Parliamentary Standing Committee
|
Context: Efforts are underway to finalise the department-related Standing Committees of Parliament.
About Parliamentary Committees:
|
Biden to host Quad Summit
|
Context: India and the United States have mutually agreed to swap hosting responsibilities for the Quad Summit.
More about the news
About the QUAD (Quadrilateral Security Dialogue):
Significance of the swap:
|
WHO Unveils Global Framework for Pathogen Origin Investigation
|
Context: The WHO has launched a comprehensive global framework to guide investigations into the origins of pathogens.
More About the News:
About the Framework:
|
Swiss Peace Process
|
Context: The Swiss-mediated peace process between Ukraine and Russia has brought the spotlight on India’s diplomatic position.
About Swiss Peace Process for Ukraine:
|
Venezuela
|
Context: Venezuela’s opposition candidate fled to Spain on Saturday amidst the political turmoil.
About Venezuela:
|
A recent study has shed light on the effects on Indian Monsoon by seasonal changes in the Arctic sea ice levels.
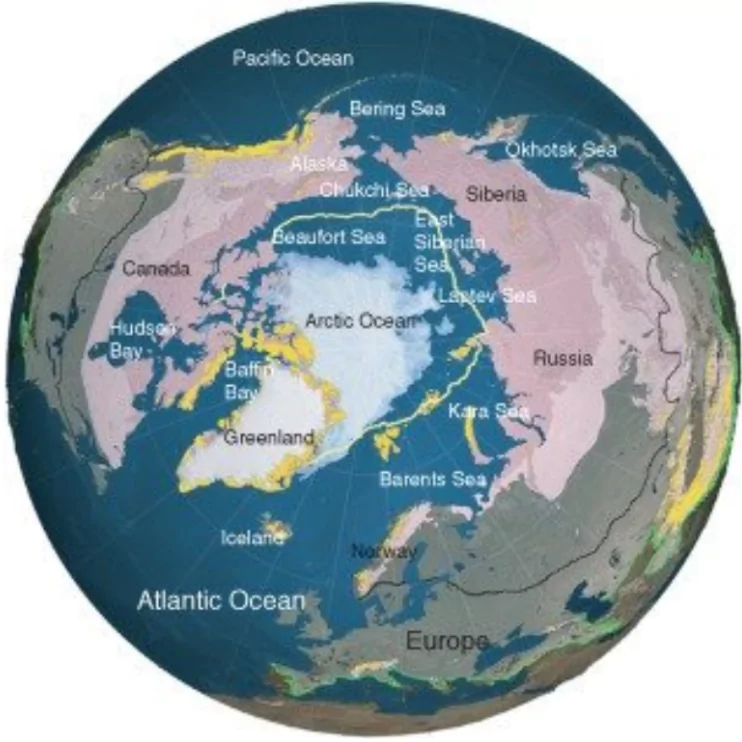 Data Source: Observational data from the period of 1980 to 2020 were used along with climate models (specifically Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phases 5 and 6)
Data Source: Observational data from the period of 1980 to 2020 were used along with climate models (specifically Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phases 5 and 6)
Indian MonsoonMonsoon is a seasonal change in the direction of the prevailing, or strongest, winds of a region.
|
India has launched its first registry for patients needing hand transplants.
Composite tissue
|
|---|
The European Space Agency/Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency BepiColombo mission has successfully completed its fourth of six gravity assist flybys at Mercury.
BepiColombo is an international mission consisting of two spacecraft riding together to Mercury to orbit and study the planet from unique vantage points.
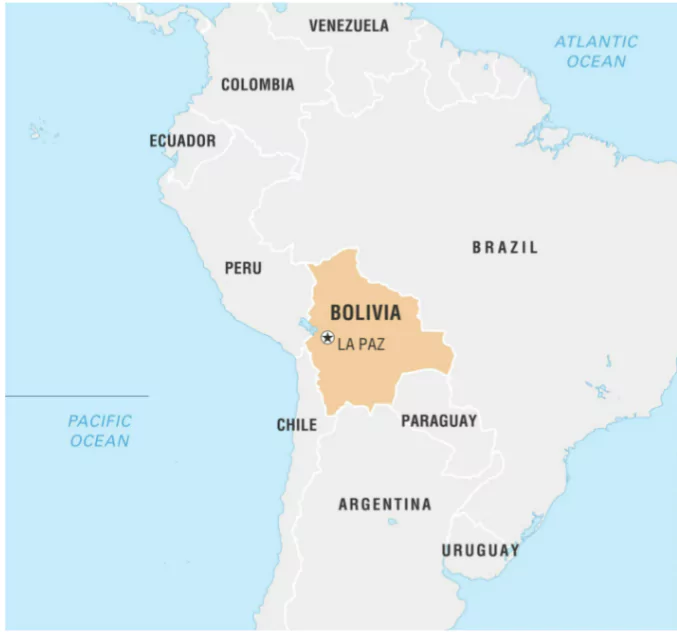
Bolivia declared a national emergency due to raging forest fires.
Assistive technologies like specialised wheelchairs, running blades, release braces have revolutionised para sports, giving athletes better inclusivity and performance.
‘Equipped for equity’ campaign
|
|---|

The restrictive nature of legal provisions for live-in couples allows social conservatism to influence the Justice System.
Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005
|
|---|
Implication of Live in Relationship on Marriage as an Institution
|
|---|
Live-in relationships in India are increasingly recognized, reflecting shifts in societal attitudes and legal frameworks. While legal protections exist, social stigma still persists. There is a need for continued reforms and awareness efforts to ensure equal rights and respect for the Live in couples in the society.
Key Judgements on Live-in Relationships in India
|
|---|
Muhammad Yunus, the head of Bangladesh’s interim government has called for reviving the the “spirit of SAARC,” underlining that the bloc can solve many of the region’s problems.


Reviving SAARC is crucial for addressing regional challenges, enhancing cooperation, promoting stability, and strengthening South Asia’s global presence through collective economic and strategic initiatives.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>