The Campi Flegrei supervolcano area near Naples, Italy, recently encountered a magnitude 4.4 earthquake, the most powerful in decades.
The earthquake was part of a series of seismic events called a “seismic storm,” with over a dozen earthquakes of magnitude 2.0 or higher in recent days.
Campi Flegrei, also referred to as the Phlegrean Fields, is a volcanic region in Italy.
Reason Behind Abundance of Volcanoes in ItalyItaly’s abundance of volcanoes stems from its location along a tectonic plate boundary, where the African Plate subducts beneath the Eurasian Plate. This geological activity fosters conditions conducive to volcanic eruptions, resulting in the formation of numerous active and dormant volcanoes. |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, NASA’s Magellan mission has discovered continuous volcanic activity on Venus, the second direct indication of such activity on the planet’s surface.
Radar ImagingA radar imaging system operates like an echo measurement tool. It emits numerous pulses of microwave radiation via the radar antenna and analyzes the properties of the resulting echoes.
|
|---|
The recent study expands upon earlier discoveries regarding continuous volcanic activity on Venus.
VenusVenus is the second planet from the Sun and the sixth-largest in the solar system in terms of size and mass.
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A new tool to detect viral infections in cells using light has been developed by researchers. The tool has been developed by researchers from Harvard University, Cambridge, and Jiangsu University, Zhenjian.
VirusesThey are microscopic organisms that can cause infection to a variety of hosts ie. Humans, plants, animals, bacteria and Fungi.
|
|---|
Standard method to detect Viral Infections in cells
|
|---|
Diffraction
It is the spreading of waves around an obstacles.
|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, Mauxi village in Sattari taluka of Goa has become a hotbed of neolithic discoveries with ancient rock carvings being discovered on the Zarme riverbed.
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) confirmed that ancient rock carvings found on the meta basalt rock along the dry riverbed of the Zarme river belong to the Neolithic period. The Rock Carvings were discovered by local residents 20 years ago, these carvings provide insight into the region’s early inhabitants.
Dhawad communityAbout: The Dhawad community, belonging to the Tirole-Kunbi group, resides in Maharashtra, India. Specifically, they are a subset of the Kunbi Tirole caste, which is predominantly an agricultural community situated in the Khandesh region of Maharashtra. |
|---|
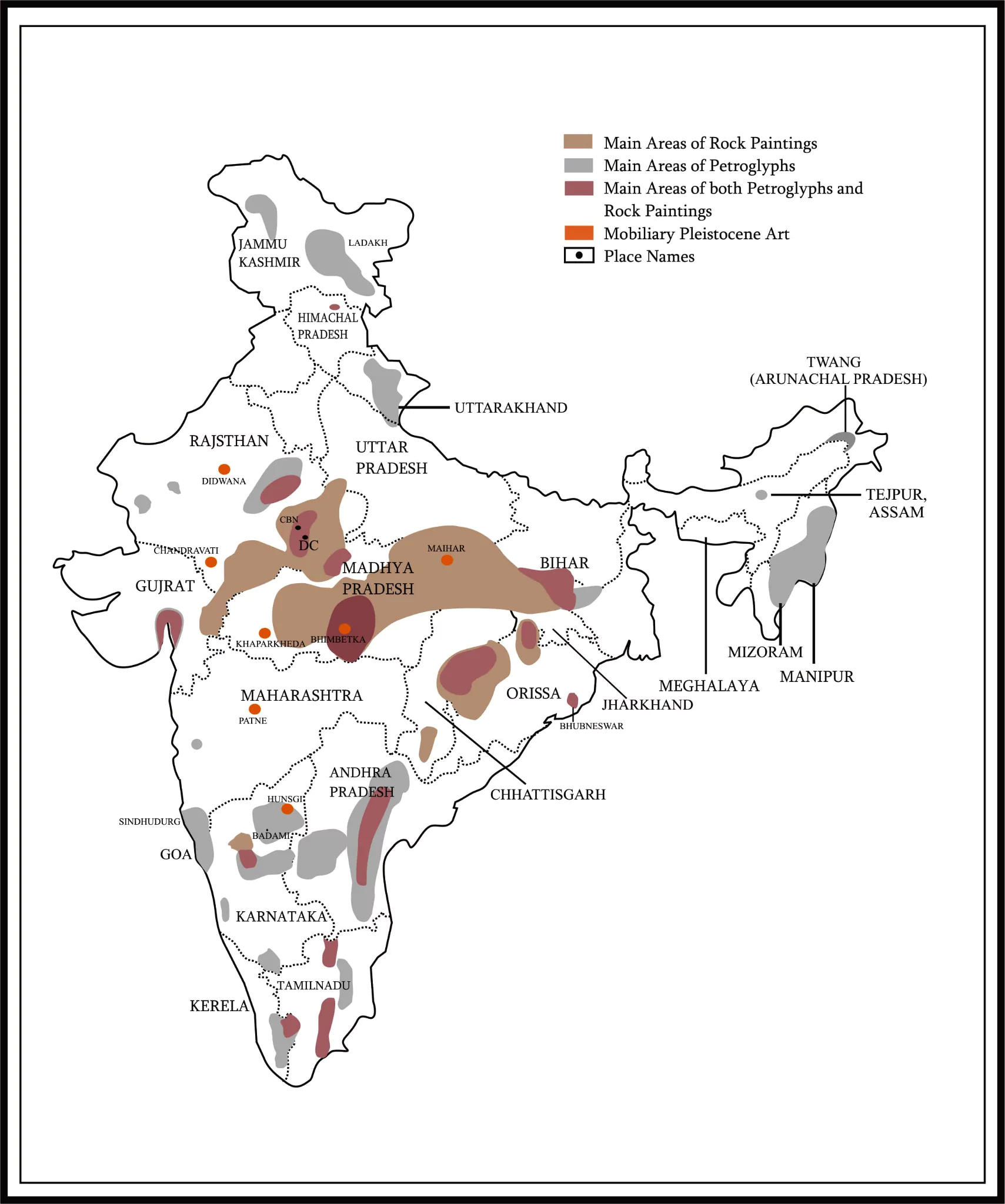
Stone AgeThe Stone Age, a prehistoric era, was defined by the use of stone tools and divided into three main periods: the Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic.
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, The Supreme Court Agreed with the Election Commission‘s view that Article 329(b) restricts judicial interference.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, President Alexander Lukashenko has signed a decree suspending Belarus’ participation in a treaty that limits the deployment of conventional forces in Europe.

The Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE) is often called the “cornerstone of European security,”. It was negotiated at the end of the Cold War and signed on November 19, 1990.
Warsaw Pact
CFE – 1A
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |

Recently, Srinivas R Kulkarni, an Indian-origin US scientist has been awarded the prestigious Shaw Prize in Astronomy for 2024.
Shaw Prize
|
|---|
ULTRASAT (Ultraviolet Transient Astronomy Satellite)It is a near-ultraviolet imaging satellite with a wide field of view (204 square degrees).
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A seven-member Council was established to restore order in Haiti after Prime Minister Ariel Henry’s resignation on April 24.
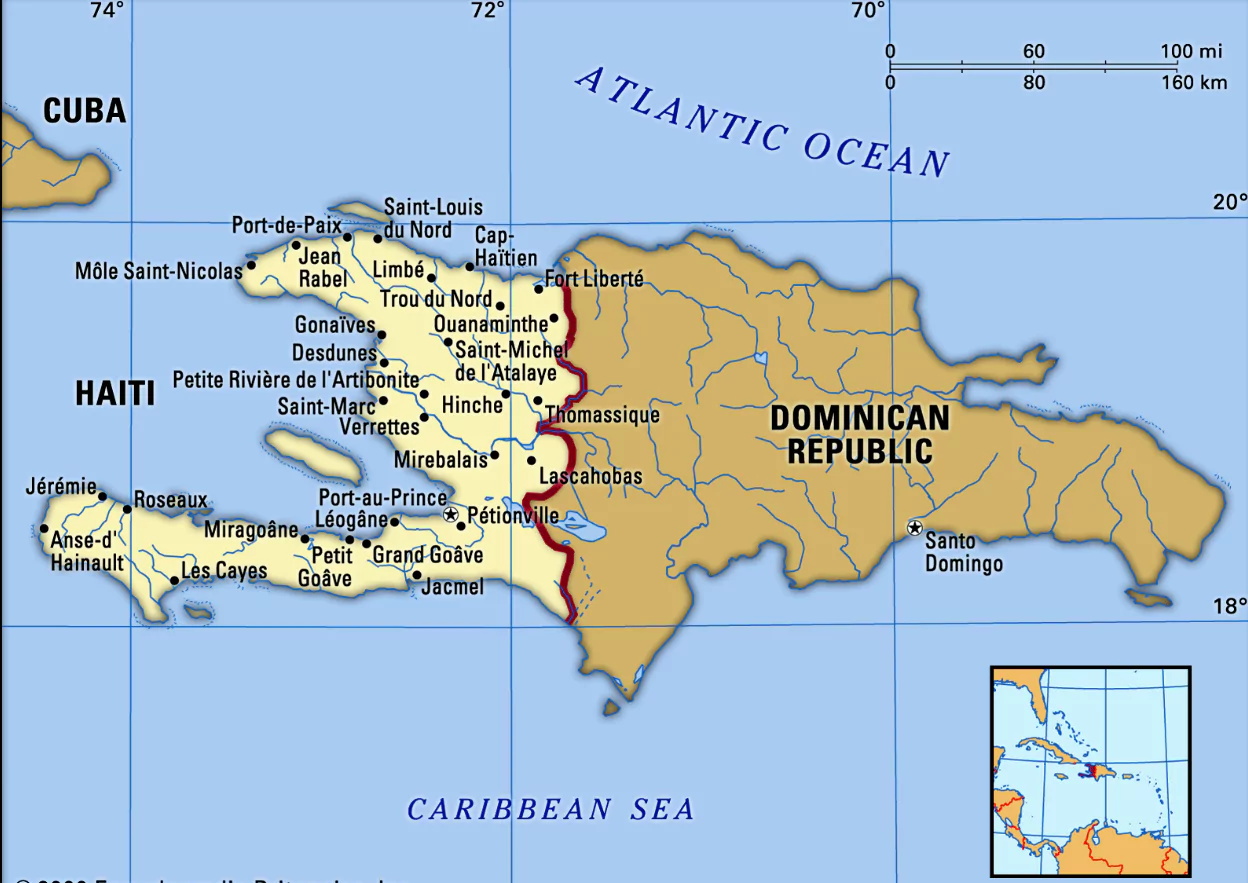 This move has support from Caribbean countries and the U.S., with the Caribbean trade bloc Caricom endorsing the Council as a hopeful new beginning for Haiti.
This move has support from Caribbean countries and the U.S., with the Caribbean trade bloc Caricom endorsing the Council as a hopeful new beginning for Haiti.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully flight-tested the RudraM-II air-to-surface missile from Su-30 MK-I platform of the Indian Air Force (IAF) off the Odisha coast.

Rudram, India’s first anti-radiation missile (ARM), is an Air-to-Surface missile developed by DRDO.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Indian Staffing Federation (ISF), said that India with almost 85% informal labor, generating more than half of the country’s GDP, requires a structural shift towards structured and formal employment.
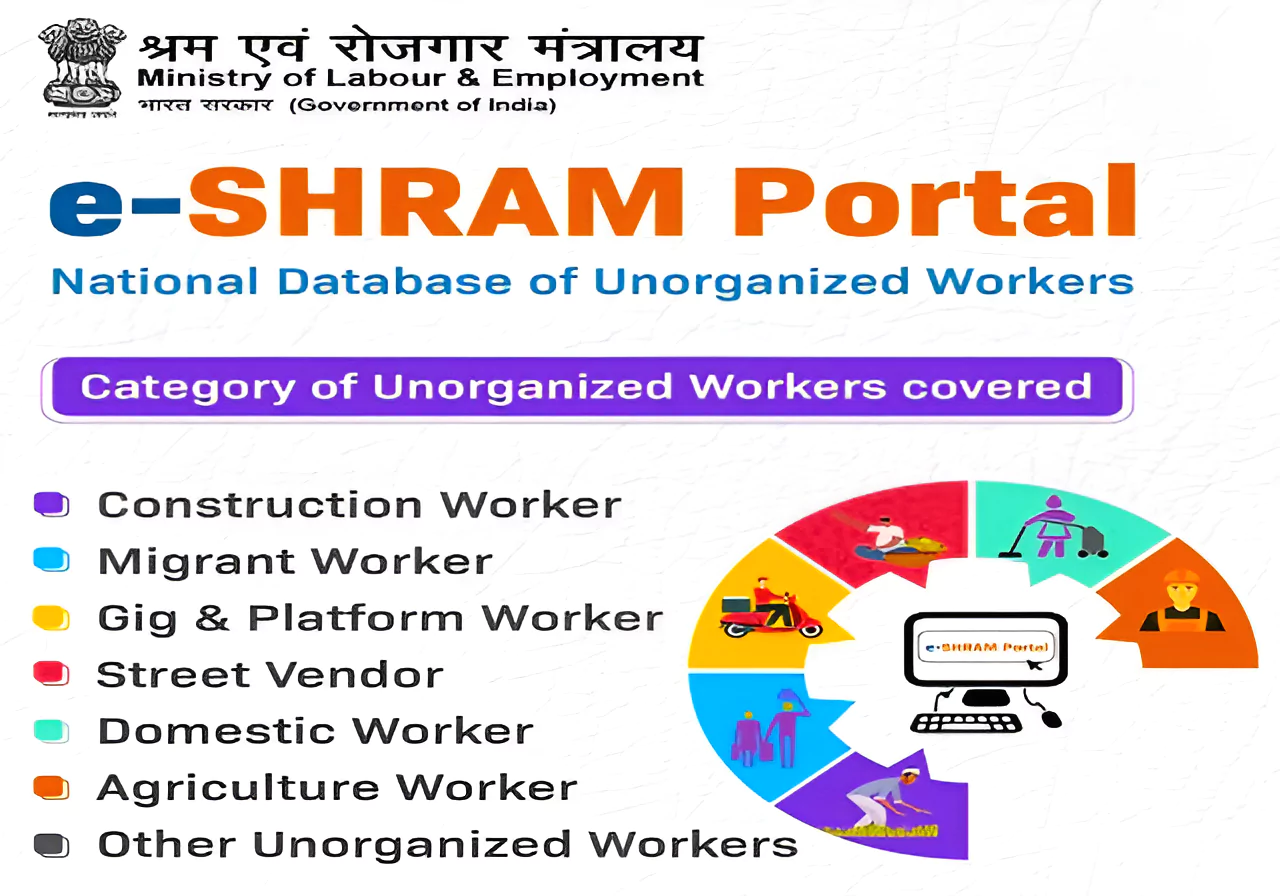
Indian Staffing Federation (ISF), known as the apex body for flexi staffing, is a platform which provides employment, work choice, compensation, social security and health benefits even for the temporary workforce.
| Basis | Formal Economy | Informal Economy |
| Contract | Has a formal contract with the employer. | Has no formal contract with his employer. |
| Work Condition | Has pre-defined work conditions and job responsibilities. | Has no systematic work conditions. |
| Salary and Wages | Gets an assured and decent fixed salary with perks and incentives. | Gets irregularly and unevenly paid. |
| Duration | Has a fixed duration of work time. | Has no fixed hours of work and mostly earns hand to mouth. |
| Grievance Redressal | Is part of an organized group of people working in the same environment and is legally and socially aware about its rights. | It lacks organized groups and people working in the same environment are rarely aware about their rights and have no forum to express their grievances. |
| Social Security | Is covered by social security for health and liferisks. | Is not covered by any kind of social security system and has poor knowledge about the need to protect himself socially and economically. |
| Example | Companies like TCS, Bajaj, Accenture etc. | Roadside hawkers and vendors |
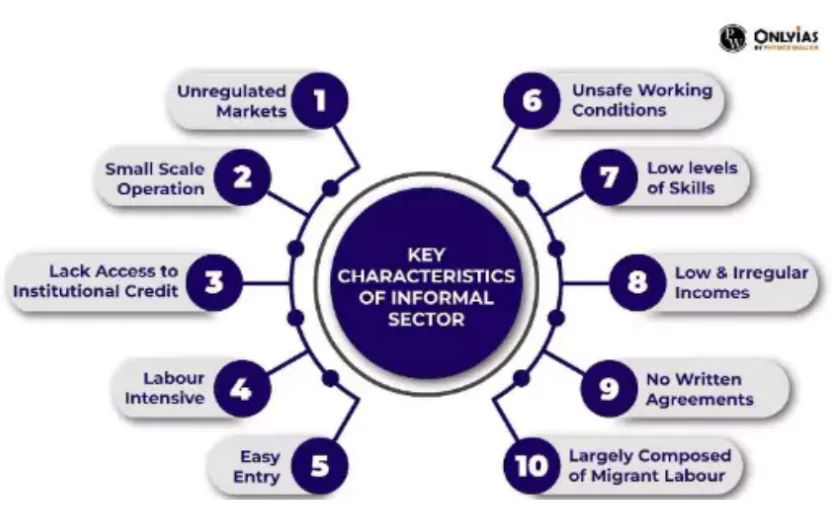
The workforce can be classified into two categories: workers in the formal sector (organized sector) and workers in the informal sector (unorganized sector).
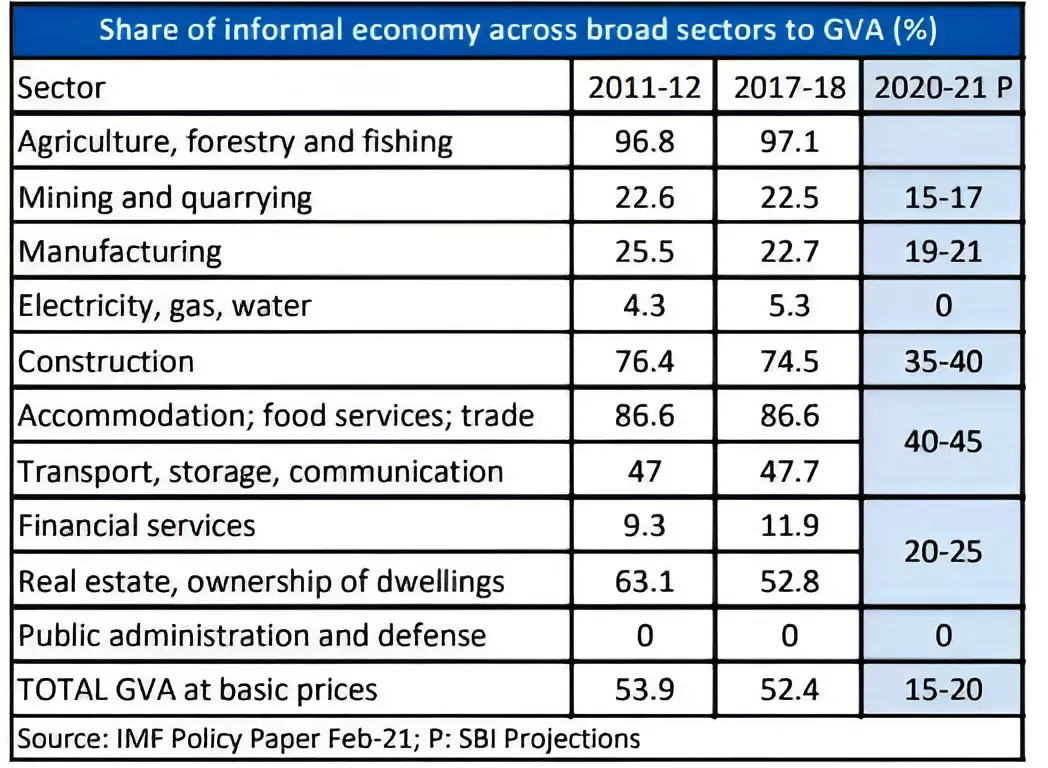 Workers in the informal sector do not enjoy the same level of social security, and their income can be irregular.
Workers in the informal sector do not enjoy the same level of social security, and their income can be irregular.
Initiatives taken by the Indian Government for Informal Laborers:
|
|---|
Transformation in Asia:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>