Balochistan Region
|
Context: In the past few weeks, Balochistan region of Pakistan has been witnessing large-scale protests.
About Balochistan:
Geo-Strategic Significance of Balochistan:
|
Vigyan Dhara Scheme
|
Context: The Union Cabinet approved continuation of the three umbrella schemes, merged into a unified central sector scheme namely ‘Vigyan Dhara’ of Department of Science and Technology (DST).
About the Vigyan Dhara Scheme:
Significance
About Department of Science & Technology (DST): It acts as the nodal department for organizing, coordinating and promoting S&T activities in the country. |
Disputed Sabina Shoal
|
Context: Chinese and Philippine vessels collided during a confrontation near a disputed Sabina Shoal in the South China Sea.
About Sabina Shoal:
|
Plea Bargaining in India |
Context: Plea bargaining’s application in India remains minimal, a recent report by the Ministry of Law and Justice has revealed.
About Plea Bargaining:
|
Right to Disconnect |
Context: Australia gave millions of workers the legal right to “disconnect”, allowing them to ignore unreasonable out-of-hours contact from employers, to the distress of big industry.
About Right to Disconnect:
|
World’s First Lung Cancer Vaccine Trial Begins |
Context: A 67-year-old man has become the first person in the UK to try what doctors hope will be a revolutionary new treatment for lung cancer – a vaccine that tells the body how to fight and kill the disease.
Overview of Trails of Lung Cancer Vaccine:
About Lung Cancer:
|
SpaceX’s Polaris Dawn Mission |
Context: SpaceX’s Polaris Dawn mission is poised to make history with the first privately managed spacewalk, a risky endeavour previously undertaken only by government astronauts.
About SpaceX’s Polaris Dawn Mission:
|
ISRO has finalized the design of a humanoid skull for testing spaceflight conditions and safety of the Gaganyaan crew module ahead of the Gaganyaan mission scheduled for 2025.
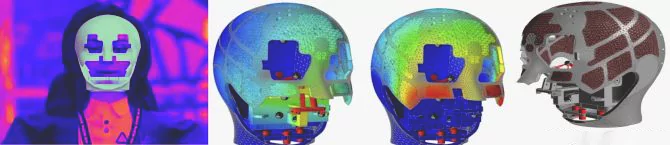

Gaganyaan Mission
|
In a letter to all States, the Ministry of Education (MoE) has defined ‘literacy,’ and what it means to achieve ‘full literacy’.
About New India Literacy Programme
|
|---|
RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das announced that the Unified Lending Interface (ULI) will soon be introduced to facilitate frictionless credit delivery.
| About Digital Public Infrastructure:
Digital Public Infrastructure refers to basic technology systems, created mainly in the public sector, that are openly available to users and other developers. It enables the delivery of public services, such as identification, payments, health, education, and governance. Features of DPI:
|
|---|
In a recent study published by the National Institutes of Health, researchers found that brain samples taken in early 2024 contained an alarming average of 0.5% plastic by weight.
Types of Microplastics: There are two categories of microplastics: primary and secondary.
A recent report by the Central Water Commission (CWC) highlights the alarming levels of heavy metal contamination in Indian rivers.
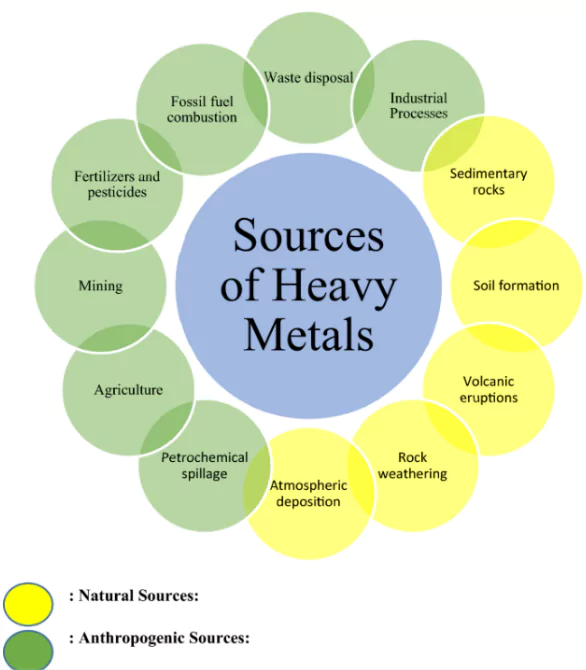
| Metal | Major Health Risks |
| Arsenic | Cancer, cardiovascular disease, dermatitis, lung and brain issues |
| Cadmium | Kidney damage, cardiovascular disease |
| Chromium | Lung cancer, respiratory issues |
| Copper | Liver and kidney damage (when excessive) |
| Iron | Iron overload disorders (when excessive) |
| Lead | Nervous system damage, brain damage, other organ damage |
| Mercury | Nervous system damage, kidney damage, brain damage |
| Nickel | Skin allergies, respiratory problems |
Developed countries generally exhibit greater governmental trust than developing countries.
A trust-based governance model represents a transformative approach to how governments interact with citizens, businesses, and institutions.
The significance of a trust-based governance model lies in its ability to create a more effective, responsive, and sustainable relationship between the government, citizens, businesses, and institutions. Here are key aspects that highlight its importance:
Policies that showcase “mistrust” in the system often reflect a governance approach that assumes individuals, businesses, or institutions may not act responsibly without stringent oversight. Following are the reason and examples:
Experiences with British
|
|---|
Outcome-based Trust v/s Process-based Trust
|
|---|
A significant step towards trust-based governance involves implementing policies and reforms that shift the focus from stringent control and oversight to fostering transparency, accountability, and collaboration:
Building trust between the government and businesses is more challenging than fostering trust with citizens due to several factors:
Following Steps must be implemented to ensure a better transitions towards trust-based governance:
India has made notable progress in trust-based governance, particularly with citizens. It’s time to extend this trust to businesses. By building and maintaining trust, governments can create a foundation for long-term stability, sustainable development, and a stronger, more cohesive society.
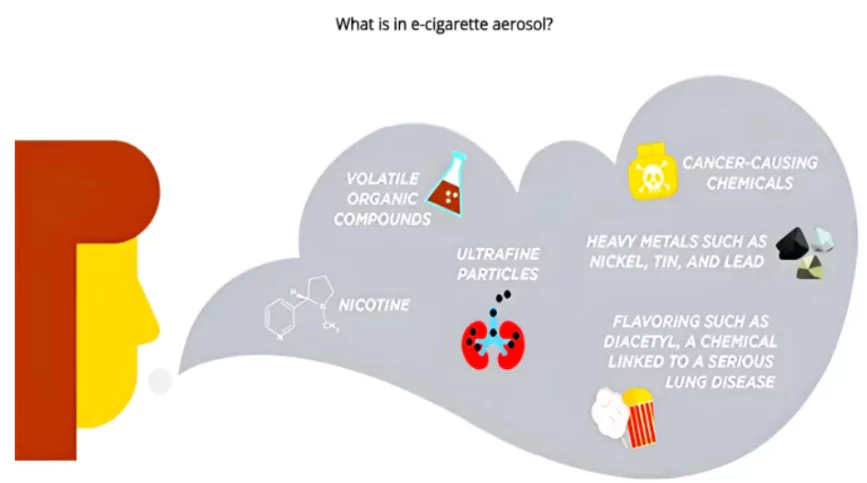
New-age gateway devices once marketed as safer alternatives to smoking, are now causing a public health crisis
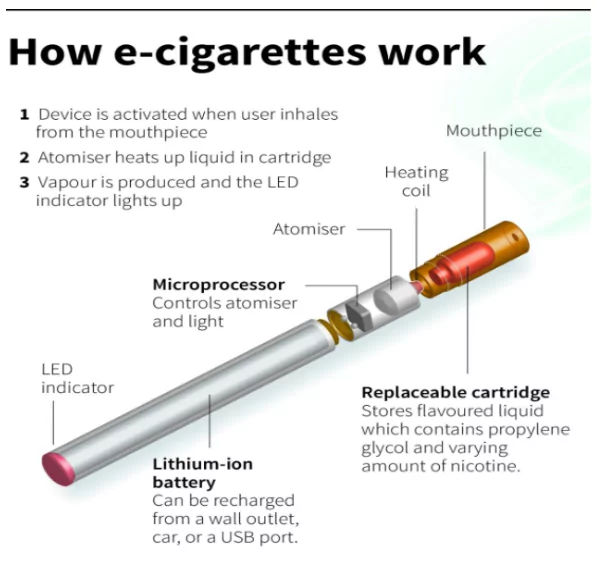
New-age gateway devices like e-cigarettes and vaping pens, Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems, or ENDS, heat-not-burn (HNB) devices and other heated tobacco products (HTPs) are modern alternatives to traditional smoking.
 Working: When the user inhales, the battery powers a heating element (atomizer) that turns the e-liquid into vapor, which is then inhaled.
Working: When the user inhales, the battery powers a heating element (atomizer) that turns the e-liquid into vapor, which is then inhaled.
The Act seeks to prohibit the production, trade, storage, and advertisement of electronic cigarettes.
Why did India ban e-cigarettes?
Global Precedence:
|
|---|
New-Age Gateway Devices users reported getting addicted to the tobacco products which led to the more tobacco consumption leading to Tobacco Epidemic in India
Various Tobacco Awareness and Control Programmes has been implemented by Government:
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
