Californium
|
Recently, Bihar police seized what they thought was a highly unusual and dangerous contraband: 50 grams of the highly radioactive metal Californium
About Californium:
|
Microbes on Microwave ovens |
According to a new study, Microwave ovens used in homes, offices, and laboratories host thriving communities of microbes.
Key Findings:
Microwave Working
|
Paetongtarn Shinawatra
|
Recently, 37-year-old Paetongtarn Shinawatra became the youngest Prime Minister of Thailand.
About Paetongtarn Shinawatra:
Neighbourhood troubles:
|
Virtual Court |
Recently, The Kerala High Court launched a first-of-its-kind virtual court called ‘24×7 ON Courts — Open and Networked Courts’ in Kollam district.
About ‘24×7 ON Courts — Open and Networked Courts’:
|
Turmoil in Bangladesh |
The ongoing crisis in Bangladesh is expected to impact the Indian textile and apparel sector in the short term.
About Indian Textile Industry
India Bangladesh Trade
Blessing in disguise to Indian textile manufactures:
|
Indonesia marked 79 years of independence on August 17, 2024 with a ceremony organised in the future capital of Nusantara.

The year 2024 is expected to witness four supermoons in a row with the first one slated to occur on August 19, Monday at about 12:00 AM IST.

According to the scientific study of the land use dynamics of the Aravali range post 1975 published in the journal ‘Earth Science Informatics’, there has been a widespread ecological degradation in the Aravali Range.
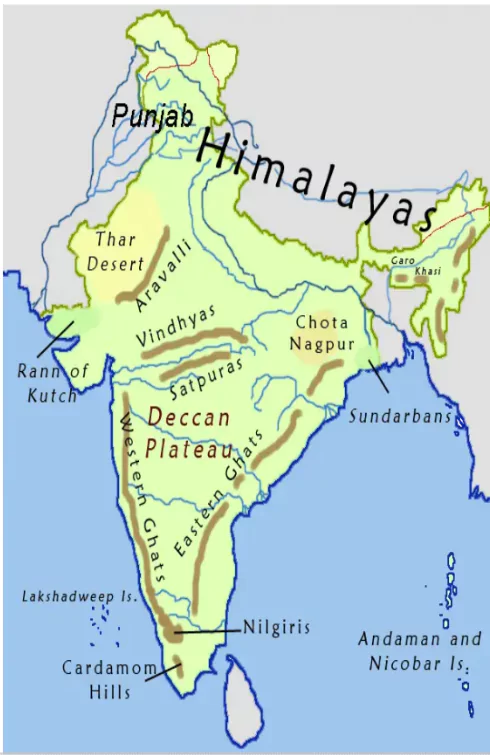 Extent & Location : It extends from Raisina Hills in New Delhi to Khedbrahma and Palanpur in Gujarat,in a south-west direction, passing through southern Haryana and Rajasthan, and ending in Gujarat.
Extent & Location : It extends from Raisina Hills in New Delhi to Khedbrahma and Palanpur in Gujarat,in a south-west direction, passing through southern Haryana and Rajasthan, and ending in Gujarat.
Positive Impact of the Protected Areas in the Aravalli:
|
|---|
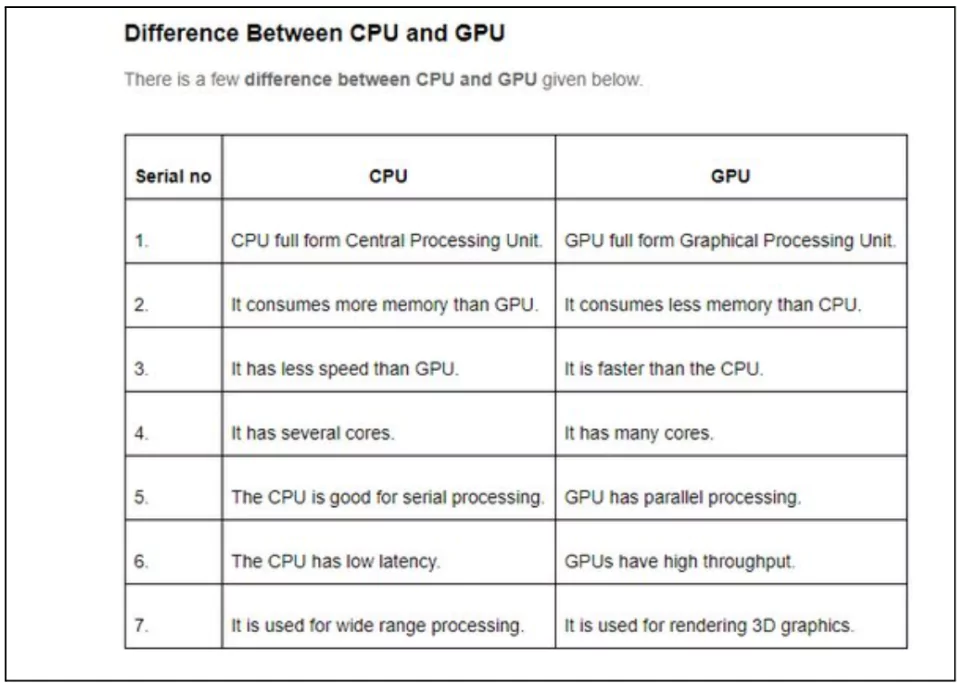
The government is preparing to buy 1,000 Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) as part of the IndiaAI Mission.
 Objective of IndiaAI Mission
Objective of IndiaAI Mission
Recently, the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) has released the World Investment Report 2024.
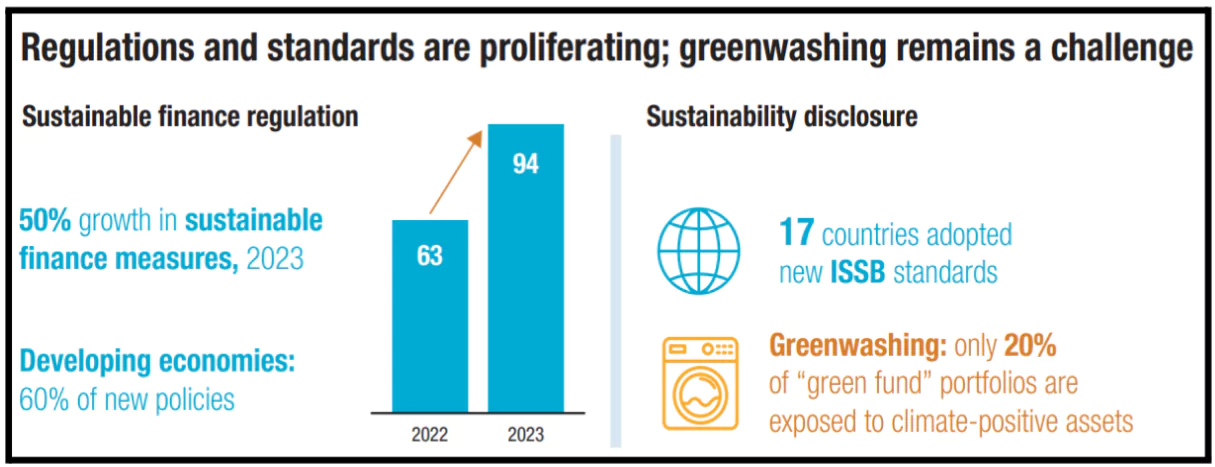
UN Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
|
|---|
This article sheds light on the Kondh Tribal Life, Culture, and Agriculture.
 Cultural Division: Divided into hill-dwelling and plain-dwelling groups but identify by clans.
Cultural Division: Divided into hill-dwelling and plain-dwelling groups but identify by clans.
Paddy Cultivation in the Hills
|
|---|
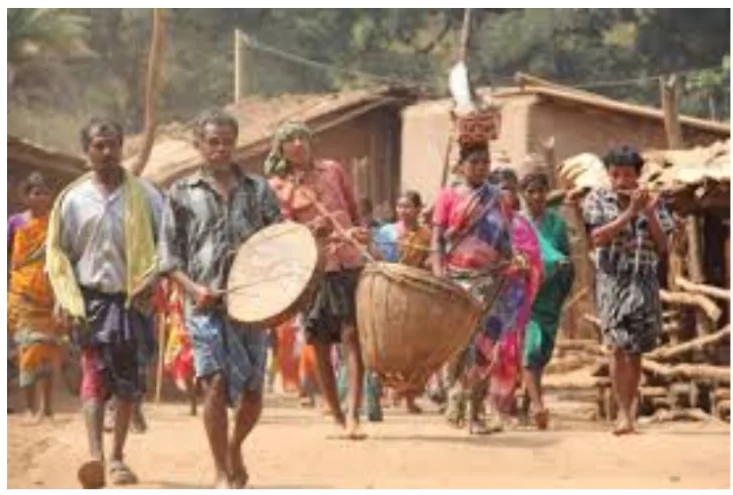
Climate change could shrink the Malabar Tree Toad’s (MTT) distribution in protected areas by up to 68.7% between 2061 and 2080, based on high emissions scenarios.
Low Emissions Scenario:
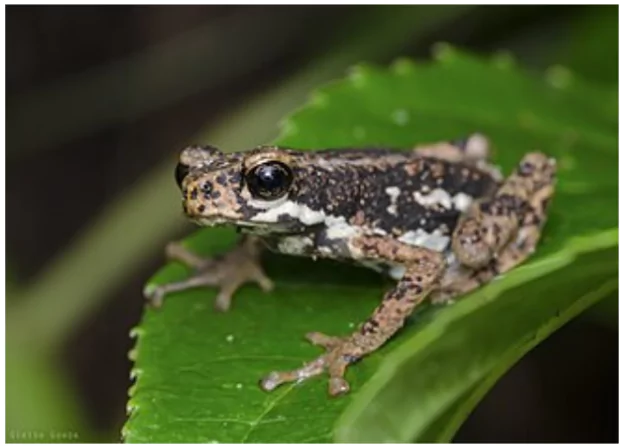

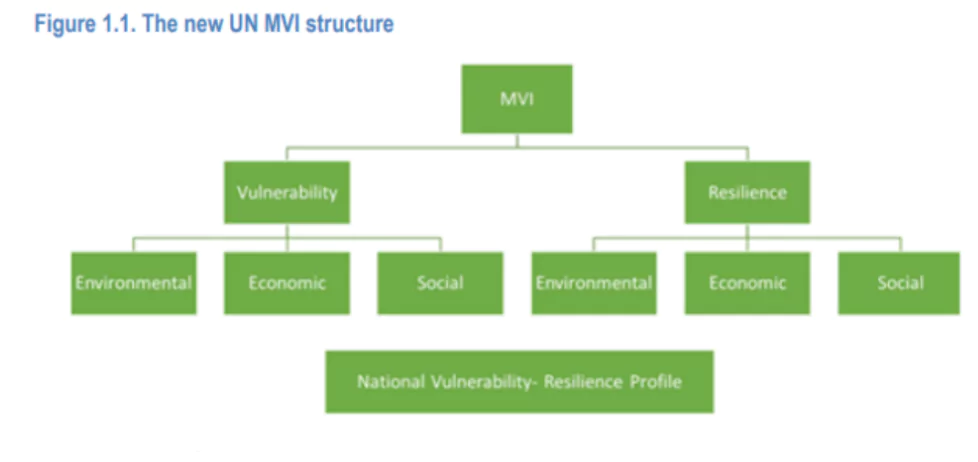
The Multidimensional Vulnerability Index (MVI), a new data-driven “vulnerability” index that would help small island states and developing nations gain access to low-interest financing was officially launched by The UN General Assembly.
Uttarakhand has become the first Indian state to launch a Gross environment product Index (GEPI).
GEP
|
|---|
Green GDP
|
|---|
Decades after the Red Fort trial, it is hoped that India’s leaders find the wisdom to commit themselves again to what unites us citizens as a people.

The Red Fort Trials, also known as the Indian National Army trials or the INA trials.
About Indian National Army (INA)The INA was formed by Indian nationalists during World War II under the leadership of Subhas Chandra Bose.
|
|---|
The INA trials, held during India’s independence struggle, were a watershed moment in the fight against British colonial rule. They represented the Indian people’s unbreakable spirit and determination in their quest for freedom.
The INA Trials, alongside the three upsurges, represent pivotal moments in India’s struggle for independence. Through legal defence efforts and relief initiatives, individuals like Bhulabhai Desai, Tej Bahadur Sapru, Kailash Nath Katju, Jawaharlal Nehru, and Asaf Ali provided crucial support to those affected by the trials. Overall, the INA Trials and accompanying upsurges serve as enduring symbols of resistance against colonial rule and the quest for freedom.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
