Recently, the 21st ASEAN-India Summit was held in Vientiane, Laos.
The Indian Prime Minister (PM) also attended the 19th East Asia Summit (EAS) on 11 October 2024 in Vientiane, Lao PDR.
Key Highlights of the 19th East Asia Summit
|
|---|
| The ASEAN-India Science and Technology Development Fund (AISTDF) was initially set up with $1 million in 2008 and later increased to $5 million in 2015 to support collaborative research projects between India and ASEAN member countries. |
|---|
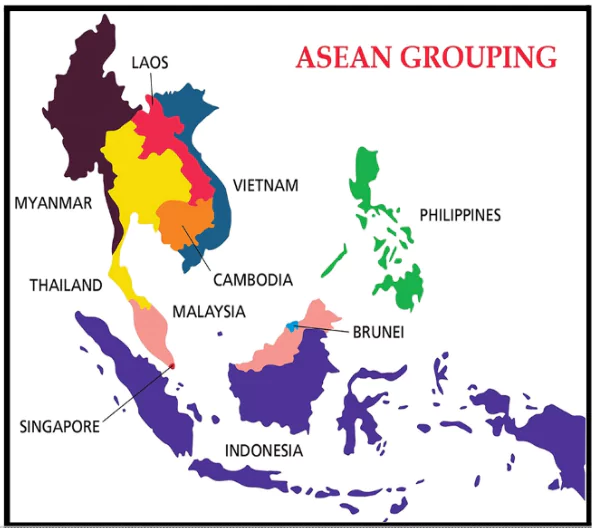
About ASEAN – Association of Southeast Asian Nations
About East Asia Summit (EAS)
|
|---|
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is an economic agreement between ASEAN members and Free Trade Agreement (FTA) partners.
|
|---|
The India-ASEAN relationship, marked by strong trade and cultural ties can ensure mutual prosperity and stability in Asia.
Researchers documented a new kind of sedimentary rock made from coastal slag deposits in the U.K. published in the journal Sedimentological.
Lithification
|
|---|
SlagSlag is a byproduct formed during the smelting or other combustion and metallurgical processes. It is essentially a molten material that forms when impurities and gangue (unwanted minerals) in ores are separated from the desired metal. It primarily consists of oxides of elements like sulphur, phosphorus, silicon, and aluminium. It can also contain metal phosphates or silicates. Uses of Slag
Examples of Slag
|
|---|
Delhi’s Environment Minister highlighted the importance of collaborating with various agencies to expedite approvals for cloud seeding.
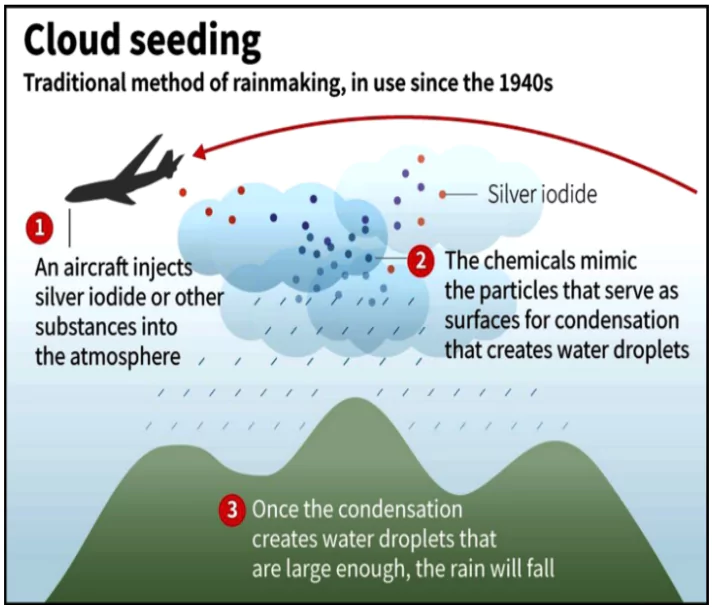
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
South Korean author Han Kang has been awarded the 2024 Nobel Prize in Literature for her “intense poetic prose that confronts historical traumas and exposes the fragility of human life”.
This comes after two consecutive years of awarding European authors (Jon Fosse in 2023, Annie Ernaux in 2022).
Notable recognition from India
|
|---|
Union Home Ministry designated Hizb-ut-Tahrir (HuT) as a terrorist organisation under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA).
| Arguments in Favour of UAPA | Arguments Against UAPA |
| National Security: Provides strong legal tools to combat terrorism and protect sovereignty. | Misuse of Power: Can be misused to target dissent and curb civil liberties. |
| Preventive Detention: Allows preventive action to disrupt potential terrorist activities. | Vague Definition of Terrorism: Broad definitions lead to arbitrary arrests. |
| Global Compliance: Aligns with international anti-terrorism protocols. | Lack of Judicial Oversight: Detentions without charge for up to 180 days weaken due process. |
| Strengthened Law Enforcement: Empowers agencies to tackle emerging terror threats. | Human Rights Concerns: Prolonged detentions and denial of bail violate fundamental rights. |
The Cabinet Committee on Security recently approved two high-profile deals for the purchase of 31 MQ-9B High Altitude Long Endurance (HALE) Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) from General Atomics of the U.S. as well indigenous construction of two Nuclear Attack Submarines (SSN).
India leased SSNs
|
|---|

|
|---|
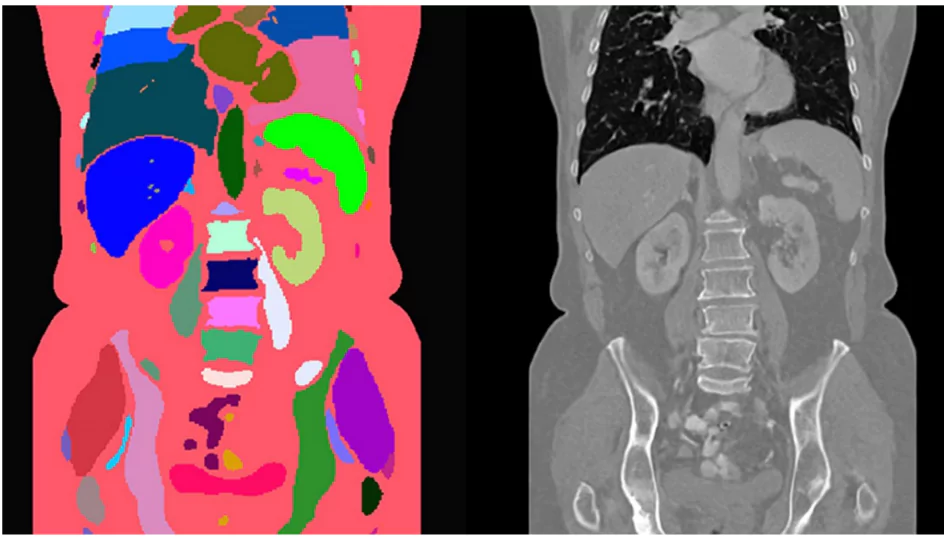
AI-generated synthetic medical images offer a scalable, ethical, and cost-effective solution to the high demand for annotated medical images, addressing both privacy concerns and resource limitations in healthcare.
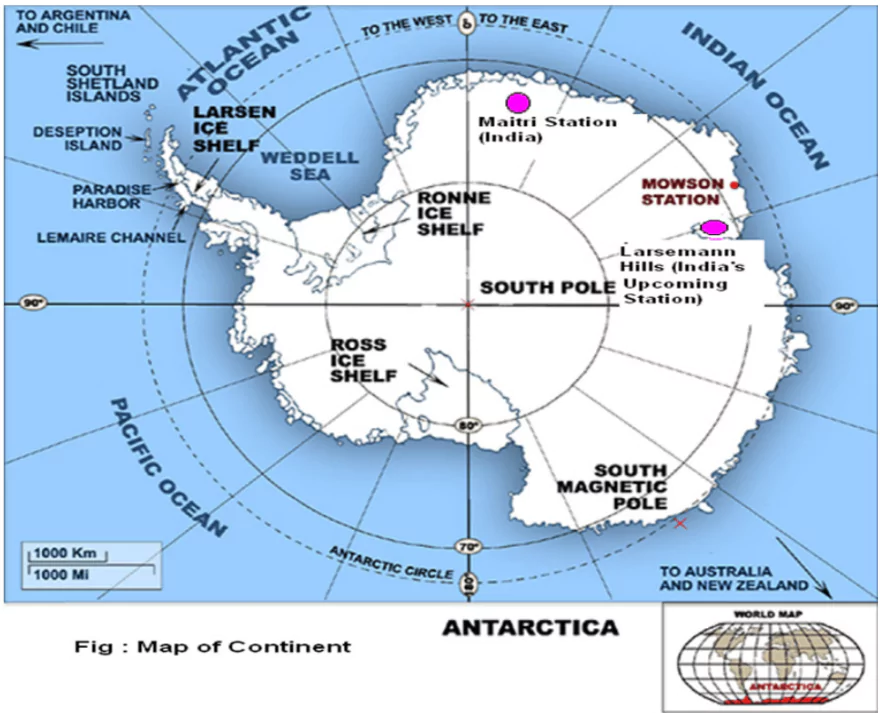
Context: Plant cover across the Antarctic Peninsula that points north towards South America, has increased more than 10 times over the past few decades due to rising temperatures, as per a new study.
Context: World Post Day is celebrated every year on October 9 to recognize the role of the postal system in communication, trade, and development.
Context: To encourage wider adoption of the unified payments interface (UPI), the RBI recently announced an increase in transaction limits on UPI123 and UPI Lite.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>