Krutrim, India’s Indigenous artificial intelligence startup has introduced graphics processing unit as-a-service (GPUaaS) for enterprises and developers to train their AI systems.
A Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) was simply a small part of the central processing unit (CPU) within computers which was used exclusively for graphics and video rendering initially.
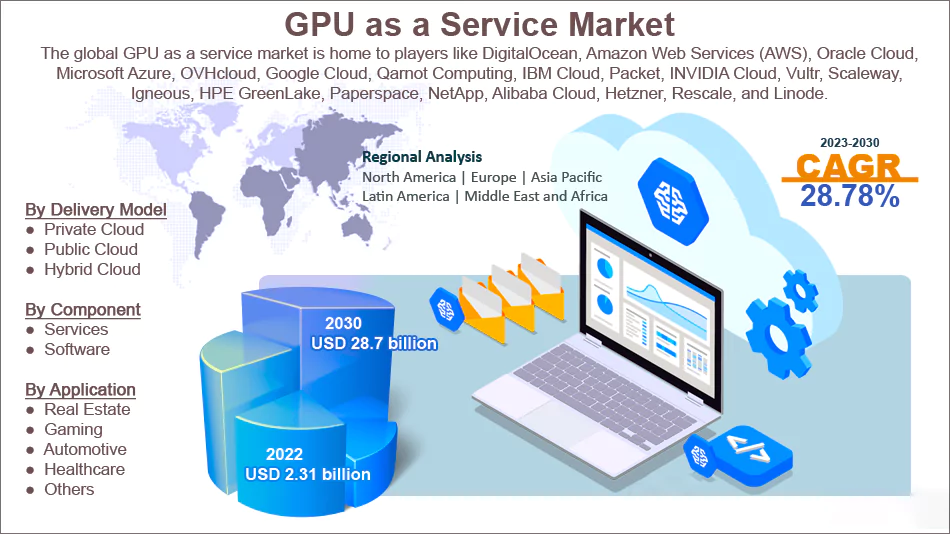
GPU As A Service (GPUaaS) is a computing service that allows businesses to access expensive GPUs for high-performance computing via the cloud without the need for installing or managing the expensive hardware in-house. It is essentially the SaaS deployment model for GPUs.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |

Auroras lights were imaged by the astronomers of the Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bengaluru (IIA) through an all-sky camera positioned around the Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) in Hanle, Ladakh.
Auroras are bright and colorful lights, formed due to an active interaction in Space between charged solar wind particles and the Earth’s magnetosphere.
Explained: Key Terms
|
|---|
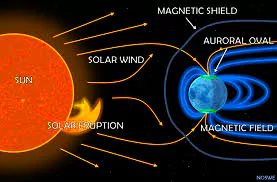 The Present Event: A geomagnetic storm was kicked off after a CME hit the Earth with The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) classifying the storm as “extreme”. A series of Coronal Mass Ejections have been predicted to come towards Earth till May 12.
The Present Event: A geomagnetic storm was kicked off after a CME hit the Earth with The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) classifying the storm as “extreme”. A series of Coronal Mass Ejections have been predicted to come towards Earth till May 12.
Effects of Solar Storms:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
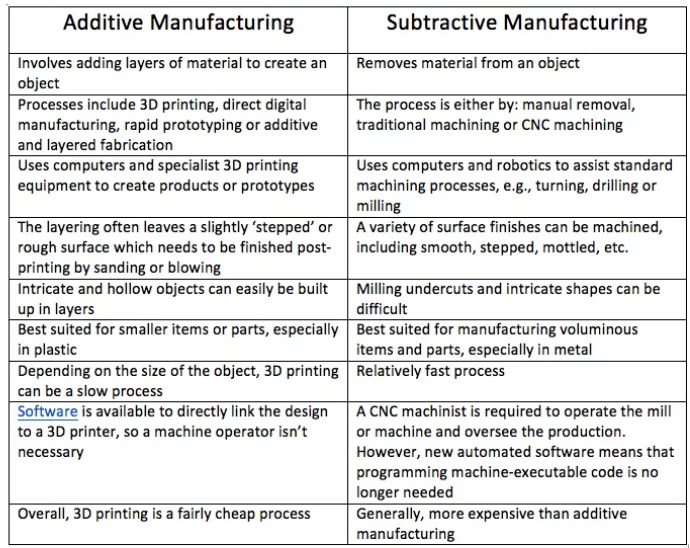
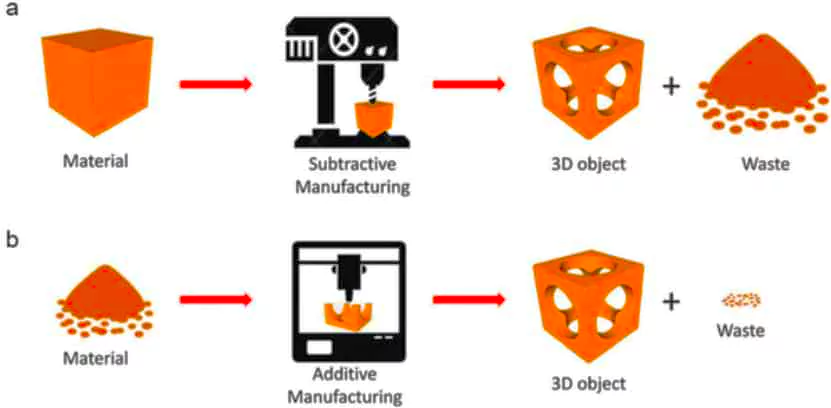
Recently, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully tested a liquid rocket engine made with the help of additive manufacturing technology commonly known as 3D printing.
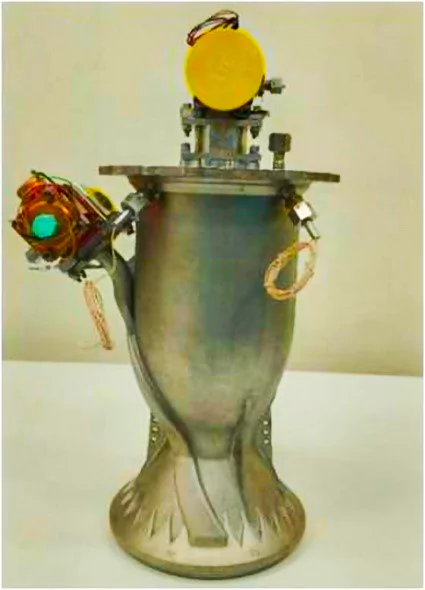
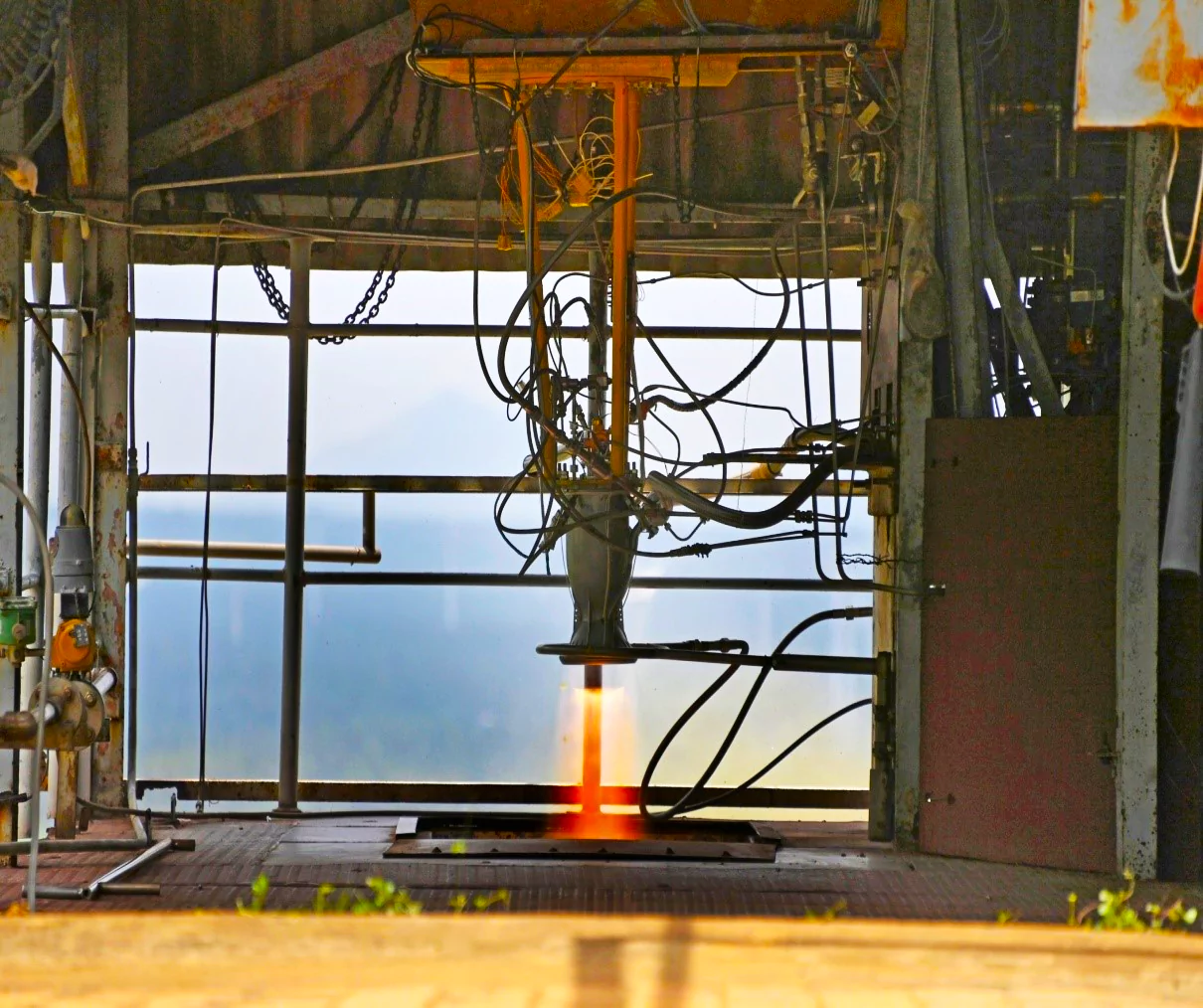
 The RCS controls a rocket, or spacecraft’s orientation, ensuring stability and maneuvering using small thrusters, enabling precise control for such tasks as attitude control during ascent, precise trajectory adjustments for stage separation, payload deployment and docking maneuvers.
The RCS controls a rocket, or spacecraft’s orientation, ensuring stability and maneuvering using small thrusters, enabling precise control for such tasks as attitude control during ascent, precise trajectory adjustments for stage separation, payload deployment and docking maneuvers.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
DigiLocker has become a digital placeholder for administrative and government-related documents. Now Students have the option of viewing their scores and even obtaining their verified marksheets.
DigitLocker app is part of the Indian government’s paper-free initiative aimed at letting users access, verify, and store essential documents in a digital wallet so that they are easy to retrieve and present to officials when required.
Benefits to Citizens
Benefits to Agencies
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, a new Covid- 19 variant named “ KP.2” has been detected increasing in the United States.
 Descendant of JN.1: KP.2 originated from the JN.1 variant.
Descendant of JN.1: KP.2 originated from the JN.1 variant.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Two Kerala government-run temple boards, responsible for 2,500 temples, have stopped using oleander flowers in offerings.

API (Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India) mentions oleander root bark oil for skin diseases.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The M4 chip introduced by Apple in the iPad Pro includes a 16-core Neural Engine, referred to by Apple as the Neural Processing Unit (NPU).
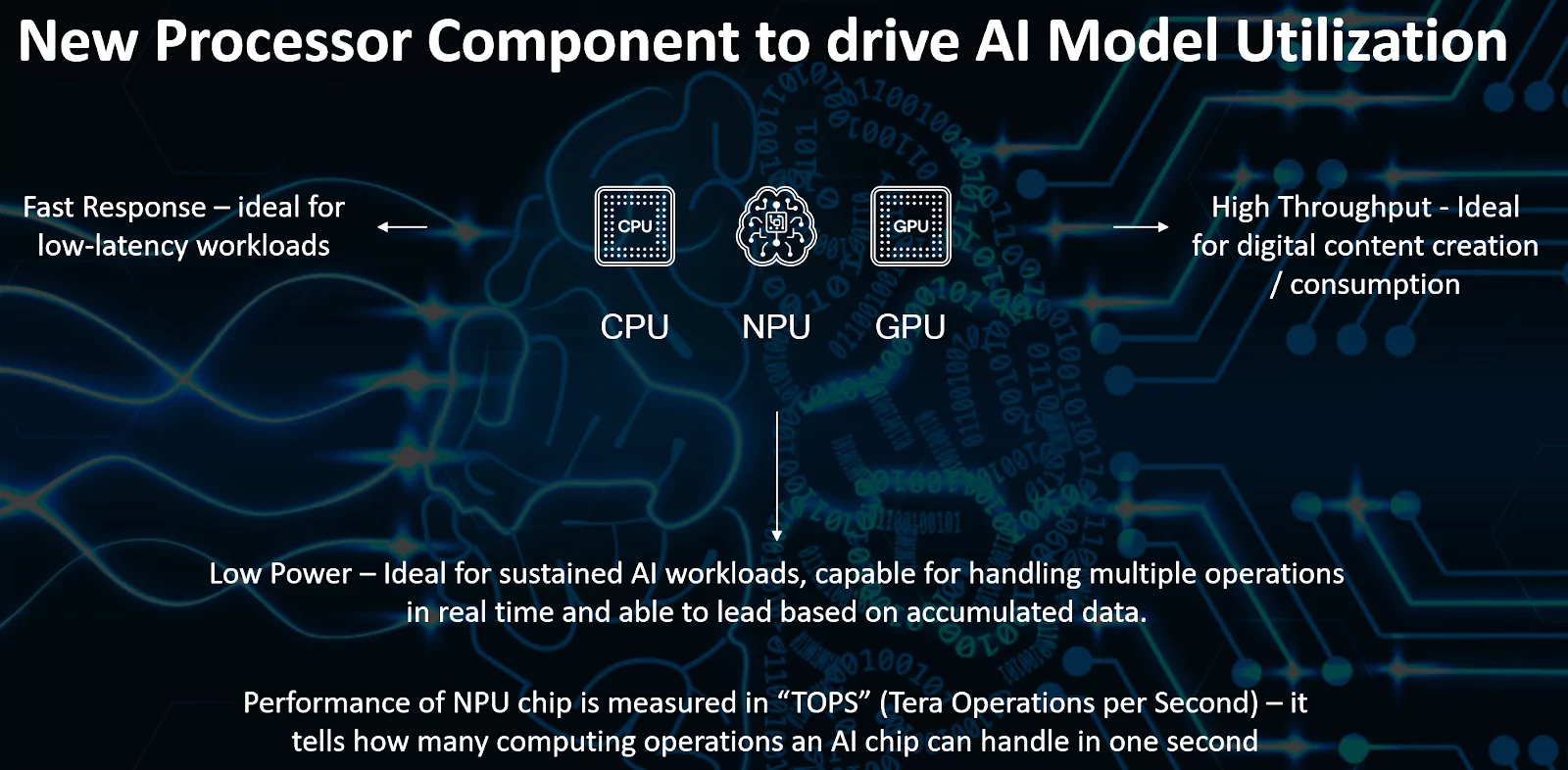 Graphic Processing Units(GPUs): These processors possess parallel computing capabilities and incorporate integrated circuits designed to execute AI workloads alongside other tasks like graphic rendering and resolution upscaling.
Graphic Processing Units(GPUs): These processors possess parallel computing capabilities and incorporate integrated circuits designed to execute AI workloads alongside other tasks like graphic rendering and resolution upscaling. | Small Language Models (SLMs): SLMs are more streamlined versions of large language models.
When compared to LLMs, smaller AI models are cost-effective to develop and operate, and
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has asked the Assam’s Chief Secretary to provide details of officers who let polling stations, schools, and other construction activities in a wildlife sanctuary and a reserve forest in gross violation of the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980.
About National Green Tribunal (NGT):
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
According to the report, Global Electricity Review 2024 by international energy analytics agency Ember, India overtook Japan to become the world’s third-highest producer of solar power in 2023.
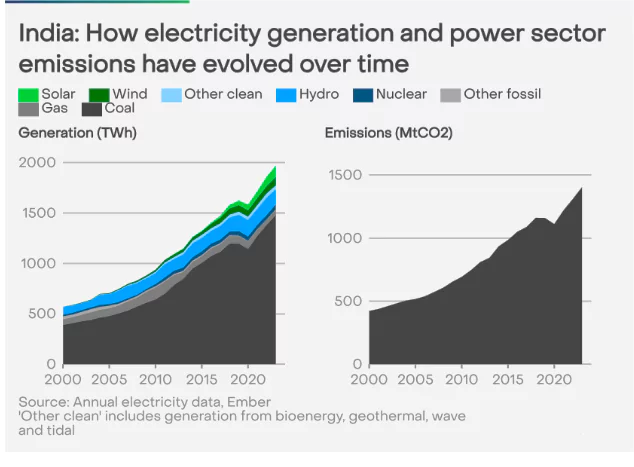 China is followed by the United States(US).
China is followed by the United States(US).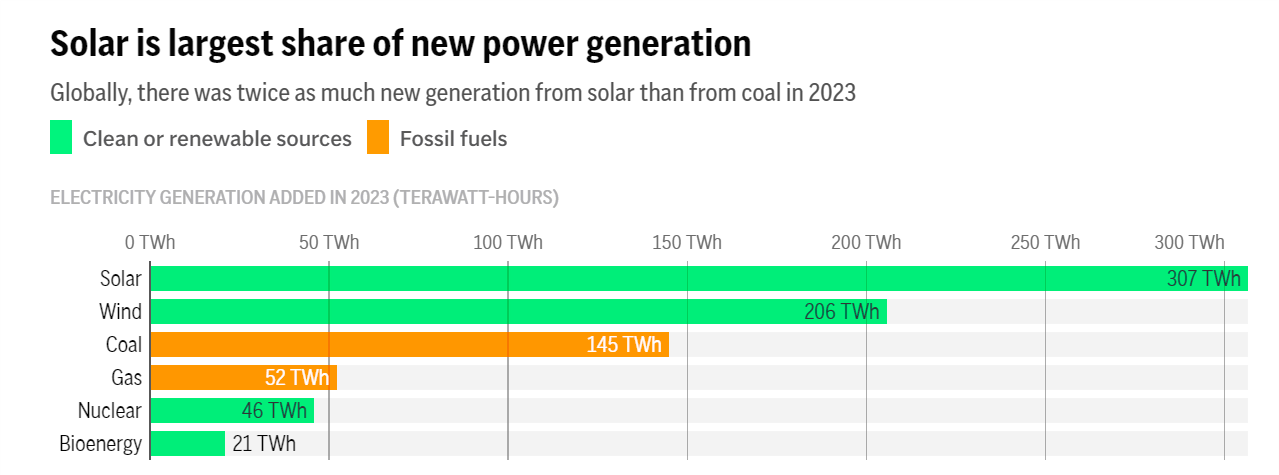 Discrepancy Between Potential and Realized Output: According to data from NITI Ayog, solar energy constituted 18% of India’s total installed electricity capacity of 442 GW as of May 2024.
Discrepancy Between Potential and Realized Output: According to data from NITI Ayog, solar energy constituted 18% of India’s total installed electricity capacity of 442 GW as of May 2024.
Solar power is energy from the sun that is converted into thermal or electrical energy.
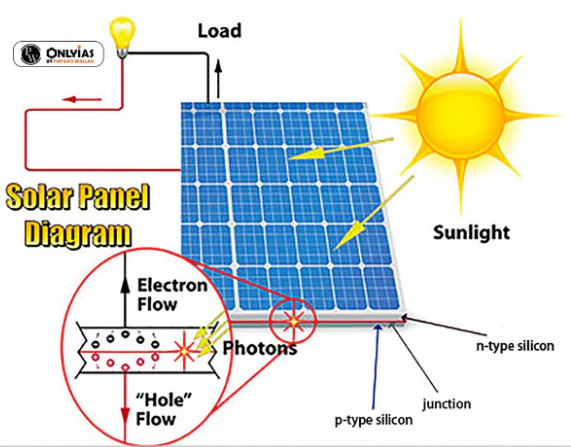
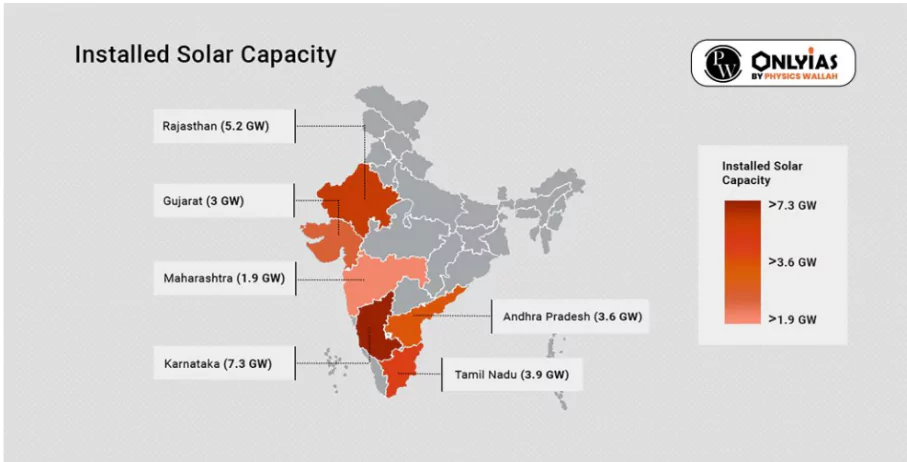 Incident Solar Energy in India: The energy of about 5,000 trillion kWh per year is incident over India’s land area with most parts receiving 4 to 7 kWh m-2 per day.
Incident Solar Energy in India: The energy of about 5,000 trillion kWh per year is incident over India’s land area with most parts receiving 4 to 7 kWh m-2 per day.
| Renewable purchase obligations (RPO): These are mechanisms designed to compel power procurers in every state, like DISCOMS, captive power producers and open-access consumers, to annually purchase a certain minimum amount of renewable energy. |
|---|
Government Initiatives to Promote Solar Power in India
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Indian Government has notified the Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs) (Command, Control, and Discipline) Act, 2023 through a Gazette notification.

Gazette Notifications:
Theaterisation Model:
|
|---|
A theatre command in the military refers to a specific geographical area where military operations are planned, coordinated, and executed under a single command.
Theatre Commands of China:
|
|---|


The Inter-Services Organisations Act 2023 comes ahead of the planned re-organisation of the Indian military into integrated theatre commands. It is essentially an ‘enabling Act’ and does not propose any change in the existing Service Acts/Rules/Regulations which are time-tested and have withstood judicial scrutiny over the last six decades or more.
| A Joint Service Command: |
|
| Controlling Power: |
|
| Role of Government: |
|
| Eligibility for Commander-in-Chie: |
|
| Function of Commander-in-Chie: |
(i) General Officer Commanding the Army, (ii) Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief of a Naval Command, (iii) Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief of an Air Command, (iv) any other officer/authority specified in the service Acts, (v) any other officer/authority notified by the government. |
| Commanding Officer (CO): |
|
| Theatre Commands: |
|
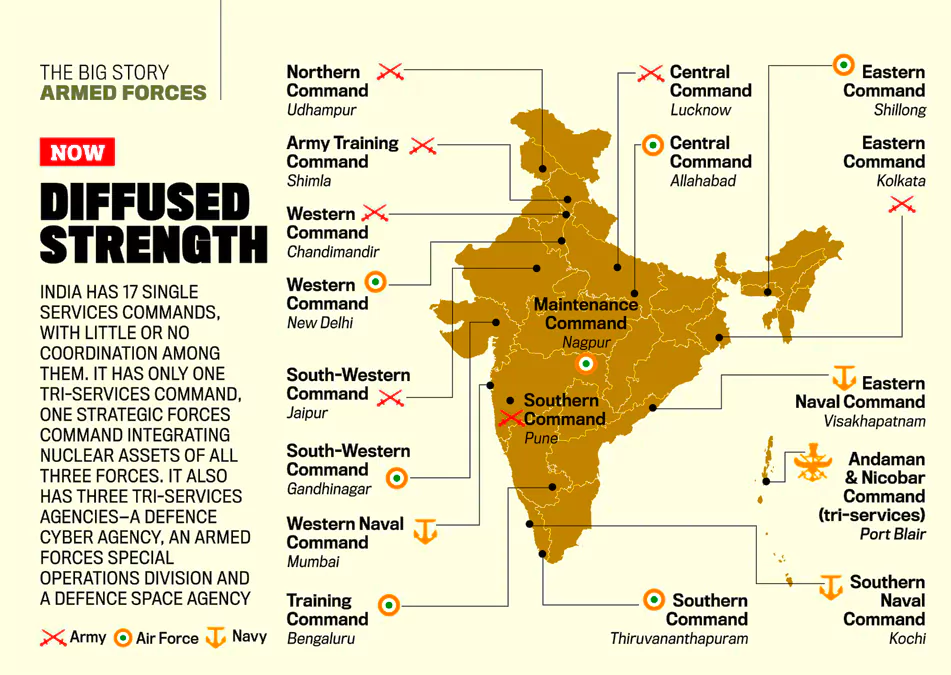 Effective Resource Utilization: The forces will be able to pool their resources efficiently, resulting in the optimum utilisation of platforms, weapon systems, and assets.
Effective Resource Utilization: The forces will be able to pool their resources efficiently, resulting in the optimum utilisation of platforms, weapon systems, and assets.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Union Cabinet Approves National Sports Policy 2025...
What are Altermagnets? A Breakthrough in Magnetism...
India’s 7-Point Strategy for Sustainable Gro...
Cabinet Approves Employment Linked Incentive Schem...
INS Udaygiri Delivered Under Project 17A to Indian...
SC Issues Implemented Reservation Roster for SC/ST...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>