Muthamizh Murugan International Conference |
Context: Muthamizh Murugan International Conference celebrates Tamil culture and spirituality, uniting devotees worldwide with various resolutions adopted.
About Muthamizh Murugan International Conference:
|
FSSAI Announces Curbs on Dairy Products |
Context: The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has recently issued a directive to food businesses to remove claims related to ‘A1’ and ‘A2’ types of milk from their product descriptions.
Overview of Classification Of Dairy Products As ‘A1’ and ‘A2’:
|
Tanager-1
|
Context: Recently, Tanager-1 satellite was launched from California, USA.
About Tanager-1 Satellite:
|
Sonoluminescence |
Context: Sonoluminescence (SL) is a scientific phenomenon that occurs when a gas bubble in a liquid emits light after being subjected to intense sound waves.
About Sonoluminescence:
Natural Occurrence in Pistol Shrimp:
|
RHUMI-1
|
Context: India launched its first reusable hybrid rocket ‘RHUMI- 1’, developed by the Tamil Nadu-based start-up Space Zone India with Martin Group, from Thiruvidandhai in Chennai.
About RHUMI-1:
|
After the Kolkata doctor’s murder, there are calls for the death penalty for the accused, but the Justice Verma Committee of 2013 had opposed it, deeming it regressive for rape cases.
Marital Rape Provisions Around the World
|
|---|
Rape is a complex issue stemming from multiple interrelated factors. Tackling it requires a holistic approach that involves reshaping cultural norms, enhancing education, fortifying legal systems, and promoting responsible and sensitive media portrayals.
A new study highlights an increase in mass wasting events (landslides and erosion) in the Sedongpu Gully, Tibetan Plateau, since 2017.
|
|---|
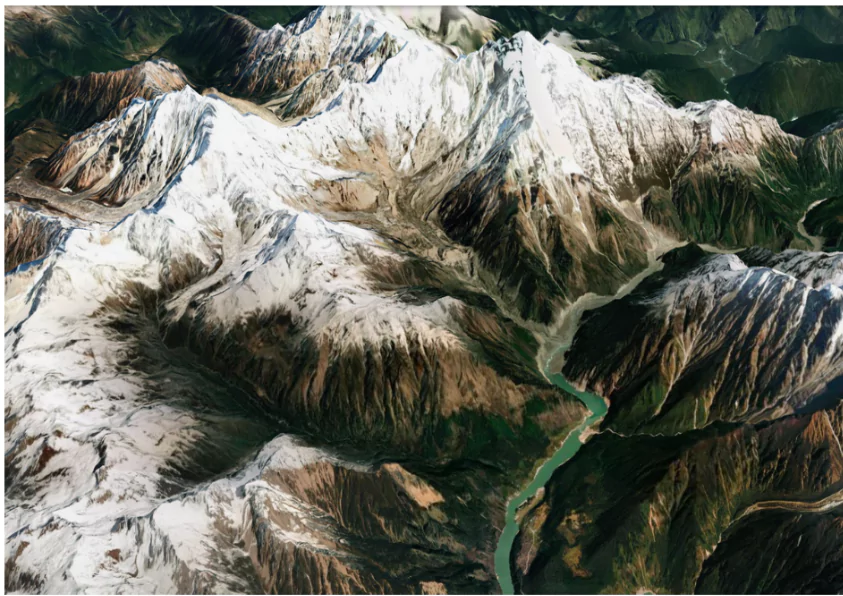 Environmental Conditions and Implications
Environmental Conditions and ImplicationsBy employing these measures, the impact of mass wasting can be significantly reduced, protecting infrastructure and reducing risks to human safety.
|
|---|
The BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) Policy for Fostering High Performance Biomanufacturing’ proposed by the Department of Biotechnology has been approved by the Union Cabinet.
Chile’s Atacama salt flat is sinking at a rate of 1 to 2 centimetres per year due to lithium brine extraction, according to a study by the University of Chile.
The most impacted region covers 8 km north to south and 5 km east to west in the southwest part of the salt flat, where lithium miners operate.

Atacama desert
|
|---|
About Lithium
Applications of Lithium
|
|---|
The second round of ministerial roundtable between India and Singapore is set to begin in Singapore soon.
ISMR is a mechanism established to set a new agenda for India-Singapore bilateral relations.
The close ties between India and Singapore have a history rooted in strong commercial, cultural and people-to-people links across a millennium.
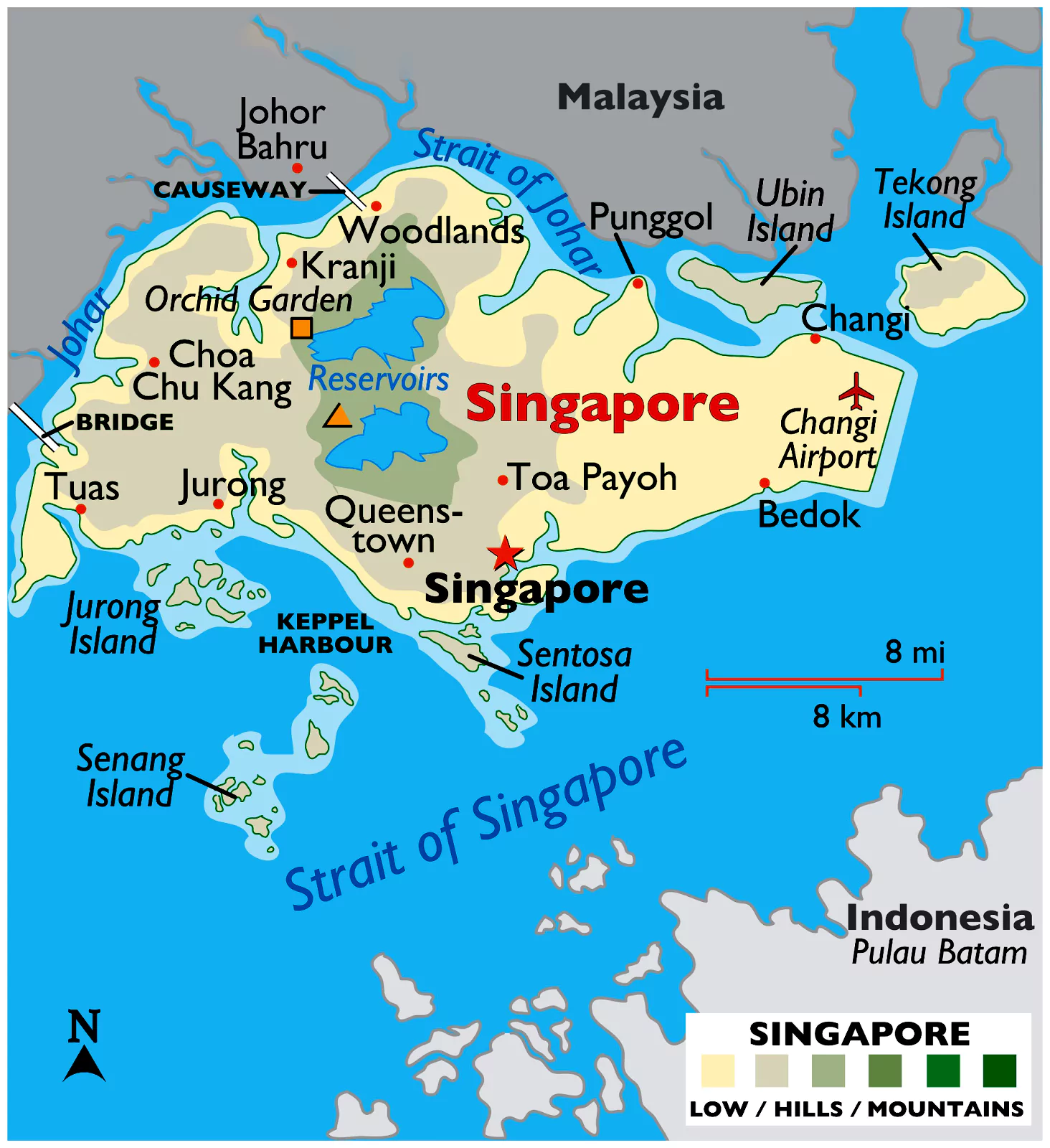 Basis of India-Singapore Relations: On shared values and approaches, economic opportunities and convergence of interests on key issues.
Basis of India-Singapore Relations: On shared values and approaches, economic opportunities and convergence of interests on key issues.
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the Unified Pension Scheme (UPS), which will be effective from April 1, 2025.scheme
The UPS pension scheme will provide government employees with assured pensions after retirement.
According to the government’s notification, the UPS has five key features:
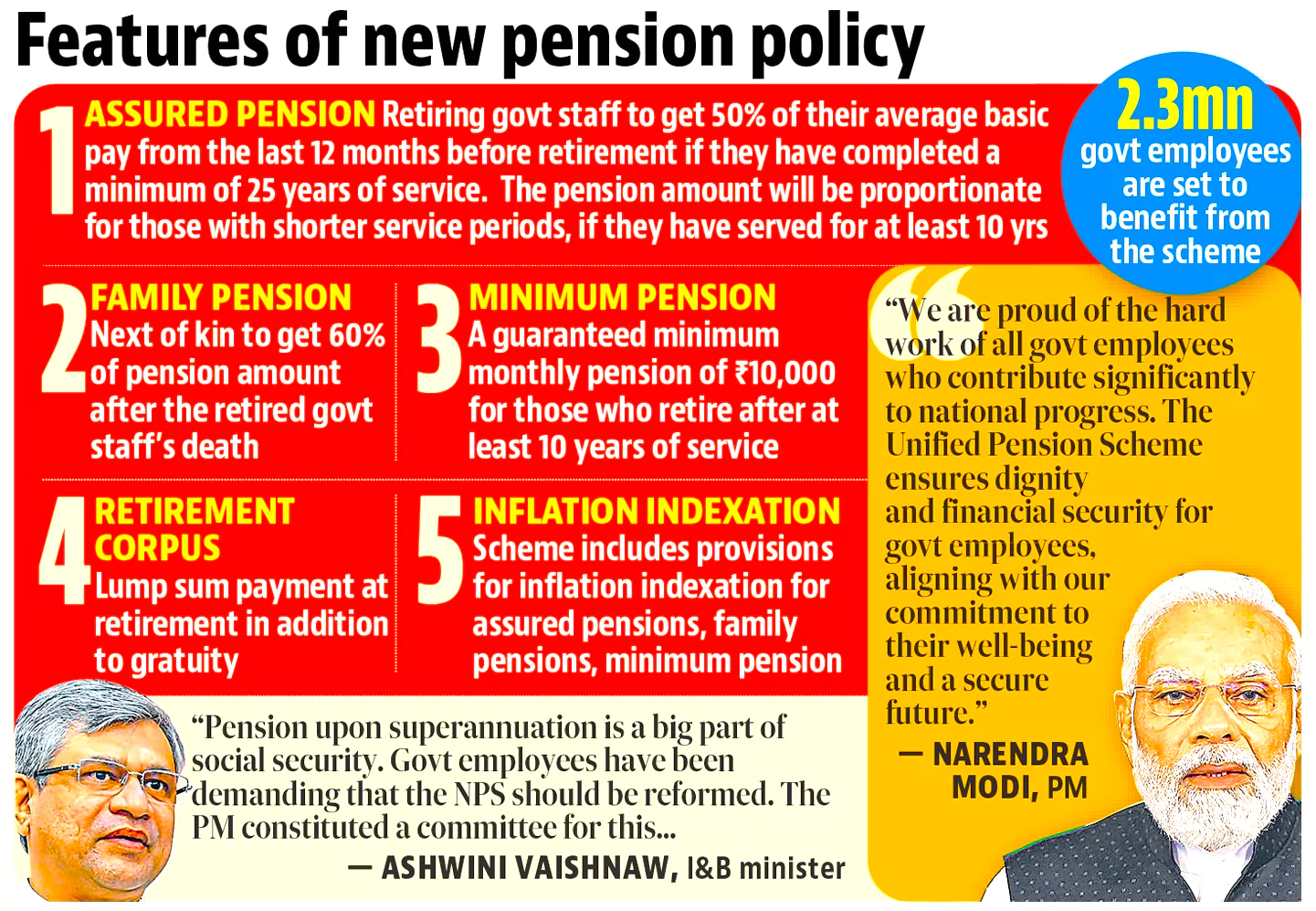 Assured Family Pension: 60% of pension of the employee immediately before her/his demise.
Assured Family Pension: 60% of pension of the employee immediately before her/his demise.| Features | UPS | NPS | OPS |
| Pension Amount |
|
|
|
| Family Pension |
|
|
|
| Employee Contribution |
|
|
|
| Government Contribution |
|
|
|
| Inflation Indexation |
|
|
|
The Unified Pension Scheme (UPS) provides following benefits:
Following are the few challenges with the Unified Pension Scheme (UPS) that need to be considered:
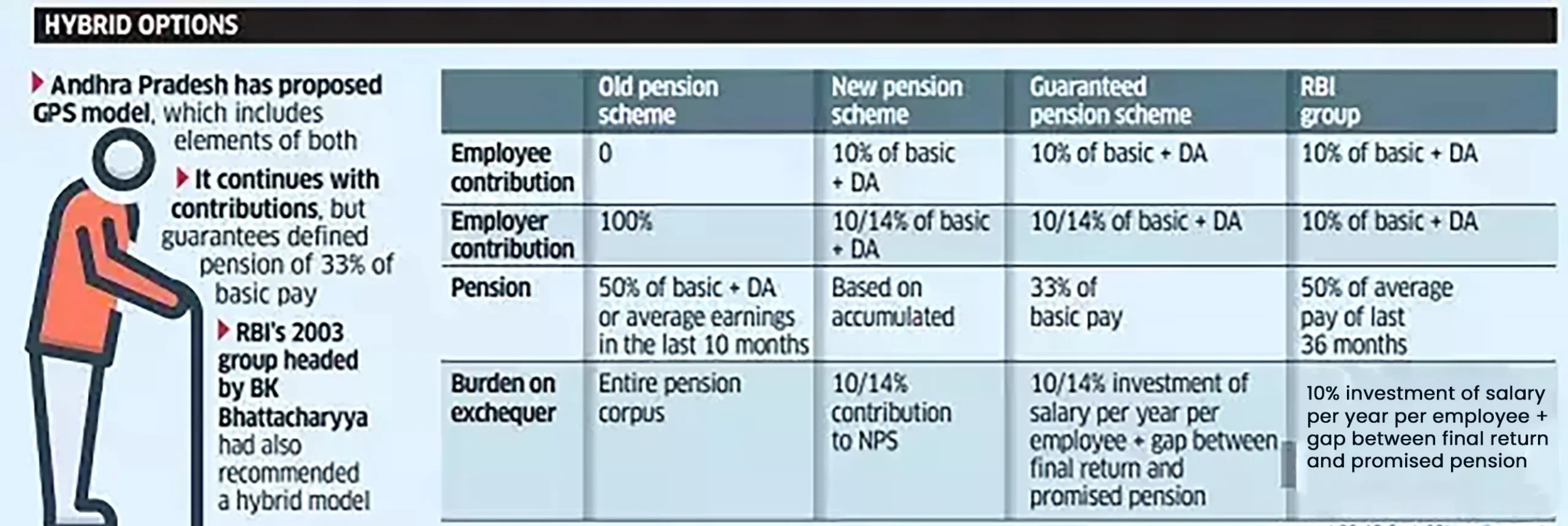 Funding and Sustainability: Ensuring the financial sustainability of the UPS is critical. This includes determining contribution rates, government support, and investment strategies to ensure long-term viability.
Funding and Sustainability: Ensuring the financial sustainability of the UPS is critical. This includes determining contribution rates, government support, and investment strategies to ensure long-term viability.
Social security for older people must cover the widest segment of the population. Government employees are an organised pressure group, and have managed to restore their guaranteed pension. The UPS is a significant step, however the government should consider that all significant reforms must come with broad political consensus.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>