Context: According to SBI research Ecowrap, better connection with credit dispensation, increased savings through PM Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) and higher participation share in MGNREGA is ushering in sustainable empowerment of women across states.
Role Played by Trinity Acts in Empowering Women in India:
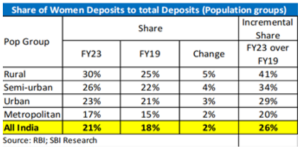
Challenges Associated with the Trinity Acts:
Way Forward
Conclusion
Context:
The Ministry of Jal Shakti Releases the 6th Census Report On Minor Irrigation (MI) Schemes with reference year 2017-18 under the centrally sponsored scheme “Irrigation Census”.
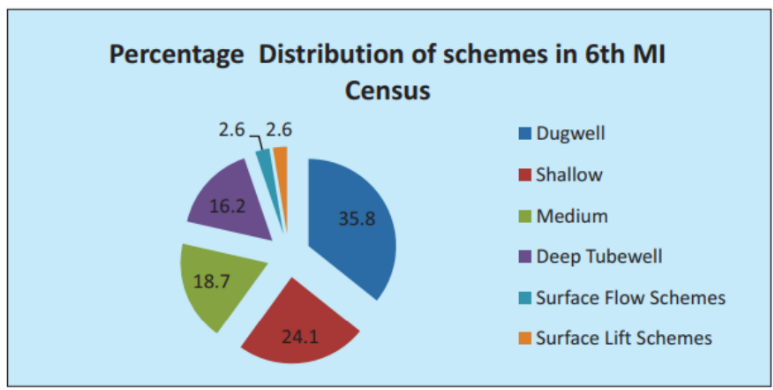
About Minor Irrigation Scheme:
Other Categories:
Initiatives Taken by the Government Related to Irrigation:
|
Key Highlights of 6th Census Report:
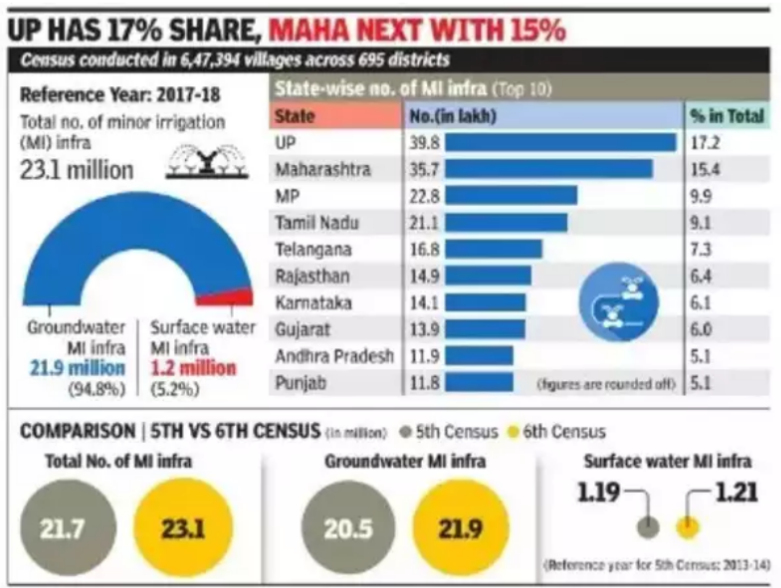

|
Challenges For Irrigation In India:
Significance of Minor Irrigation:
Way Forward:
News Source: PIB
Context:
Rajasthan-based Sahasra Semiconductor will start the commercial production of first made-in-India memory chips from September or early October.
What are Semiconductors?
News Source: Business Standard
Context:
Recently, the ISRO released preliminary data from instruments called RAMBHA and ILSA, both installed on the lander module and another called APXS which is on the rover.
Key Findings:
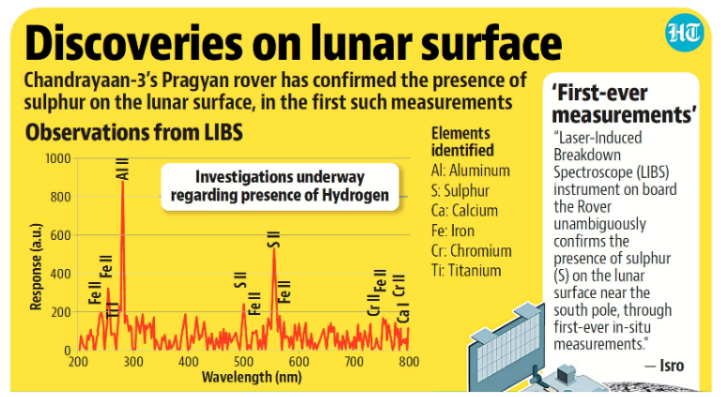 Finding: The initial assessment indicates that the plasma encompassing the lunar surface is relatively sparse (5-30 million electrons per cubic metre).
Finding: The initial assessment indicates that the plasma encompassing the lunar surface is relatively sparse (5-30 million electrons per cubic metre).News Source: Indian Express
Context:
The government has convened a special session of Parliament from September 18 to 22.
About the News
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
More about the News:
| Organised Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP) |
About OCCRP:
|
| 2023 Ramon Magsaysay Award |
Ramon Magsaysay Award:
|
| Kakrapar Atomic Power Project |
About KAPP-3:
|
| Sree Narayana Guru |
About Sree Narayana Guru(20 August 1856 – 20 September 1928):
|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>