Context:
The Government launched the ‘Startup India initiative’ in January 2016 to foster India’s startup culture, promote economic growth, support entrepreneurship, and generate employment opportunities.
Key Points:
Measures to Promote Women Entrepreneurship in Startup India:
News Source: PIB
Context:
The Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying is implementing the Credit Guarantee Scheme under the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF).
About Credit Guarantee Scheme:
AHIDF Scheme Features:
Credit Guarantee Fund Trust under AHIDF Scheme
News Source: PIB
Context:
There are 8 types of intellectual property rights covered under Intellectual Property Rights Policy Management (IPRPM) framework.
National IPR Policy 2016:
Types of Intellectual Property Rights Covered under IPRPM Framework:
Under the National IPR Policy, various objectives and activities have been undertaken to promote and protect intellectual property rights:
News Source: PIB
Context:
Recently, the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare launched several new technological initiatives under the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana to empower farmers and streamlining the operations.
YES-TECH Manual:
WINDS Portal:
AIDE Mobile App:
News Source: PIB
Context:
The Government has initiated the procurement of tomatoes under the Price Stabilization Fund to address the increase in tomato prices.
Key Points:
About Price Stabilization Fund (PSF):
Other initiatives by the Government to stabilize prices:
News Source: PIB
Context:
More about the news:
News Source: pib
Context:
More About the news:
National Programme for Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NPNCD):
News Source: TOI
Context:
More about the news:
News Source: Financial Express
Context:
| Probable Question:
Q. Although the food processing industry in India has experienced steady growth, there is still significant untapped potential to be realised. Examine. (250 words) |
Food Processing Industry:
About food processing industry:
Key Facts:
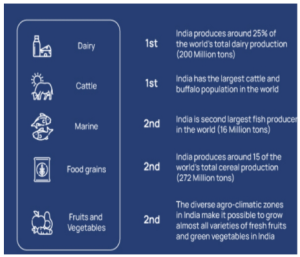 Job creation: This sector is expected to generate 9 million jobs by 2024.
Job creation: This sector is expected to generate 9 million jobs by 2024.Key Drivers:
Opportunities:
Upstream requirements of Food processing industry:
Downstream Requirements in Food processing industry:
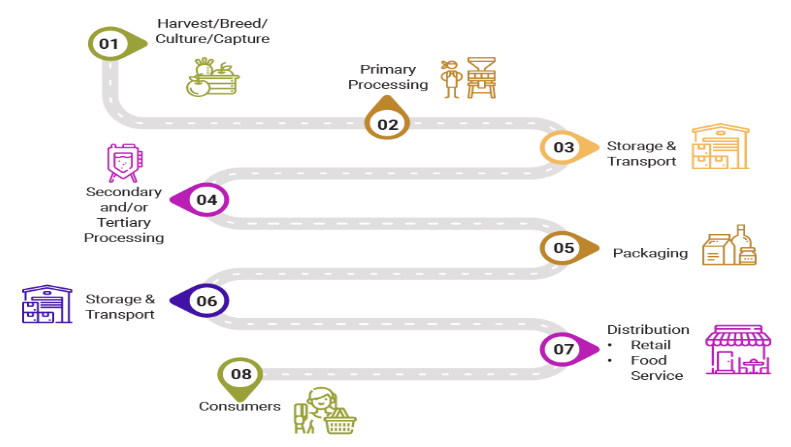
Challenges of food processing industry in India:
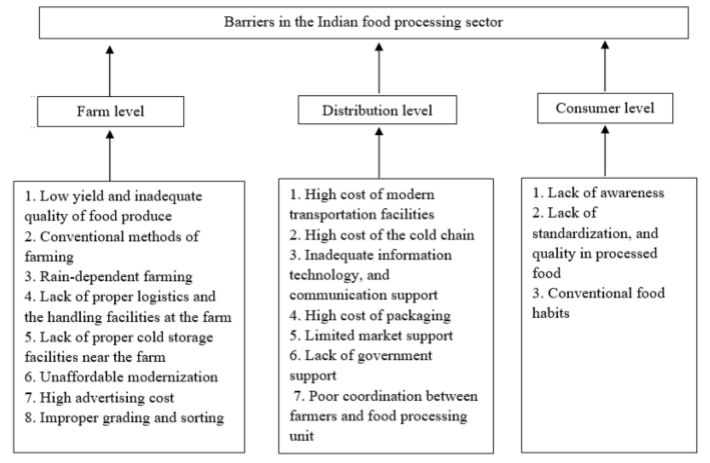
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES:
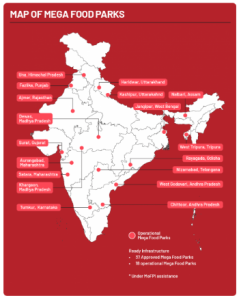 The Mega Food Parks Scheme covering a minimum area of 50 acres, operates using a cluster-based approach, following a hub and spokes model that aims to establish a vital link between agricultural production and the market. By bringing together farmers, processors, and retailers, the scheme seeks to maximize the value addition of agricultural products, minimize wastage, boost farmers’ income, and create employment opportunities, especially in rural areas.
The Mega Food Parks Scheme covering a minimum area of 50 acres, operates using a cluster-based approach, following a hub and spokes model that aims to establish a vital link between agricultural production and the market. By bringing together farmers, processors, and retailers, the scheme seeks to maximize the value addition of agricultural products, minimize wastage, boost farmers’ income, and create employment opportunities, especially in rural areas.
Way Forward:
News Source: pib
Context:
Recently, Sri Lanka’s President Ranil Wickremesinghe visited Delhi for an official visit.
| PYQ:
Q. India is an age-old friend of Sri Lanka.’ Discuss India’s role in the recent crisis in Sri Lanka in the light of the preceding statement. (2022) |
Major Pillars of India-Sri Lanka Relations:
Challenges in India-Sri Lanka Relations:
Importance of Sri Lanka to India:
India’s Role in Recent Sri Lanka Economic Crisis:
Way Forward:
Key Highlights of Visit:
|
News Source: The Hindu
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
