| World Water Week 2023: Stockholm International Water Institute (SIWI) |
|
| Highly Water Stressed Conditions: World Resource Institute (WRI) Report |
|
Context: Sugar millers have urged the government to totally exempt sugar from the mandatory 20 percent jutebag packaging from the 2023- 24 season.
Why has relaxation been sought?
Importance of Jute for the domestic economy:
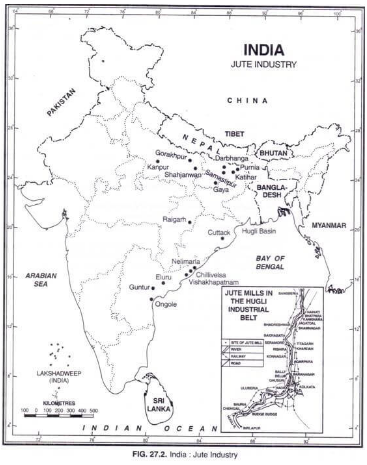
Geography of Jute in India:
Conditions for Jute Production:
News Source: Business Standard
Context:
The private credit alternative investment fund (AIF) space is witnessing heightened action this financial year (2023-24), with the change in taxation of debt mutual funds (MFs).
About Alternative Investment Fund (AIF):

Benefits of Investing in AIFs:
News Source: Business Standard
Context: The Reserve Bank of India announced the launch of the Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit (PTPFC) pilot project.
About Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit (PTPFC):
“Plug and Play”
Frictionless Credit:
|
Benefits:
News Source: The Hindu
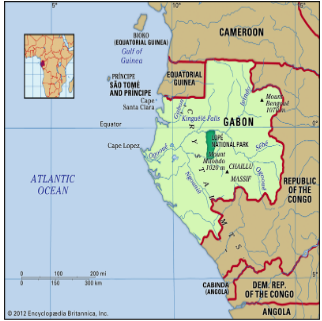
| Gabon
Recently, Gabon announced a $500 million debt-for-nature swap. Gabon Borders: Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Republic of Congo and the South Atlantic Ocean. About Debt for Nature Swap
|
 |
Context:
A large number of megalithic hat stones were found during a recent archaeological salvage excavation conducted by the Kerala Archaeology Department at Nagaparamba in Kuttippuram village, near Tirunavaya.
About Hat Stones:
What is Salvage excavation?
Megaliths
Commemorative non-sepulchral memorials:
|
 Geographical Spread: Megaliths are spread across the Indian subcontinent, though the bulk of them are found in peninsular India, concentrated in the states of Maharashtra (mainly in Vidarbha), Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
Geographical Spread: Megaliths are spread across the Indian subcontinent, though the bulk of them are found in peninsular India, concentrated in the states of Maharashtra (mainly in Vidarbha), Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.Thirunavaya
|
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
More about the news:
What is animal husbandry?
|
Overview of various animal husbandry sectors in India:
| Milk |
|
| Meat |
|
| Egg |
|
| Wool |
|
Challenges of Animal Husbandry:
Extension Services:
|
Government Programs:
|
Way Forward:
News Source: Business Standard
Context:
Recently, two Major General-level talks between India and China were held on August 18 as a follow-up to the 19th round of Corps Commander-level talks held earlier this week.
More on the News:
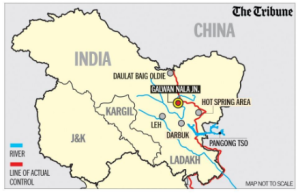
India-China Border Dispute
About India Border Dispute and Challenges
Existing Border Dispute Settlement Mechanisms with neighbors such as:
Other Border Dispute of India with Neighbours
| Country | Dispute |
| Pakistan |
|
| Bangladesh |
|
| Nepal |
|
| Myanmar |
|
| Bhutan |
|
Way Forward:
Department of Border Management (BM), Ministry of Home Affairs
|
News Source: The Hindu
<div class="new-fform">
</div>