Context:
India could end up importing as much as 15.5 million tonnes of edible oils in 2022-23, surpassing the past record of 15.1 million tonnes in 2016-17.
Possible Reason for record imports of cooking oil:
Why is India so dependent on imports?
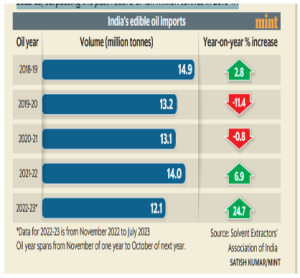 Oilseed productivity of a tonne per hectare is less than half the global average, due to lack of access to the latest seed technology.
Oilseed productivity of a tonne per hectare is less than half the global average, due to lack of access to the latest seed technology.What steps has the government taken?
News Source: Livemint
Context: India has enacted a five-year anti-dumping duty targeting specific types of Chinese steel.
Reason:India enacted an anti-dumping duty on china due to a 62% rise in steel imports from China to India between April and July, compared to the same timeframe last year.
What is Anti-dumping duty?
Dumping:
|
WTO’s Provisions Related to Anti-Dumping Duty:
Importance of Anti Dumping measures:
News Source: Livemint
Context:
Recently, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, unveiled five transformative initiatives to improve the lives of persons with disabilities across the nation.
Overview of Five pioneering initiatives:
News Source: PIB
Context:
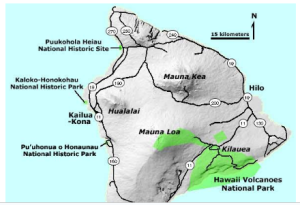
About Kilauea volcano:
Image Source: U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY
Context:
Saudi Arabia’s Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman Al Saud and Prime Minister Narendra Modi held bilateral talks recently (post G-20), agreeing to expand trade and security ties.
More On News:
India-Saudi Arabia Strategic Partnership Council (SCP)
|
The Importance of India- Saudi Arabia Relations:
MoUs were signed in various fields:
|
Challenges in Bilateral Relation:
Way Forward:
News Source: The Indian Express

Context:
The inclusion of the African Union into the G20 Grouping as its 21st member has given a new voice to the global south, providing an opportunity in ensuring global critical mineral security.
More on News:The global shift toward low-carbon economies and ambitious net-zero emission targets has driven the race for critical minerals.
About African union (AU):
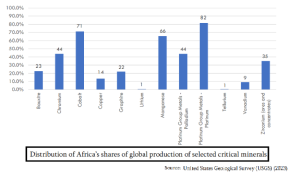
SWOT Analysis of Role of Africa in Solving World’s Critical Mineral Challenge
Strengths:
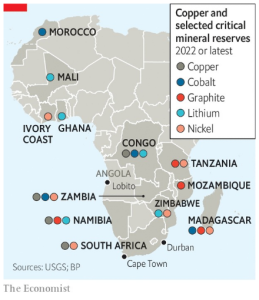
Opportunities Available:
Associated Weaknesses:
Threats:
Way Forward:
Conclusion:
Collaborative efforts among African countries, India, and the international community can create a win-win situation, promoting economic development, technological advancement, and sustainability for all stakeholders.
News Source: Mint
| Achanakmar Tiger Reserve | Teams in Chhattisgarh’s Achanakmar Tiger Reserve are monitoring a tigress released in April 2023 to help boost the dwindling tiger population.
About Achanakmar Tiger Reserve:
|
| Acharya Vinoba Bhave
|
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra paid tributes to Acharya Vinoba Bhave on his birth anniversary.
About:
|
| India-UK holds the 12th Economic and Financial Dialogue (EFD) | The 12th Round of Ministerial India-UK Economic and Financial Dialogue was recently held in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
|
| Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Awards |
About the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar (SSB) awards:
About Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR):
|
Union Cabinet Approves National Sports Policy 2025...
What are Altermagnets? A Breakthrough in Magnetism...
India’s 7-Point Strategy for Sustainable Gro...
Cabinet Approves Employment Linked Incentive Schem...
INS Udaygiri Delivered Under Project 17A to Indian...
SC Issues Implemented Reservation Roster for SC/ST...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>