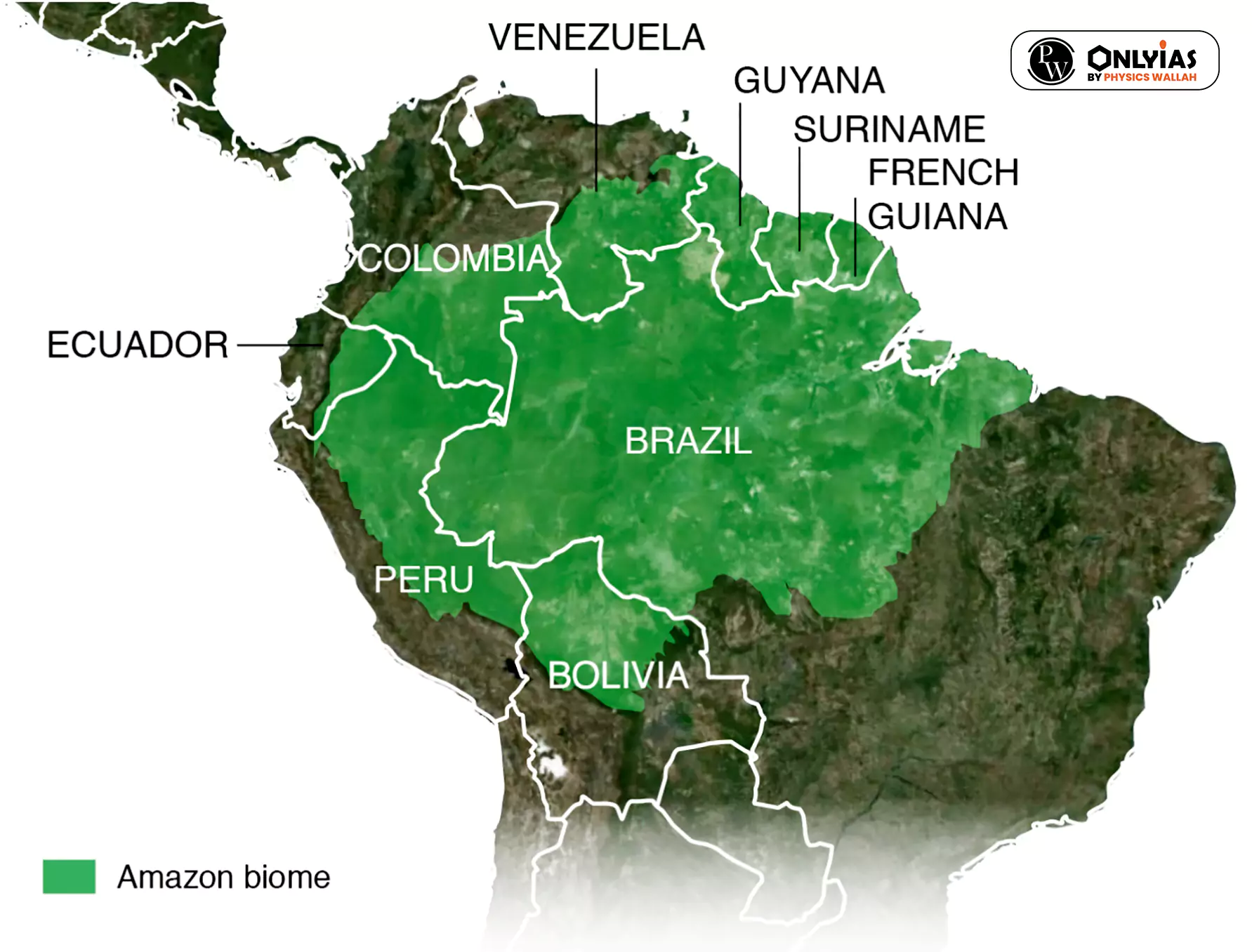
News Source: Indian Express
| Prelims Question (2023)
Which one of the following is a part of the Congo Basin? (a) Cameroon (b) Nigeria (c) South Sudan (d) Uganda Ans: (a) |
|---|
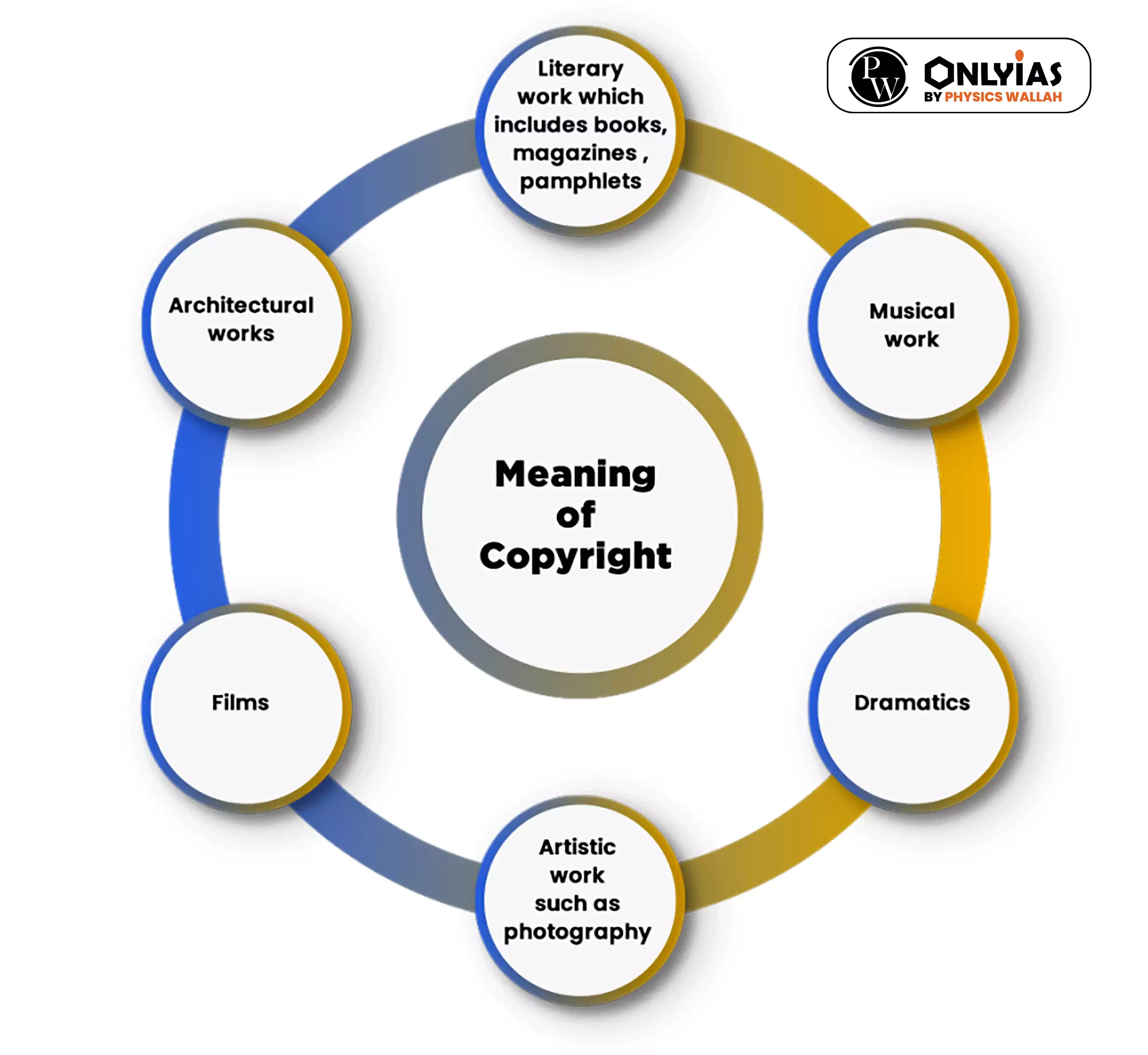
Copyright Law in India; Salient features of Copyright Act, 1957
Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Artistic Works
|
|---|
News Source: Indian Express
| Prelims Question (2017)
With reference to the ‘National Intellectual Property Rights Policy’, consider the following statements: 1. It reiterates India’s commitment to the Doha Development Agenda and the TRIPS Agreement. 2. Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion is the nodal agency for regulating intellectual property rights in India. Which of the above statements is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (c) |
|---|
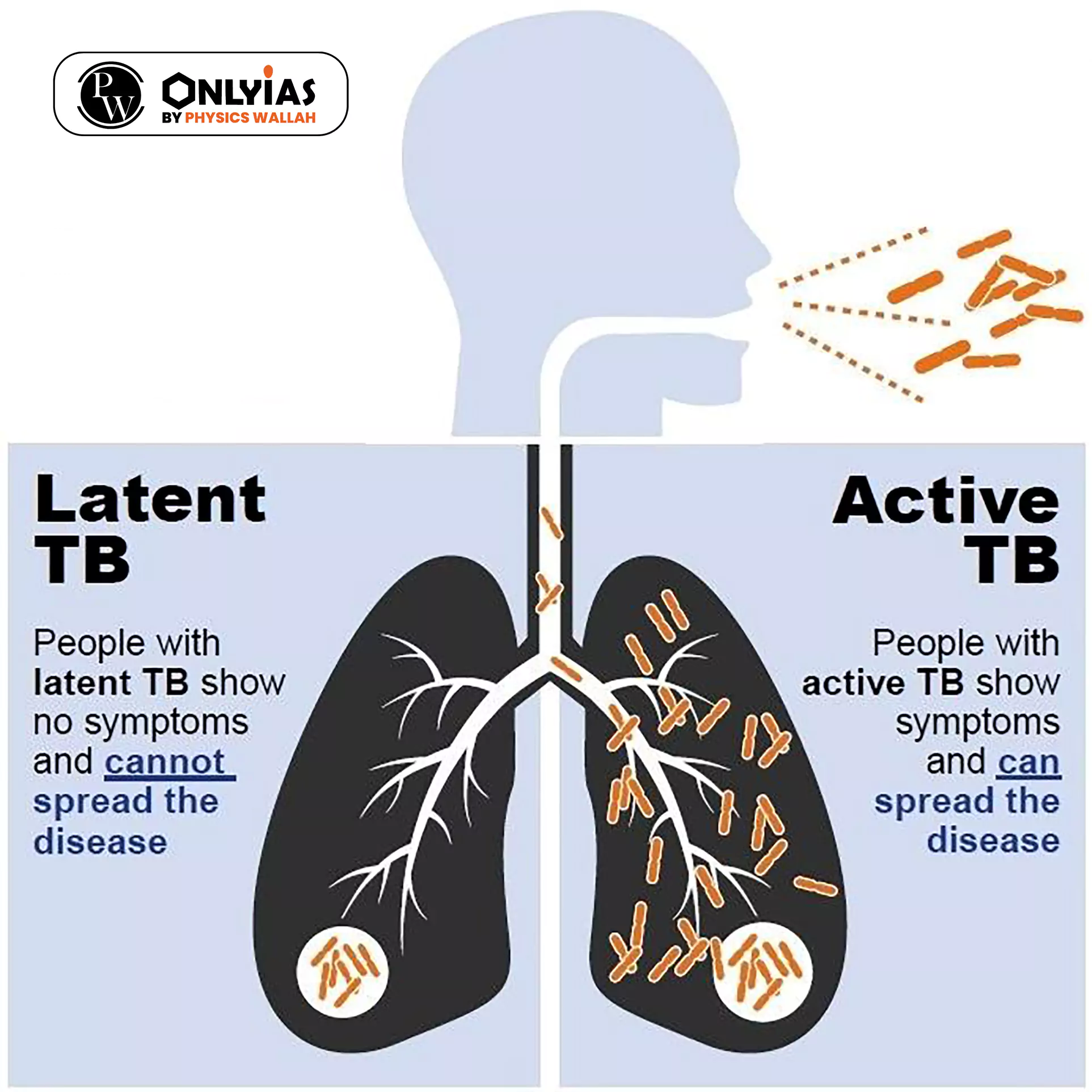
News Source: Economic Times
| Prelims Question (2016)
In the context of the developments in Bioinformatics, the term ‘transcriptome’, sometimes seen in the news, refers to (a) A range of enzymes used in genome editing (b) The full range of mRNA molecules expressed by an organism (c) The description of the mechanism of gene expression (d) A mechanism of genetic mutations taking place in cells Ans: (b) |
|---|
What is microalgae?
Light Absorption Mechanism
|
|---|
News Source: DTE
| Prelims Question (2021)
In the nature, which of the following is/are most likely to be found surviving on a surface without soil? 1. Fern 2. Lichen 3. Moss 4. Mushroom Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1 and 4 only (b) 2 only (c) 2 and 3 (d) 1, 3 and 4 Ans: (c) |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: India’s informal economy, Informal sector, India’s GDP Growth Rate, Workforce, and Goods And Services Tax (GST).
Relevancy for Mains: Periodic Labour Force Survey Report 2023, Informal economy of India, Problems with the India’s informal economy, and Government initiatives are in place to formalize the Indian Economy. |
|---|
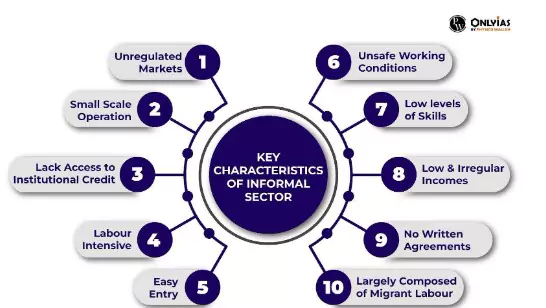
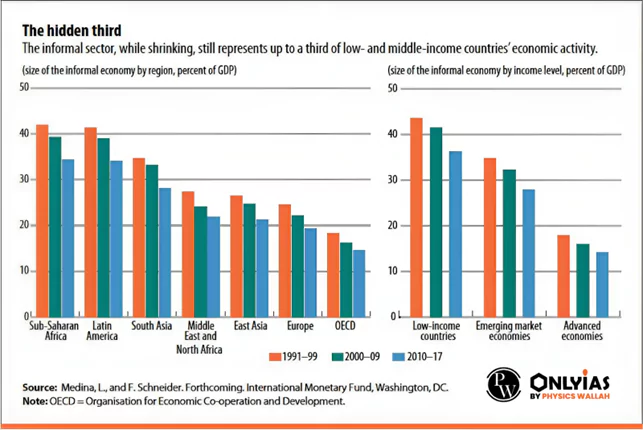
Over 90% of workers in India are informal and out of these, those engaged in rural areas (dominated by farm and agriculture activities) are significantly more than those of urban areas.Informal employment lacks a written contract, paid leave, and may not pay minimum wages or pay attention to working conditions.
Also read: Nobel Prize 2023: Insights on Indian Women at Workforce
Key Terms
|
|---|
What are the problems with the informal economy?
|
|---|
What Government Initiatives are in Place to Formalize the Indian Informal Economy?
|
|---|
India’s informal economy, comprising over 90% of the workforce, faces challenges such as tax evasion, limited social security, and hindrances to formalization; addressing these issues requires comprehensive measures, including database creation, equal wage enforcement, and rationalizing regulations to uplift the vast “invisible workforce” and integrate them into formal arrangements.
| Prelims Question (2015)
With reference to Indian economy, consider the following: 1. Bank rate 2. Open market operations 3. Public debt 4. Public Revenue Which of the above is/are component/components of Monetary Policy? (a) 1 only (b) 2, 3 and 4 (c) 1 and 2 (d) 1, 3 and 4 Ans: (c) |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: APAAR: One Nation One Student ID Registration Scheme, APAAR, Student ID, National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, Digital Education, Information and Communication Technology (ICT), and Edtech industry.
Relevancy for Mains: Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry (APAAR); ‘One Nation, One Student ID, Edtech, or education technology, growth of the ed-tech industry in India, Government initiatives in education technology, and challenges in educational technology. |
|---|
What are the reasons for growth of the Edtech industry in India?
|
|---|
Also read: Aligning Higher Education in India with the UN SDGs
In the digital age, technology has transformed education, but finding the right balance between its benefits and challenges while fostering critical thinking and addressing the digital divide is essential for a holistic learning experience.
| Prelims Question (2020)
In India, the term “Public Key Infrastructure is used in the context of (a) Digital security infrastructure (b) Food security infrastructure (c) Health care and education infrastructure (d) Telecommunication and transportation infrastructure Ans: (a) |
|---|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
