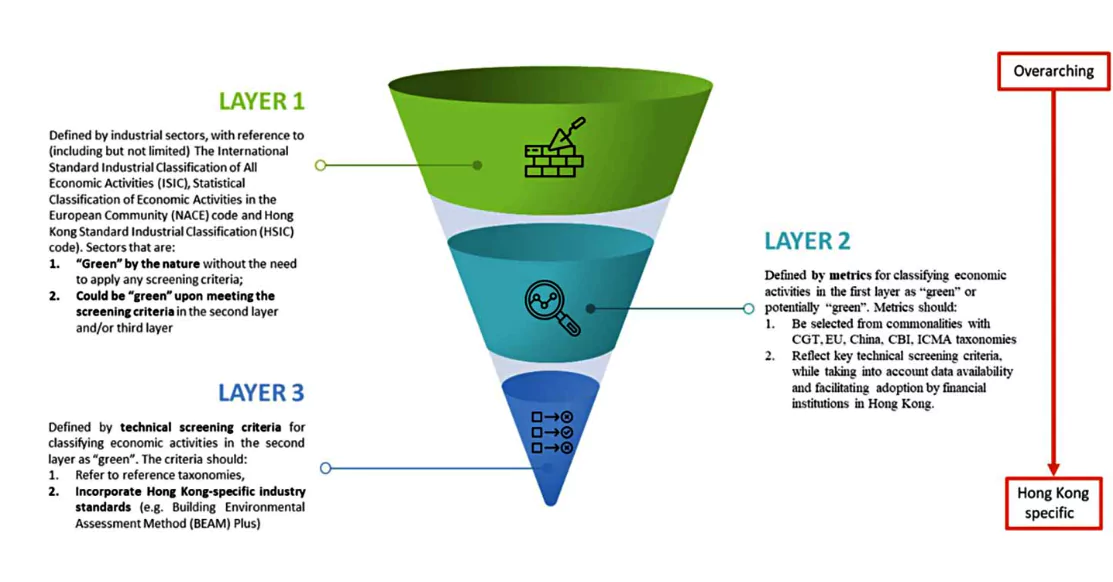
Sovereign Green Bonds (SGrBs) in India:
|
|---|
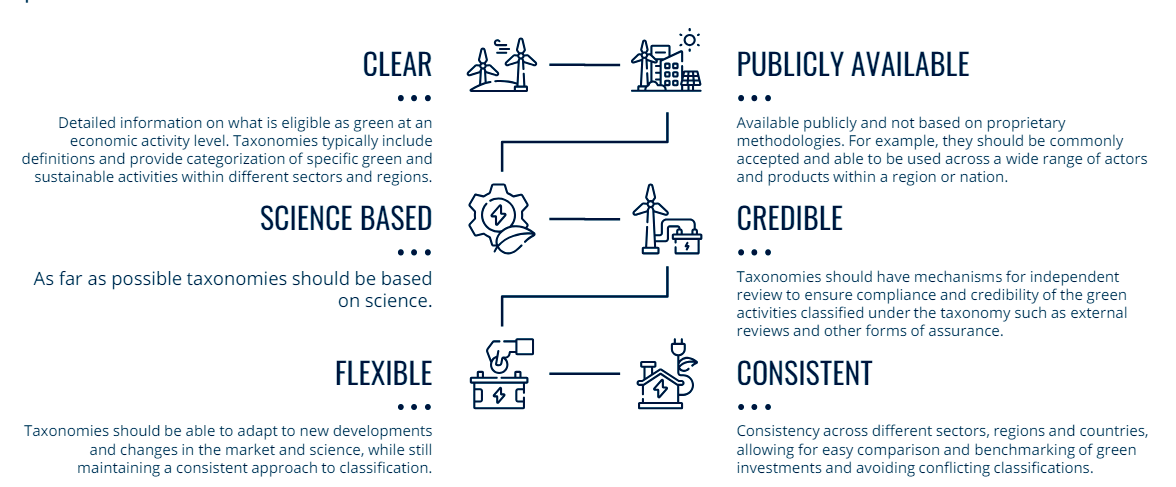
A well-defined and structured green taxonomy can support better-informed and more efficient decision making and response to investment opportunities that contribute to achieving national environmental objectives. It will influence India’s ambitious green transition and the introduction of a national taxonomy will display India’s aspiration of ramping up its contribution to the global net-zero vision.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Union Cabinet Approves National Sports Policy 2025...
What are Altermagnets? A Breakthrough in Magnetism...
India’s 7-Point Strategy for Sustainable Gro...
Cabinet Approves Employment Linked Incentive Schem...
INS Udaygiri Delivered Under Project 17A to Indian...
SC Issues Implemented Reservation Roster for SC/ST...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>