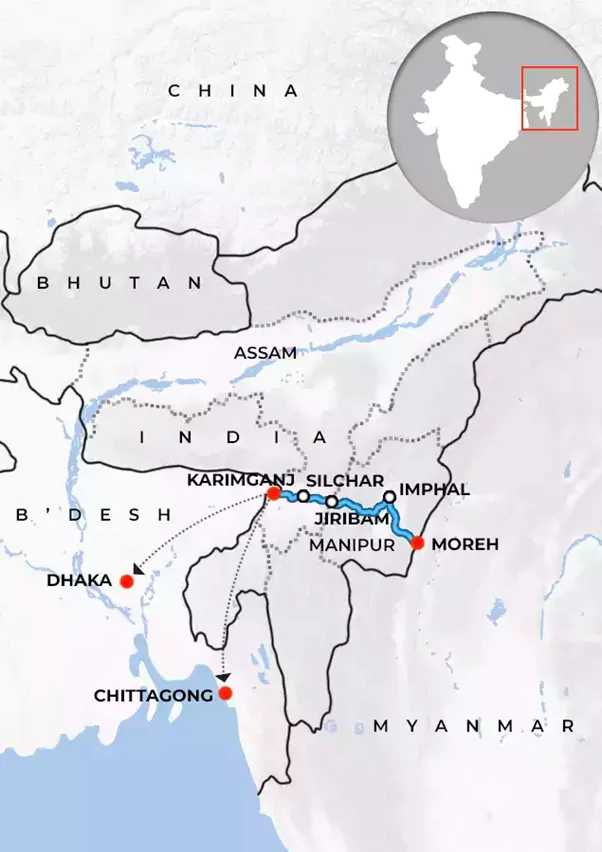
What is the GPMB?
|
|---|
News Source: /reliefweb.int/report
News Source: The Indian Express
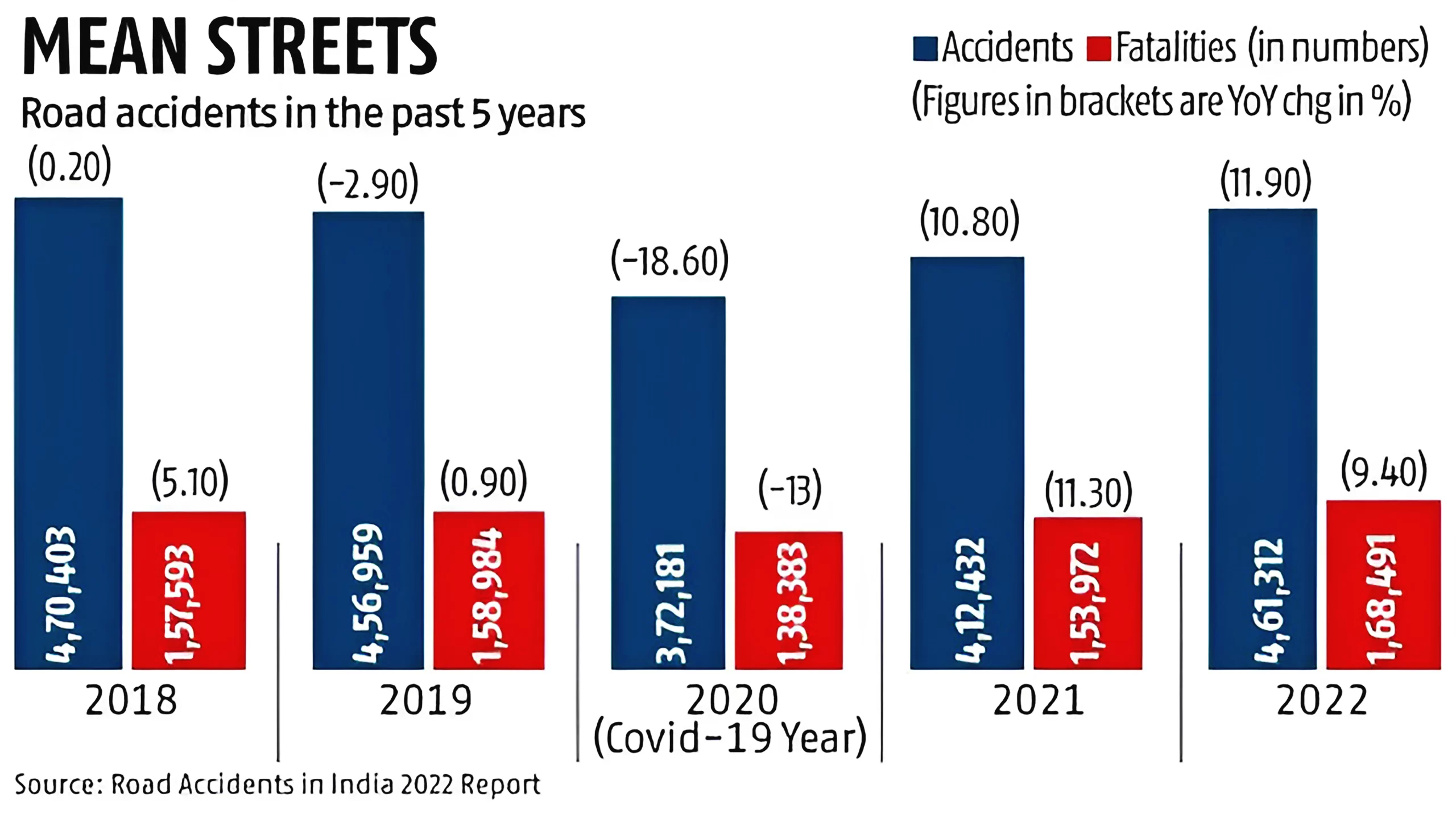
Various Initiatives: Road Safety
|
|---|
News Source: Business Standard
Amundsen Sea
|
About Ice Sheet:
|
News Source: The Indian Express
Congo Basin
Amazon Basin
The Borneo-Mekong-Southeast Asia Basin
|
|---|
The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework:
|
|---|
News Source: Down to Earth
In 2006, the West Bengal government acquired nearly 1,000 acres of land in Singur, Hooghly, to build a manufacturing facility for the Tata Nano.
Know more about the Singur Land Acquisition Case
RFCT-LARR (Amendment) Ordinance, 2014:
|
|---|
The importance of improving land laws in India has gathered traction in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic as a necessity to enhance India’s attractiveness to global businesses.
Other Disputes over Land Acquisition in India
|
|---|
Gujarat’s Land Acquisition Practices:
|
|---|
Strengthening the rehabilitation and resettlement measures for affected communities while ensuring sustainable livelihoods, adequate housing, and essential amenities with proper planning and execution of these measures are essential for successful land acquisition.
| Prelims Question (2021)
What is the position of the Right to Property in India? (a) Legal right available to citizens only (b) Legal right available to any person (c) Fundamental Right available to citizens only (d) Neither Fundamental Right nor legal right Ans: (b) |
|---|
| Mains Question: State the objectives and measures of land reforms in India. Discuss how land ceiling policy on landholding can be considered as an effective reform under economic criteria. |
|---|
| What is Artificial Intelligence?
It is a machine-based system that can, for a given set of human-defined objectives, make predictions, recommendations, or decisions influencing real or virtual environments. |
|---|
What is meant by Data scraping?
What are Web crawlers or data scrapers?
|
|---|
Also Read: Empowering Legislation: Harnessing Artificial Intelligence for Better Governance
Other Global Governance Initiatives to Regulate AI
Role of G 20 in AI Governance
|
|---|
Global AI Summit London 2023 highlights the imperative for unified global governance in regulating AI, addressing ethical concerns, and mitigating potential risks, emphasizing the need for inclusive collaboration and a decolonial-informed approach to ensure responsible and equitable AI governance.
| Prelims Question (2017)
In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents? 1. Service providers 2. Data centres 3. Body corporate Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (d) |
|---|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>