| GI Tags |
|
| Lokmanya Tilak Award |
Bal Gangadhar Tilak:
|
Context:
About Polypills:
Fixed Dose Combinations(FDC):
Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs):
Context:
About UDAN (Ude Desh ka Aam Naagrik)Scheme:
Key Features:
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
PM SVANidhi(Pradhan Mantri Street Vendors Atmanirbhar Nidhi) Scheme:
Scheme Benefits:
News Source: Indian Express
Context:
About IPCC:
What are the IPCC assessment cycles?
Assessment Reports:
| Assessment Report | Highlights |
| First(1990) |
|
| Second(1995) |
|
| Third(2001) |
|
| Fourth (2007) |
|
| Fifth(2014) |
|
| Sixth(2021) |
|
News Source: Indian Express
Context:
Key Highlights from the Report:
MPOWER measures:
Second Hand Smoke:
|
Dangers of e-cigarettes:
E- Cigarette:
|
How does India fare?
News Source: Indian Express
Context:
About the bill:
Significance:
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
According to an updated analysis of the 2022 tiger census released recently, India’s tiger population increased to 3,682 in 2022, from 2,967 in 2018.
About All India Tiger Estimation 2022:
Methodology used in all India Tiger Estimation:
Protection Status of Tiger:
Tiger Landscapes of India:
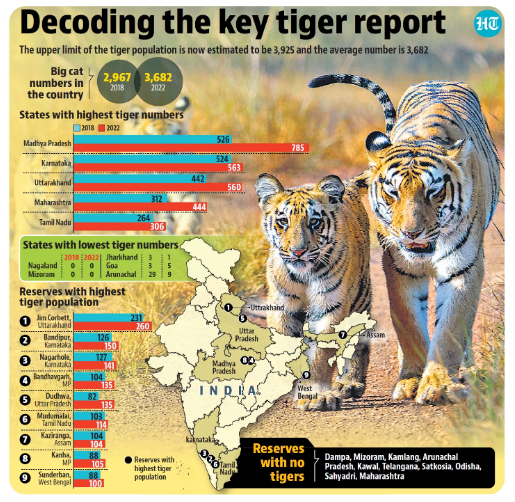 Image Credits: Hindustan Times
Image Credits: Hindustan Times
Challenges:
Benefits of Conserving Tigers:
Indian initiatives to Protect Tiger:
Global Initiatives to Protect Tiger:
Way Forward:
| Key Facts:
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA):
Merger of Project Tiger and Project Elephant:
|
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Recently, India has mooted the concept of a partnership between like-minded countries to work together on digital public infrastructure (DPI) that can be used by everyone.
| UPSC Probable Question
What is Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) and how does it facilitate the flow of people, money and information in India? Discuss the benefits and challenges of DPI for India’s economy and society. |
More on News
About digital public infrastructure (DPI)
 DPI can help solve global challenges such as poverty reduction, climate resilience, and digital transformation by improving the efficiency, transparency, inclusion, and innovation of public service delivery.
DPI can help solve global challenges such as poverty reduction, climate resilience, and digital transformation by improving the efficiency, transparency, inclusion, and innovation of public service delivery.India and Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
Significance of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
Challenges faced in Development of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI):
Steps to make DPI more robust and efficient are:
| Additional Information
Digital India Mission
|
News Source: Financial Express
How Climate Change is Creating Refugees Across the...
View India’s Gender Gap Report Ranking as a Warn...
Aiding India’s Progress with Choice, Control and...
Bridge too Far: On the Bridge Collapse in Vadodara
How India’s Biofuel Potential Complements its Le...
As PM Modi lands in Namibia, this is why the Count...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
