Sakthan Thampuran |
Context: Recently, the Minister of State for Tourism of Thrissur, Kerala said to replace a statue of Sakthan Thampuran.
About Sakthan Thampuran:
|
Arab League |
Context: Turkey heads to the Arab League meet for the first time in 13 years.
About Arab League:
|
Su-30MKI Aircraft
|
Context:
Recently, the Defence Ministry signed a ₹26,000-crore contract with Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for 240 AL-31FP aero engines for Su-30MKI aircraft.
|
Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS)
|
Context:
Recently, the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has dissolved the Standing Committee on Statistics on concerns raised over the delay in conducting the census. About Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS):
Mandates of Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS):
|
Planetary Protection
|
Context: China has recently announced the preponement of its Mars sample-return mission, Tianwen-3, to 2028 and has committed to adhering to the planetary protection principle.
About Planetary Protection Principle
|
NIDHI i-TBI
|
Context: The Union Minister, while celebrating the 8 years of the Department of Science and Technology’s initiative (DST-NIDHI), inaugurated eight new NIDHI i-TBIs.
About NIDHI initiative:
About NIDHI-iTBI
|
Agrometeorology Advisory
|
Context: Recently, India Meteorological Department (IMD) is planning to revive District Agro-Meteorology Units (DAMUs) under the Gramin Krishi Mausam Sewa (GKMS) scheme.
About District Agro-Meteorology Units:
|
Clade-2 Strain
|
Context: A travel-related Mpox (monkeypox) case has been confirmed, with lab tests detecting the West African clade 2 virus in the patient.
About Clade-2 Strain:
|
Anti-Submarine Warfare Vessels Launched
|
Context: Two anti-submarine warfare shallow water crafts vessels (ASW-SWC) of the Indian Navy were launched at Cochin Shipyard, recently.
About Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Crafts (ASW-SWC)
|
NSA Ajit Doval to visit Russia for BRICS meet
|
Context: National Security Advisor Ajit Doval is visiting Russia amid discussions about India’s potential role in resolving the Ukraine conflict.
More About the News:
About the BRICS:
Key Initiatives of BRICS
|
Joint Doctrine For Amphibious Operations
|
Context: Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) released the joint doctrine for amphibious operations during the Chiefs of Staff Committee (COSC) meeting.
About the Joint Doctrine for Amphibious Operations:
|
In a first, critically endangered elongated tortoise spotted in Aravallis.
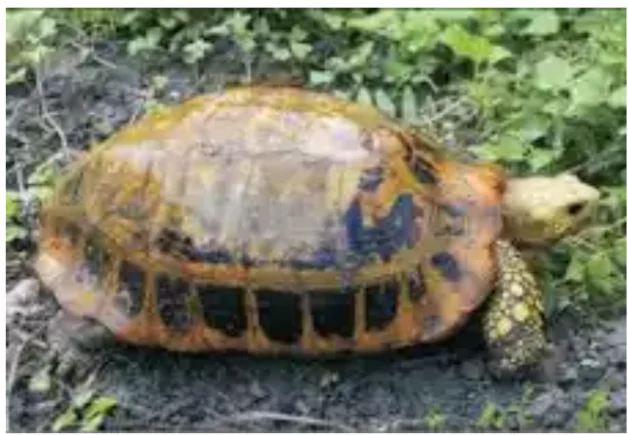 Habitat: It is widely distributed over eastern as well as northern India and Southeast Asia.
Habitat: It is widely distributed over eastern as well as northern India and Southeast Asia.
Aravalli Range
|
|---|
A Bench led by Chief Justice of India (CJI) D.Y. Chandrachud ordered the protesting doctors to resume work soon.
The 54th GST Council met under the Chairpersonship of the Union Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs in New Delhi.
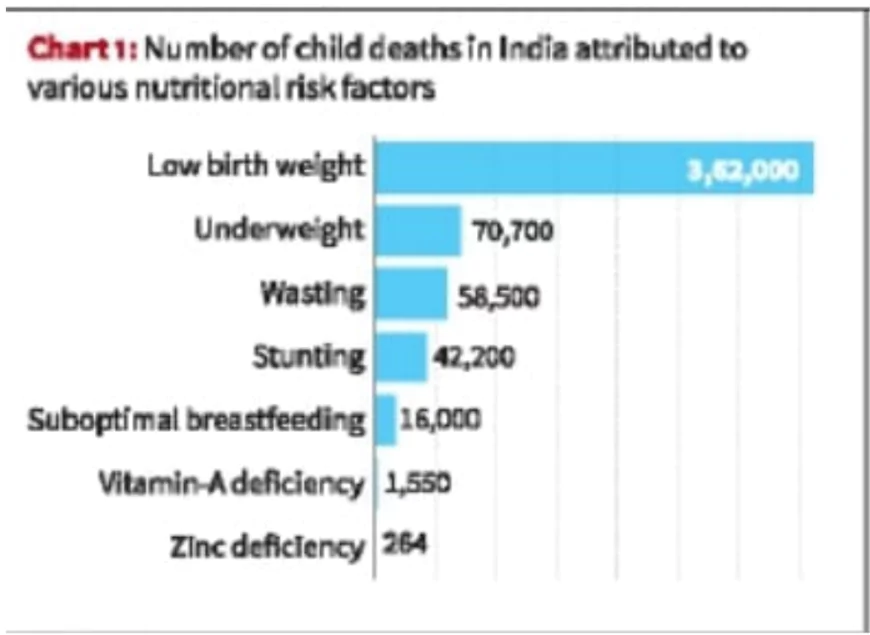
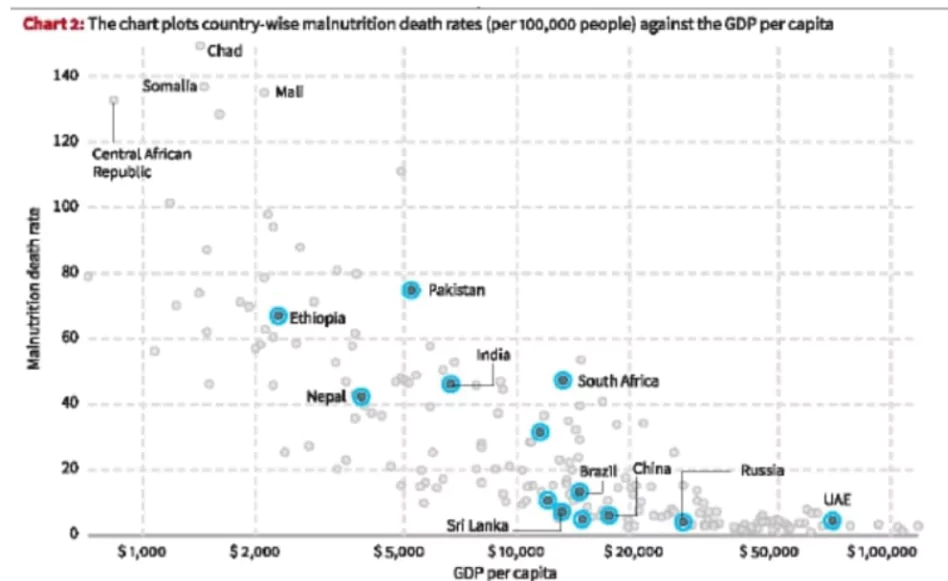
Death rates from malnutrition are much higher in low-income countries, where children often don’t get the diversity of nutrients.
In 2021, in India, 0.7 million children under the age of five died. Of these, 0.5 million of the deaths were attributed to child and maternal malnutrition. It means, over 70% of them were linked to nutritional deficiencies.
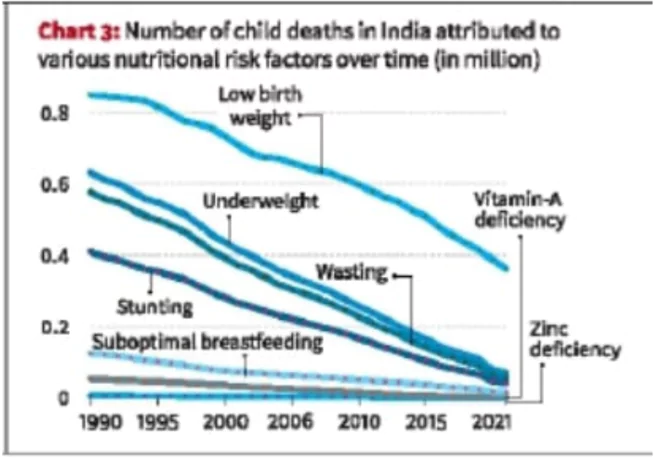 Factors of Improvement:
Factors of Improvement:
The “India Status Report on Road Safety 2024” by IIT Delhi highlights India’s slow progress in reducing road fatalities.
Necessity of Crash Surveillance in India
|
|---|
Global Initiatives Related to Road Safety
|
|---|
Recently, India and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for civil nuclear cooperation.
About Barakah Nuclear Energy Plant
|
|---|
India has signed civil nuclear cooperation agreements with France, United States, Russia, Namibia, Canada, Argentina, Kazakhstan, Republic of Korea, Australia, Sri Lanka and the United Kingdom etc.
These agreements are pivotal in helping India achieve its long-term goals in nuclear energy, while also enhancing its global standing.
Major concerns revolve around issues of safety, security, environmental impact, geopolitical implications, and public opposition.
To maximize the potential of these agreements and address emerging challenges, India needs to take certain strategic steps.
By focusing on advanced research, thorium utilization, public engagement, and regulatory reforms, India can unlock the full potential of nuclear energy to meet its energy, environmental, and economic objectives in the coming decades.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
