A recent study revealed that Summer 2023 was the hottest season in the northern hemisphere in the past 2,000 years.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Bihar’s only Ramsar site, Kanwar Lake (aka Kabartal), which is in an appalling condition, has not found its mention in any election agenda.
The Kanwar Lake is Asia’s largest oxbow lake situated in the Begusarai district of Bihar. It is a residual oxbow lake, formed due to the meandering of Gandak River, a tributary of Ganga.
About Ramsar Convention
|
|---|
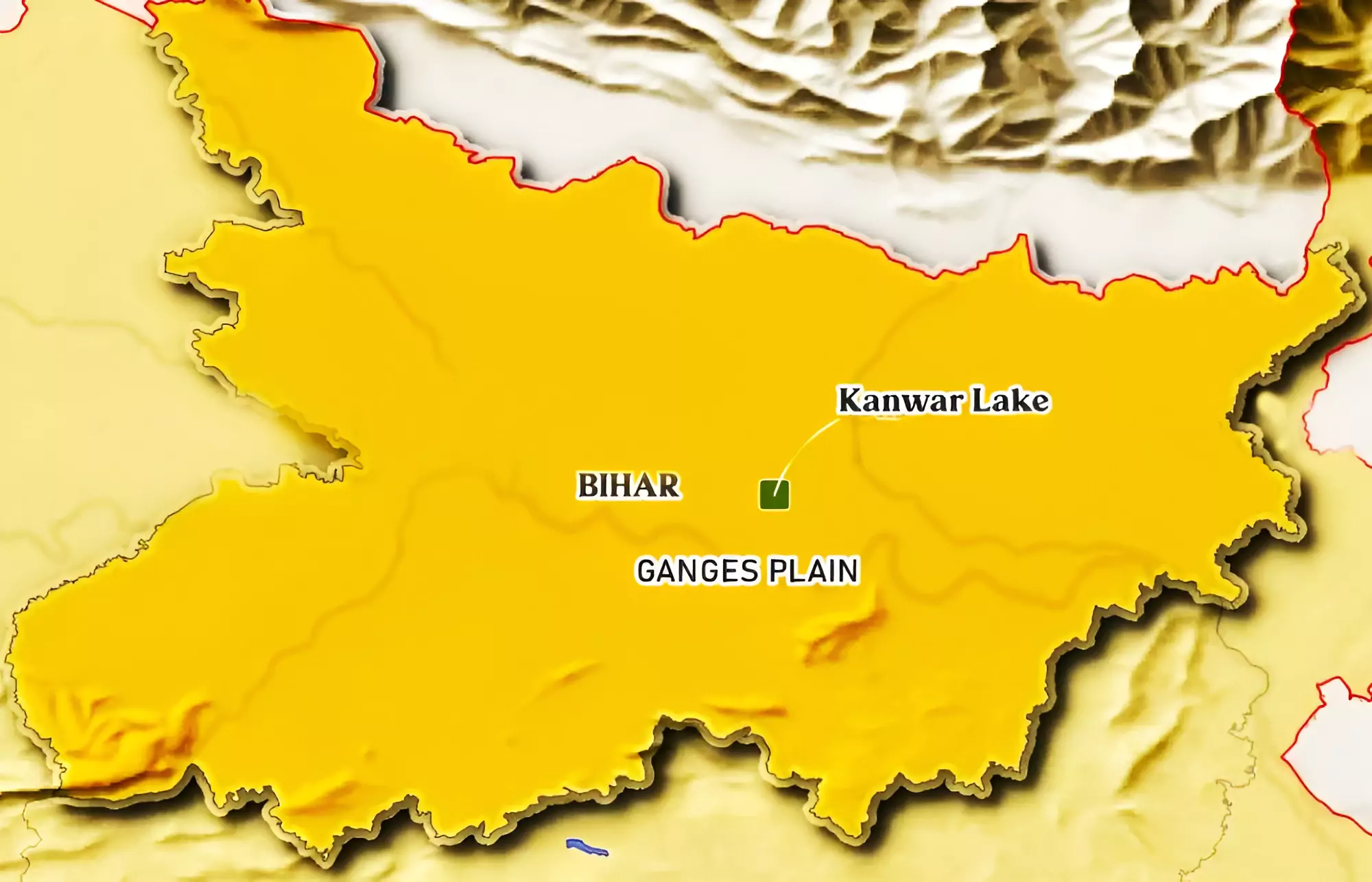 Seasonal Water Levels: The lake is predominantly rainfed, experiencing fluctuations in water levels with seasonal changes, peaking during the monsoon and shrinking in the summer.
Seasonal Water Levels: The lake is predominantly rainfed, experiencing fluctuations in water levels with seasonal changes, peaking during the monsoon and shrinking in the summer.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The World Health Organisation (WHO) recently announced the prequalification of a second vaccine for dengue, called TAK-003, made by a Japanese drug maker.
Live Attenuated VaccinesLive vaccines are derived from “wild” viruses or bacteria which have been attenuated (weakened) in a laboratory, usually by repeated culturing. For example, the measles virus used as a vaccine today was isolated from a child with measles disease in 1954. |
|---|
India’s DNA Vaccine Candidate against Dengue
DNA Vaccines:
|
|---|
Dengue is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus (Genus Flavivirus), transmitted by several species of mosquito within the genus Aedes, principally Aedes aegypti.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
India’s merchandise exports, which shrank over 3% in 2023-24 — a year marred by multiple geopolitical and logistical disruptions to global trade — are off to a positive start this year.
Trade Deficit:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, Governments of Albania, Burkina Faso, India, Montenegro and Uganda have united to combat chemical pollution today, launching a $134-million project to eliminate the use of mercury in medical devices.
Mercury naturally occurs in the Earth’s crust. The World Health Organization (WHO) regards it as among the top ten chemicals or chemical groups posing significant public health risks.
Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining (ASGM):
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Indian Army is prepared to start
The Army is also set to receive the first of two Israeli Hermes-900 Medium Altitude Long Endurance Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) assembled by ADSTL in Hyderabad next month.
Emergency Procurement:
|
|---|
Igla-S stands out as a prominent and highly efficient Man-portable air defense system (MANPADS) manufactured by Russia.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, Fourteen officials of Hindustan Copper Limited (HCL) trapped inside a mine at Khetri in Rajasthan’s Neem Ka Thana district.
It is situated at the foothills of the Aravalli Range, at Khetri Nagar, Neem Ka Thana district of Rajasthan.
Hindustan Copper Limited (HCL),
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
In 2023, India had the most internet shutdowns in the world for the 6th year in a row (116 out of 283 globally).
This makes up over 40% of all internet shutdowns worldwide.
A complete restriction on the use of internet services imposed by a government order.
Provisions related to internet shutdown
Violation of rights due to internet shutdown
|
|---|

Economic and Social Impact of Internet Shutdowns in India
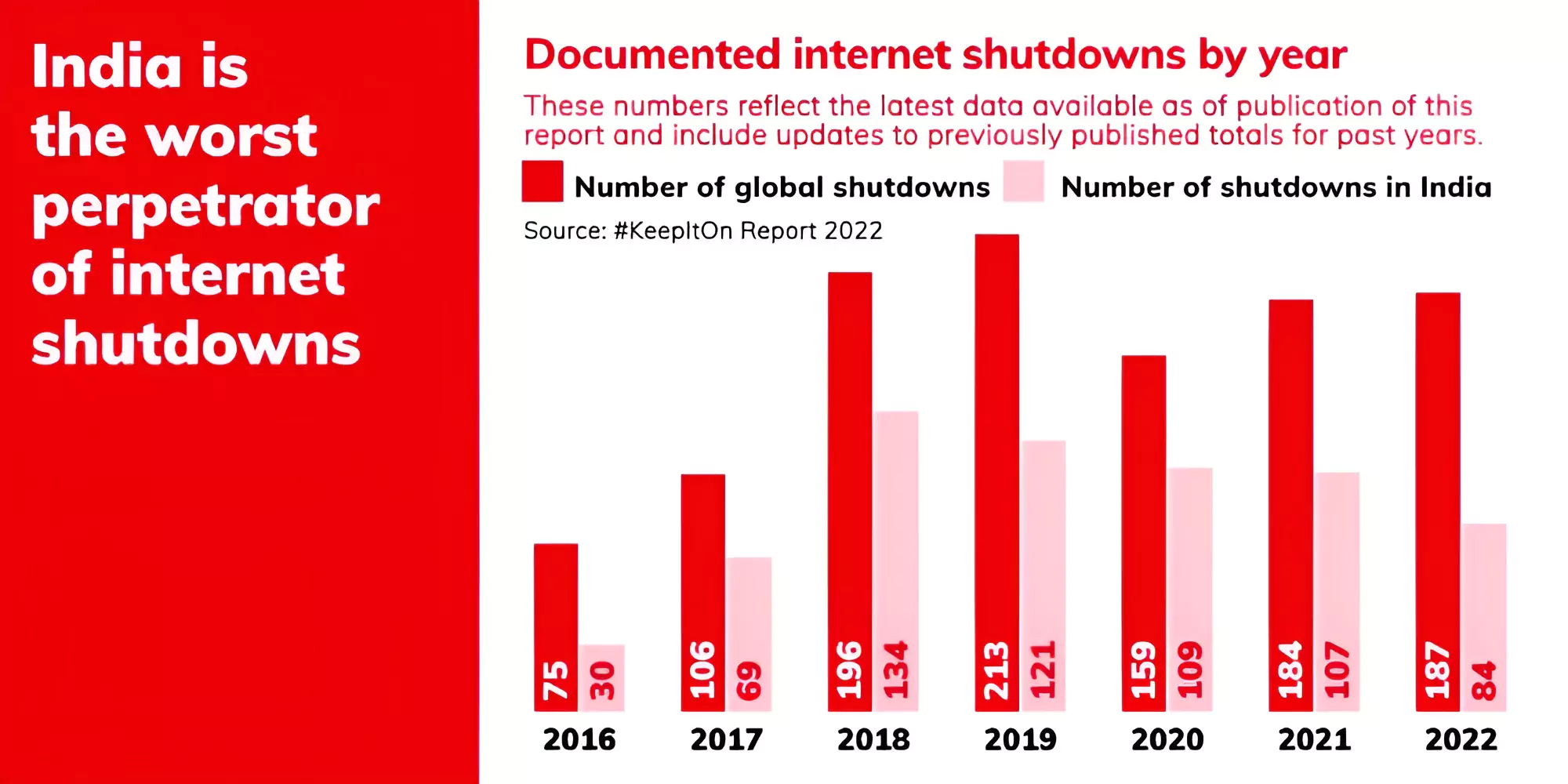 The high number of multi-district shutdowns in March can be attributed to two specific events:
The high number of multi-district shutdowns in March can be attributed to two specific events:

| Reason for internet shutdown | Count |
| Conflicts (across 9 countries) | 74 |
| Protests (across 15 countries) | 63 |
| Exam Cheating (across 6 countries) | 12 |
| Natural Disasters (across 4 countries) | 4 |
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
For the first time, India has set up its own pavilion at the World Hydrogen Summit 2024 held in Rotterdam, Netherlands.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
According to a recent report from 13 states prepared by NITI Aayog (Niti Aayog’s alarm bells on cancer detection: C the signs), ‘huge gap’ in cancer screening at Ayushman centers is detected.
NITI AayogIt is a premier policy think tank of the Government of India.
|
|---|
Cancer is a disease in which some of the body’s cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body.
C the Signs:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Maldives was on his first bilateral visit to India after President Mohamed Muizzu came to power last year.
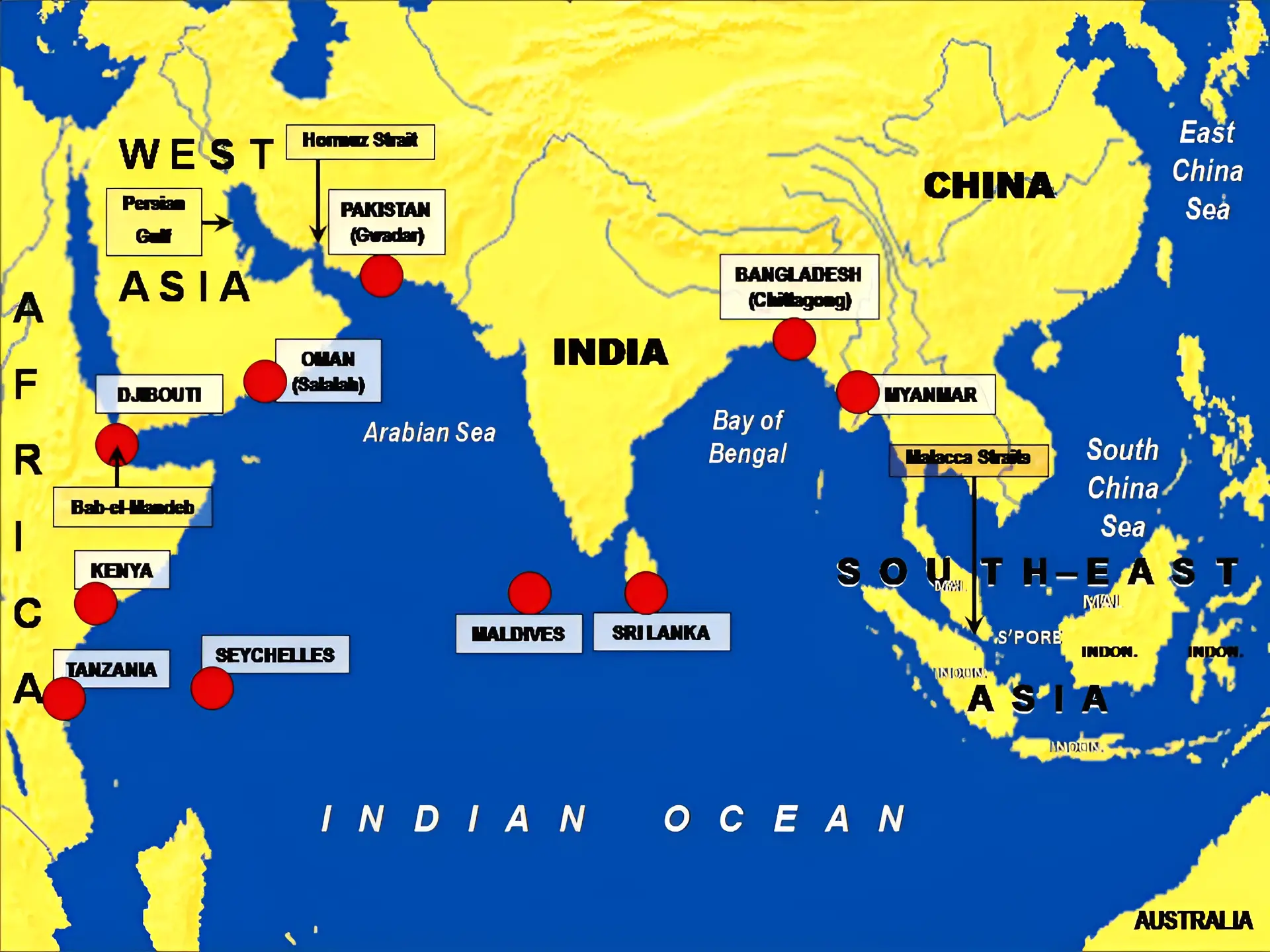
It extends from the eastern coast of Africa to the western coast of Australia including the Arab Gulf, East Africa, South Asia, East Asia to the Straits of Malacca and Southern Ocean Islands encompassing nearly 38 countries within it.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
