The constitution of the Capacity Building Commission (CBC) as part of Mission Karmayogi has completed 3 years.
Capacity Building Commission (CBC) is an independent body with full executive power being operational from April 2021. It is core to the overall institutional framework of Mission Karmayogi.
An aide to Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu has indicated Israel’s acceptance of a peace deal with Hamas.
Biden’s proposal consists of three phases peace plan for Gaza
The Indian Council of Medical Research has invited Expressions of Interest for the joint development and commercialisation of low dose or pediatric oral formulation of hydroxyurea to treat sickle cell disease in children.
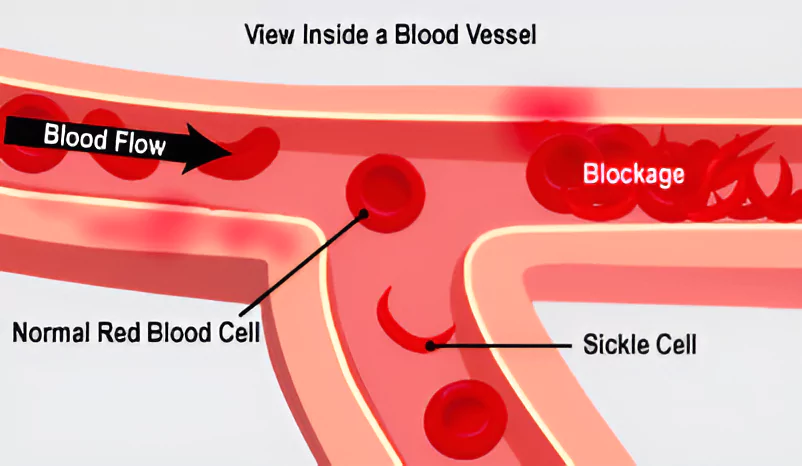
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic blood disorder that affects the production of hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body.
National Mission on Sickle Cell Anaemia
|
|---|
Claudia Sheinbaum will become the first woman President of Mexico in the country’s 200-year history.

Claudia Sheinbaum is a physicist with a doctorate in energy engineering.
Recently, The 80th anniversary of D-Day was celebrated.
In this event, Parachutists jumped from World War II-era C-47 planes over Normandy to commemorate the D-Day.
Why is D-Day such a famous event?
|
|---|
 It is geographically positioned both in the Northern Hemisphere and the Eastern Hemisphere of the Earth.
It is geographically positioned both in the Northern Hemisphere and the Eastern Hemisphere of the Earth.
Theoretical concept of the Green-beard genes could explain the reason, as to how the universal virtue of altruism arose in nature.
The Green-beard EffectGreen-beard Effect is a theoretical genetic trait that motivates individuals possessing a distinctive visible trait eg. A Green Beard, to cooperate with others displaying the same trait. It operates through recognition and offers cooperative advantages.
|
|---|
Around 373 million citizens across the 27 member states of the European Union are eligible to vote on June 6-9 in elections to the European Parliament.
European Council
|
|---|
India-EU Relation
|
|---|
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has developed Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software named (PraVaHa).
About Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
|
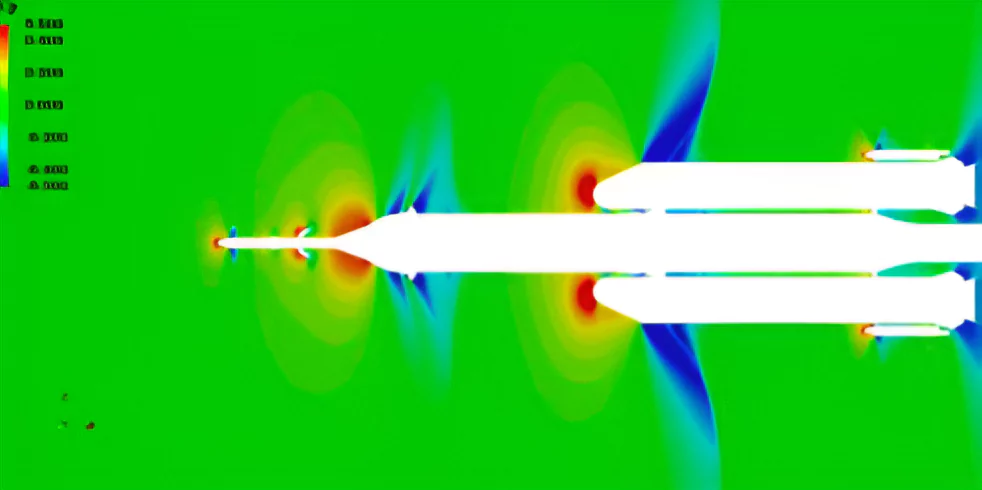 Scramjet Vehicles: Validations of the code are underway for simulating the effect of chemical reactions that occur during air dissociation upon ‘earth re-entry’ and ‘combustion’ as in scramjet vehicles.
Scramjet Vehicles: Validations of the code are underway for simulating the effect of chemical reactions that occur during air dissociation upon ‘earth re-entry’ and ‘combustion’ as in scramjet vehicles.
Addressing the Assistant Secretaries of IAS 2022 batch at Vice-President’s enclave, the Vice President of India urged the civil servants to uphold highest ethical principles.
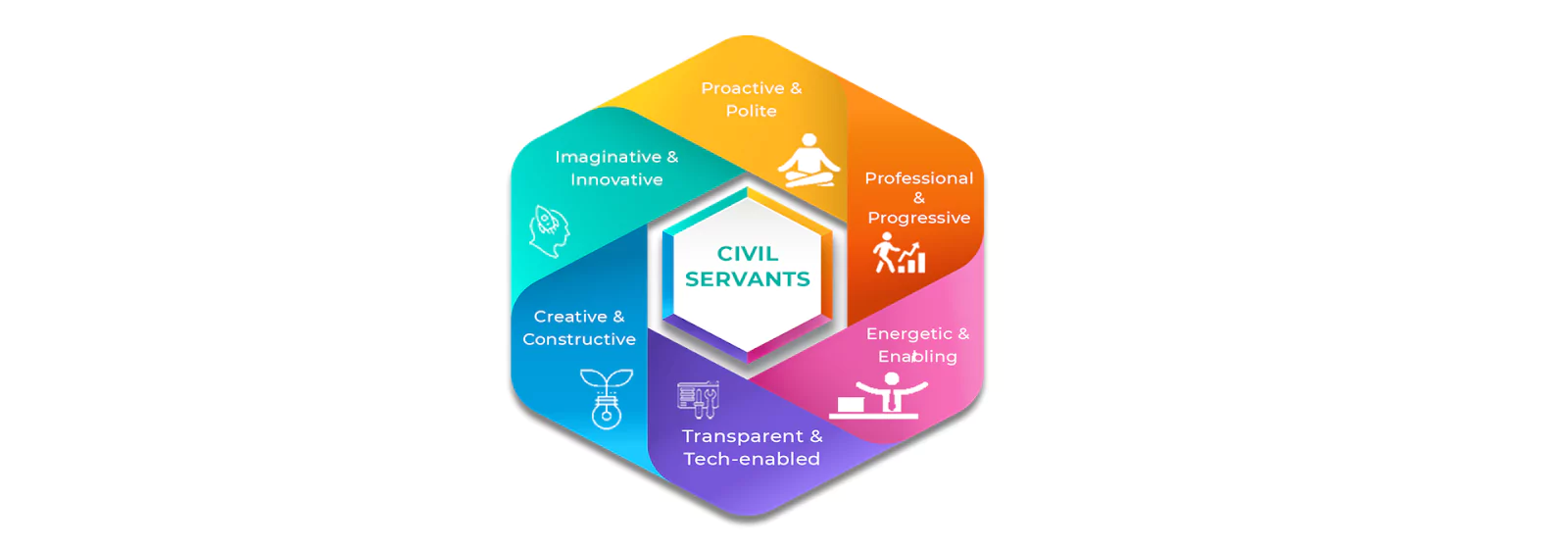
Modern Civil Services in India
|
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
What according to Patel should be the important characteristics of a civil servant of free India?
|
|---|
The Nolan Committee’s Seven Principles of Ethical Conduct
|
 Need to Strictly Follow the Code of Conduct: The Central Civil Services (Conduct) Rules, 1964, outline the ethical behavior expected of all public servants in India.
Need to Strictly Follow the Code of Conduct: The Central Civil Services (Conduct) Rules, 1964, outline the ethical behavior expected of all public servants in India.
Going ahead, the reinforcement and practice of foundational values like integrity, empathy, equity, social justice, and inclusiveness are imperative for the evolution of a more effective and equitable public administration. These values not only guide civil servants in serving the weaker sections of society but also ensure a robust, transparent, and inclusive governance framework for the future.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>