Context:
Recently, the Supreme Court made public the report of the Committee on Prison Reforms.
More on News:
Status in India:
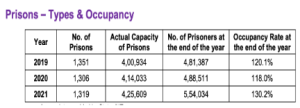 Prisoners: As per the NCRB, a total of (5,54,034) prisoners were confined as on 31st December, 2021 in various jails across the country.
Prisoners: As per the NCRB, a total of (5,54,034) prisoners were confined as on 31st December, 2021 in various jails across the country. Key Findings of the Report:
| Women Prisoners: |
|
| Overcrowding Concerns |
|
| Transgender Prisoner |
|
| Suicide |
|
Model Prisons Act 2023:
Factors Contributing to Overcrowding in Jails:
|
Committee’s Recommendations:

United Nations Environment Assembly
|
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
Recently, the intergovernmental negotiating committee (INC) of the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA) released a zero draft to end plastic pollution.
More on News:
Significance:
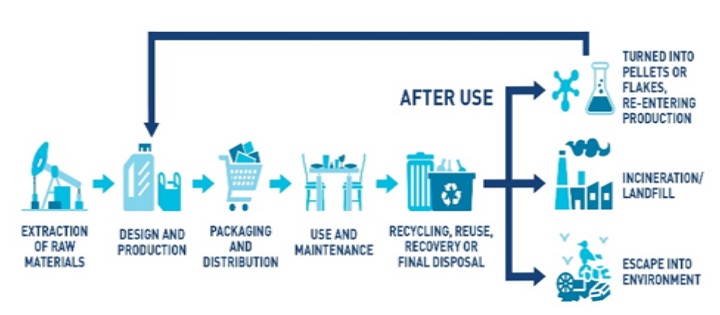
Challenges:
Initiatives to Address Plastic Pollution:
Way Forward:
Best Practices:
|
Conclusion:
The Government of India must bring about a comprehensive and circular economy approach to reduce plastic waste, increase plastics value recovery, and tackle plastic pollution with a goal to achieve SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
(For more about plastic pollution, refer to the hyperlink)
News Source: Down To Earth
Context:
The Tribunal for the Rights of Nature called Mexico’s Maya train project responsible for causing “crimes of ecocide and ethnocide”.
About Ecocide:
Genocide
|
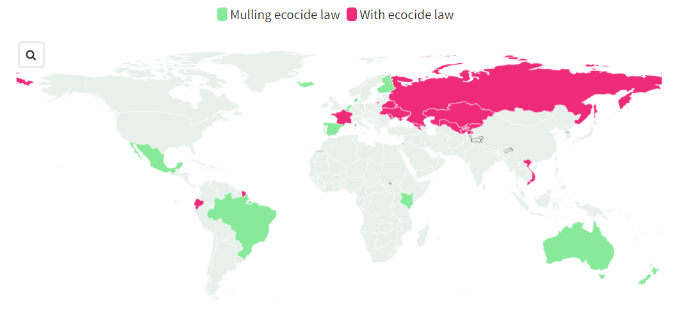
Global Standing on Ecocide Laws:
Importance of Ecocide Laws:
What has been India’s stance?
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Banks have enabled the interoperability of Unified Payments Interface’s (UPI) Quick Response (QR) code with their central bank digital currency (CBDC).
About Digital Rupee
About QR code
|
About Interoperability:
Benefit of UPI QR code-CBDC Interoperability:
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
Six billion tonnes of annual sand extraction from the world’s ocean floors is causing irreversible harm to marine benthic life, as revealed by a new global data platform on marine sediment extraction.
About Marine Sand
Dredging:
|
Key Findings of Marine Sand Watch Platform:
Benthic organisms:
|
News Source: Down to Earth
Context:
Recently, the Mizoram Assembly unanimously passed a resolution opposing the Forest (Conservation) Amendment Act, 2023, “to protect the rights and interest of the people of Mizoram”.
Why did the Mizoram Assembly unanimously pass a resolution?
Premises upon which Mizoram Assembly unanimously passed a resolution:
For More Details: Refer July 27, 2023 Daily Gist: Forest (Conservation) Amendment Bill 2023
News Source: The Hindu
| T+0 settlement cycle/ one-hour settlement of trades |
|
| Malaviya Mission – Teachers Training Programme |
About Malaviya Mission:
|
| India or Bharat |
About Bharat:
Origin of name ‘Hindustan’:
Origin of name ‘India’:
|
| Centre signs MoU with Adobe to Train Children in Classroom |
|
Union Cabinet Approves National Sports Policy 2025...
What are Altermagnets? A Breakthrough in Magnetism...
India’s 7-Point Strategy for Sustainable Gro...
Cabinet Approves Employment Linked Incentive Schem...
INS Udaygiri Delivered Under Project 17A to Indian...
SC Issues Implemented Reservation Roster for SC/ST...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>