Context: Justice Sanjay Kishan Kaul recommended the creation of a Truth and Reconciliation Commission for Jammu and Kashmir in his concurring but separate opinion on the abrogation of Article 370.

Must Read: Supreme Court Verdict On Abrogation Of Article 370
News source: Livemint
Context: A boat carrying over 60 Europe-bound migrants, including women and children, capsized off the coast of Libya.
| International Organization for Migration (IOM)
About: IOM is the leading intergovernmental organization in the field of migration and works closely with governmental, intergovernmental, and non-governmental partners. Genesis: Established in 1951 Members: 175 member states, 8 observer status and offices in 171 countries. Objective:
Mandate: IOM works in the four broad areas of migration management:
|
|---|
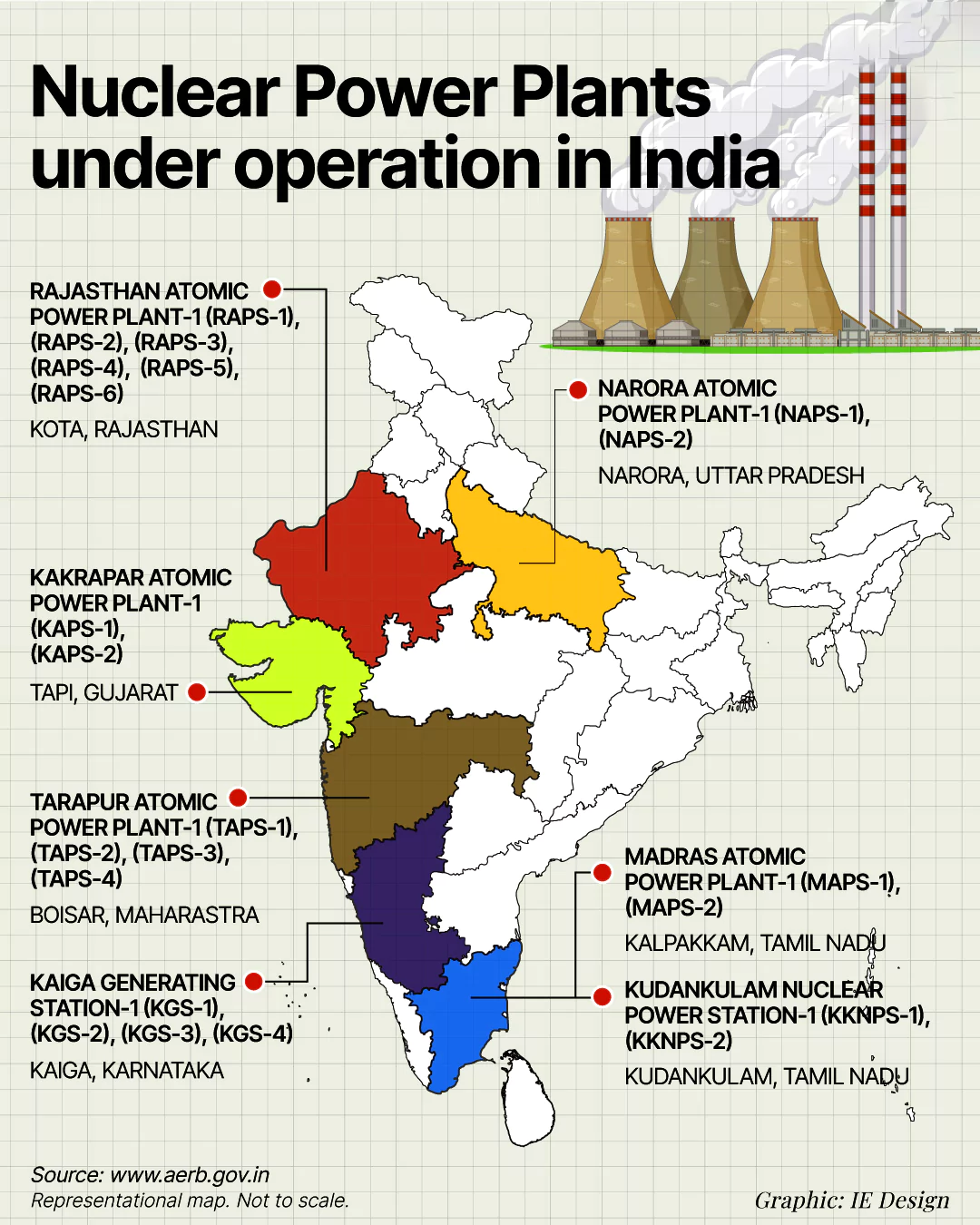
Context: The fourth unit of the Kakrapar Atomic Power Project (KAPP-4) in Gujarat, with 700 MWe capacity, started controlled fission chain reaction and thus became critical.
| A pressurized heavy water reactor (PHWR) is a nuclear power reactor, commonly using unenriched natural uranium as its fuel, that uses heavy water (deuterium oxide D2O) as its coolant and moderator. |
|---|
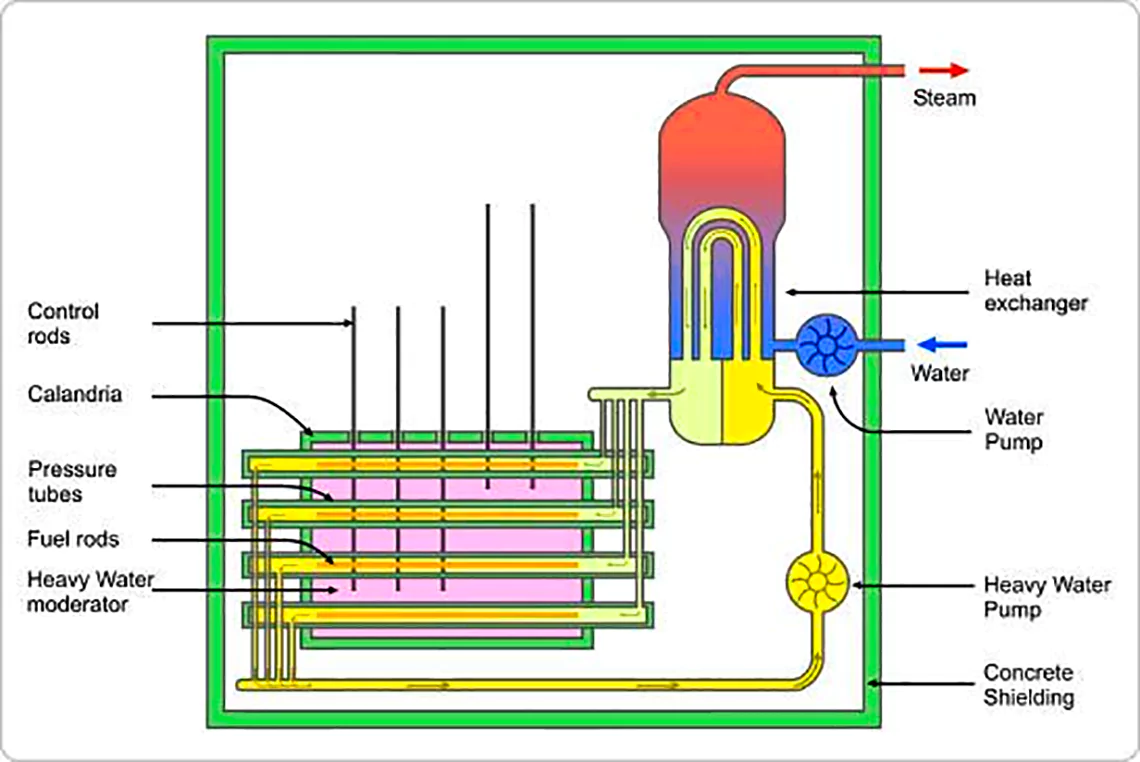
 The first criticality is the start of a controlled fission chain reaction.
The first criticality is the start of a controlled fission chain reaction.Also Read: Nuclear Power Plants In India 2023, here.
Context: Recently, the Prime Minister inaugurated Surat Diamond Bourse (SDB), the world’s largest center for international diamond and jewellery business.
Source: The Hindu
Context: In a recently released report, the International Energy Agency (IEA) has said that the global coal demand is expected to decline by 2026.
About International Energy Agency (IEA)
|
|---|
Must Read: World Energy Outlook 2023
Context: A top state-run Chinese think-tank Chinese Academy of Sciences has warned that China might go into a potential “middle-technology trap”.
Source: Business Standard
Must Read: India’s Supply Chain Opportunity
Context: Odisha is to host a grand event in Puri from January 15-17 for the inauguration of the beautification drive of the Jagannath temple corridor.
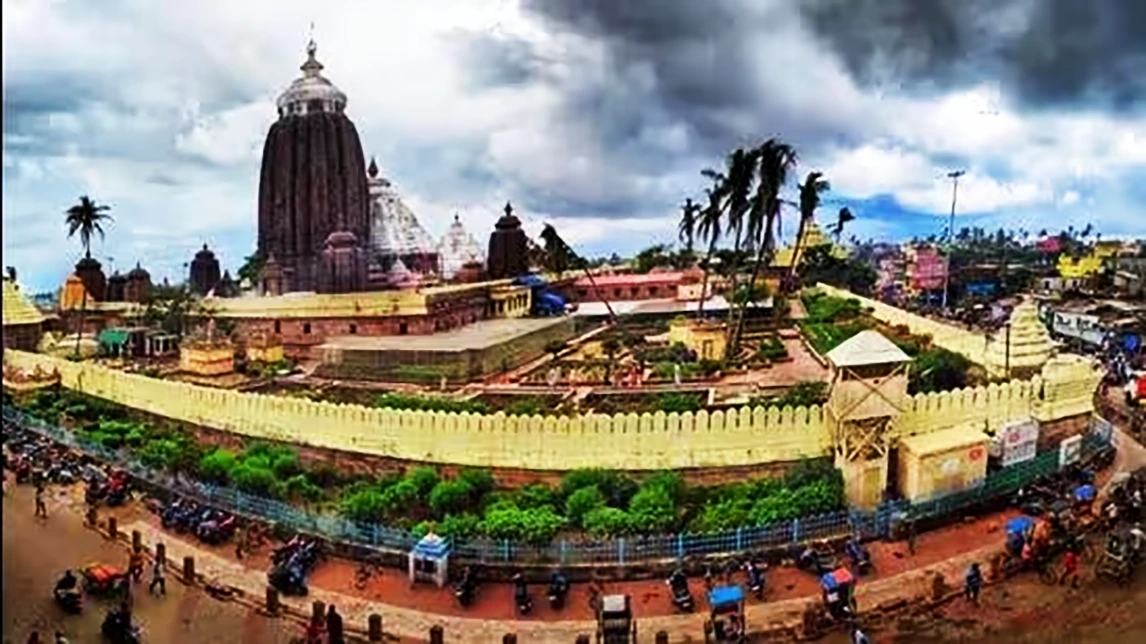

 It is one of the 4 Dhams (Holiest of the holy places in Hinduism) i.e., Puri, Dwarika, Badrinath & Rameswar.
It is one of the 4 Dhams (Holiest of the holy places in Hinduism) i.e., Puri, Dwarika, Badrinath & Rameswar.News Source: Hindustan Times
Context: A case of Covid Subvariant JN.1 are spreading in the US and China, was discovered in Kerala.
About Influenza
About INSACOG’s (Indian SARS-CoV-2 Genomics Consortium)
|
|---|
News Source: Indian Express
Context: The Ministry of Commerce & Industry has recently released the “LEADS Report 2023 (Logistics Ease Across Different State)”
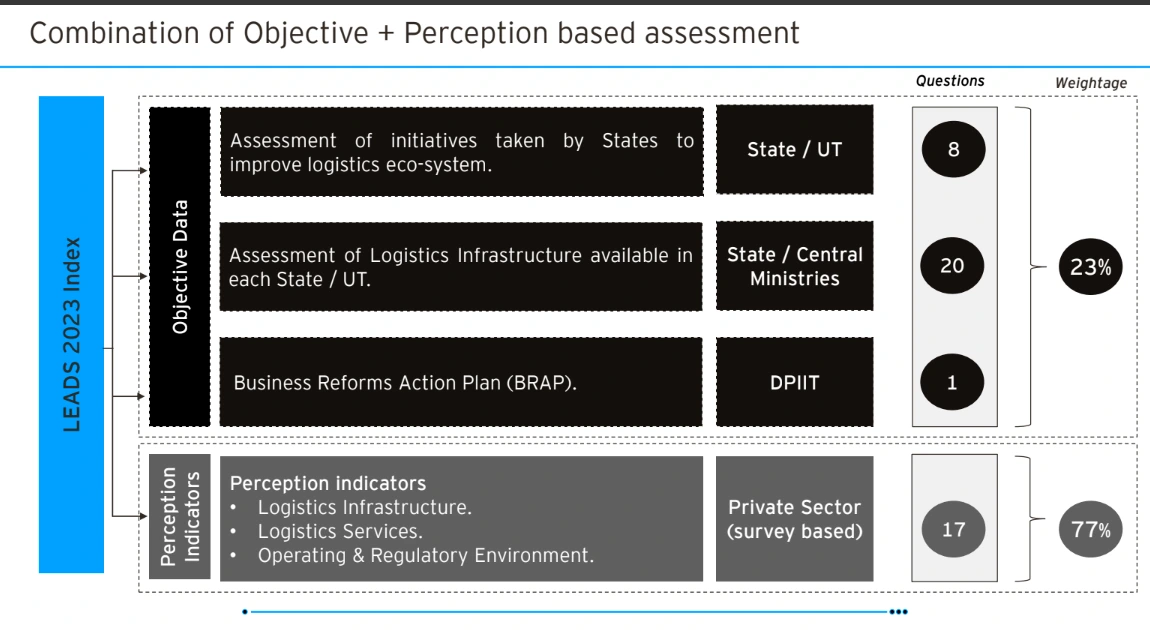

Also Read: Logistics Cost in India: Assessment and Long-Term Framework: Ministry of Commerce and Industry
News Source: FE
Context: Recently, the Prime Minister inaugurated the second edition of Kashi Tamil Sangamam at Namo Ghat, Varanasi.
Ancient Connect: Kashi and Tamilakam
|
|---|
Learn more about the SANGAM AGE: THE HISTORY OF SOUTH INDIA, here.
News Source: Indian Express
Context: PM participated in the Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra programme at Barki Gram Sabha of Sewapuri development block in Varanasi.
Learn more about the Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana (PMJAY), here.
News Source: The Hindu
Context: The Lok Sabha passed the Post Office Bill 2023 to replace the Indian Post Office Act of 1898.
| The Indian Post Office Act, 1898 | Post Office Bill 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| – |
|
| – |
|
| – | Recovery of Unpaid Postal Service Charges as Land Revenue:
|
News Source: The Indian Express
Context: This article is based on the news “PM Modi, Oman’s Sultan adopt vision document, discuss Gaza” which was published in the Indian Express. The Sultan of Oman recently visited India marking the first State visit from Oman to India in the last 26 years.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), Oman-India Investment Fund, Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), and Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC).
Relevancy for Mains: India-Oman Vision Document, India Oman Relations, Significance, Challenges and Wayforward. |
|---|
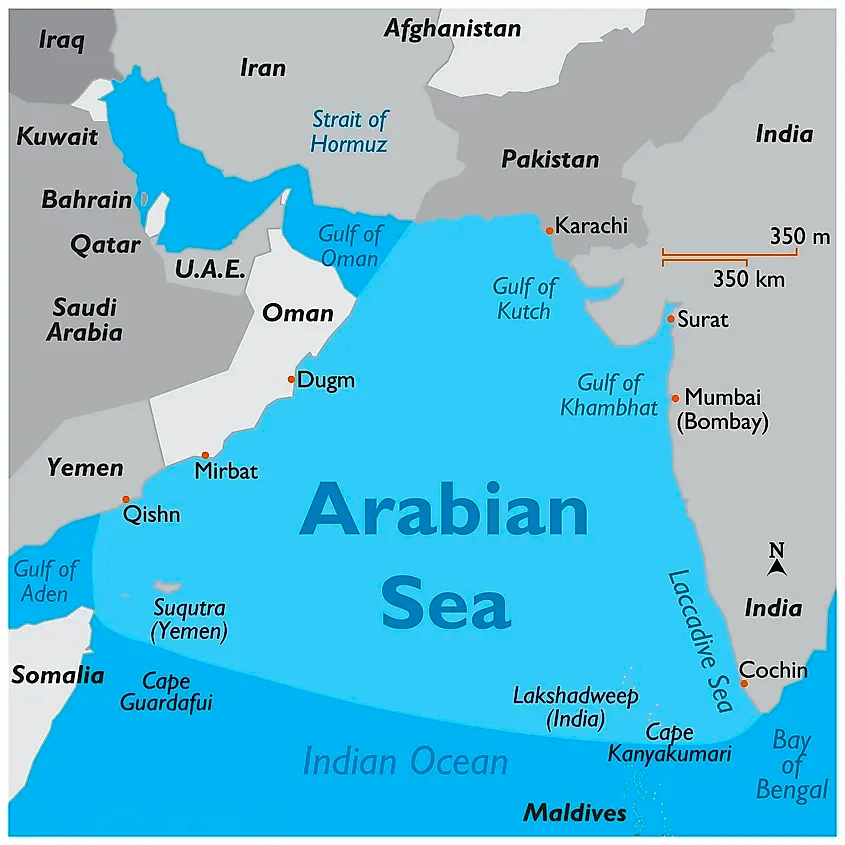
| Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC): It is a political and economic union of the Middle Eastern countries bordering the Persian Gulf and constituting the Arabian Peninsula.
Members: UAE, Bahrain, Saudi Arabia, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC): The OIC aims to represent the Muslim world in order to protect and safeguard vital interests of Muslims. Arab League: It is a union of Arabic-speaking African and Asian countries that promotes the interests of its member countries and observers. |
|---|
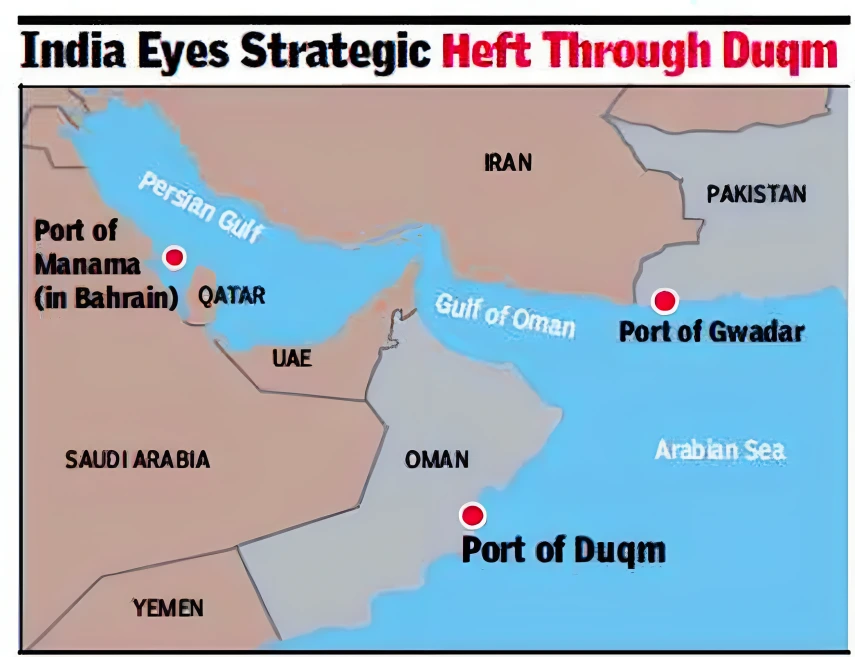 Maritime Security: In recent years, both countries have cooperated in ensuring maritime security in the Indian Ocean region.
Maritime Security: In recent years, both countries have cooperated in ensuring maritime security in the Indian Ocean region.About Duqm Port
|
|---|
Must Read: West Asia: India’s Geopolitical Opportunity And Challenge
India-Oman Vision Document marks a significant step in strengthening bilateral relations, encompassing economic, strategic, and cultural dimensions.
| Prelims Question (2016)
Which of the following is not a member of ‘Gulf Cooperation Council’? (a) Iran (b) Saudi Arabia (c) Oman (d) Kuwait Ans: (a) |
|---|
Context: This article is based on the news “Homegrown benefit: Why ‘desi’ should be the catchword for India’s dairy sector” which was published in the Down to Earth. The Indian dairy sector needs to shift from exotic and crossbred to indigenous cattle breeds to help the sector stay profitable and sustainable.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Indigenous Cattle Breeds in India, Operation Flood, National Kamdhenu Breeding Centre, and Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM).
Relevancy for Mains: Indigenous Cattle Breeds Over Exotic Crossbreeds in India: Reasons, Challenges and Wayforward. |
|---|
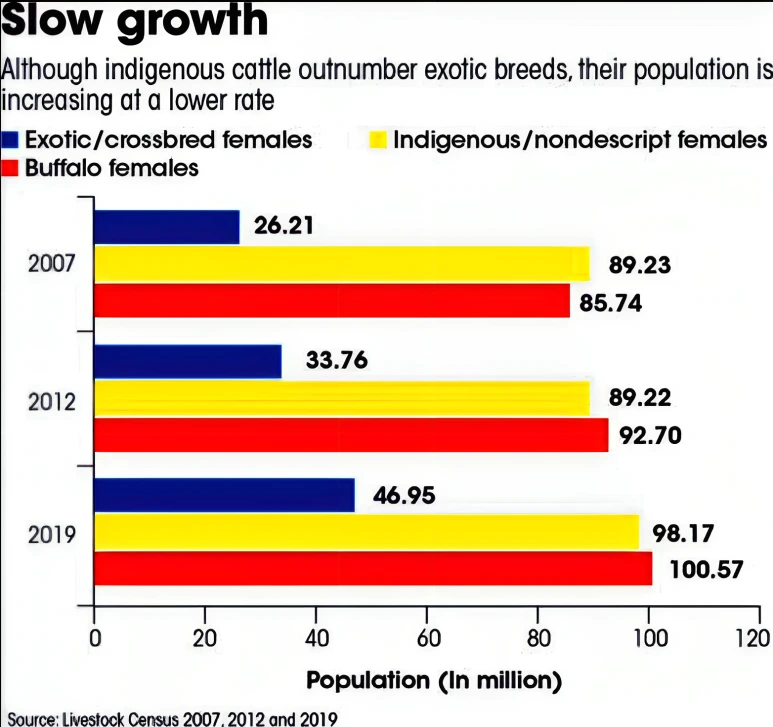 Milch Breeds: Milch cattle are breeds specifically raised for milk production. Five of these viz. Sahiwal, Gir, Red Sindhi, Tharparkar, and Rathi are known for their milking prowess.
Milch Breeds: Milch cattle are breeds specifically raised for milk production. Five of these viz. Sahiwal, Gir, Red Sindhi, Tharparkar, and Rathi are known for their milking prowess. About Operation Flood
Must Read: National Milk Day 2023 |
|---|
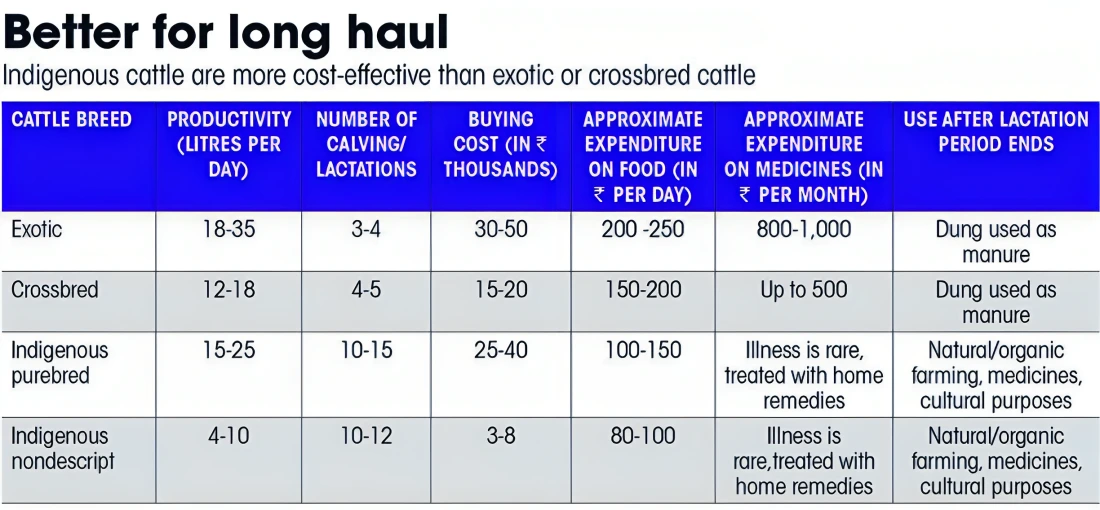 Disease Resistance: Global warming is likely to increase the incidence of animal diseases in Crossbred and Exotic animals with a lesser impact on Indigenous Breeds.
Disease Resistance: Global warming is likely to increase the incidence of animal diseases in Crossbred and Exotic animals with a lesser impact on Indigenous Breeds. About National Bureau of Animal Genetic Resources (NBAGR)
|
|---|
National Kamdhenu Breeding Centre
|
|---|
Must Read: Credit Guarantee Scheme for Livestock Sector
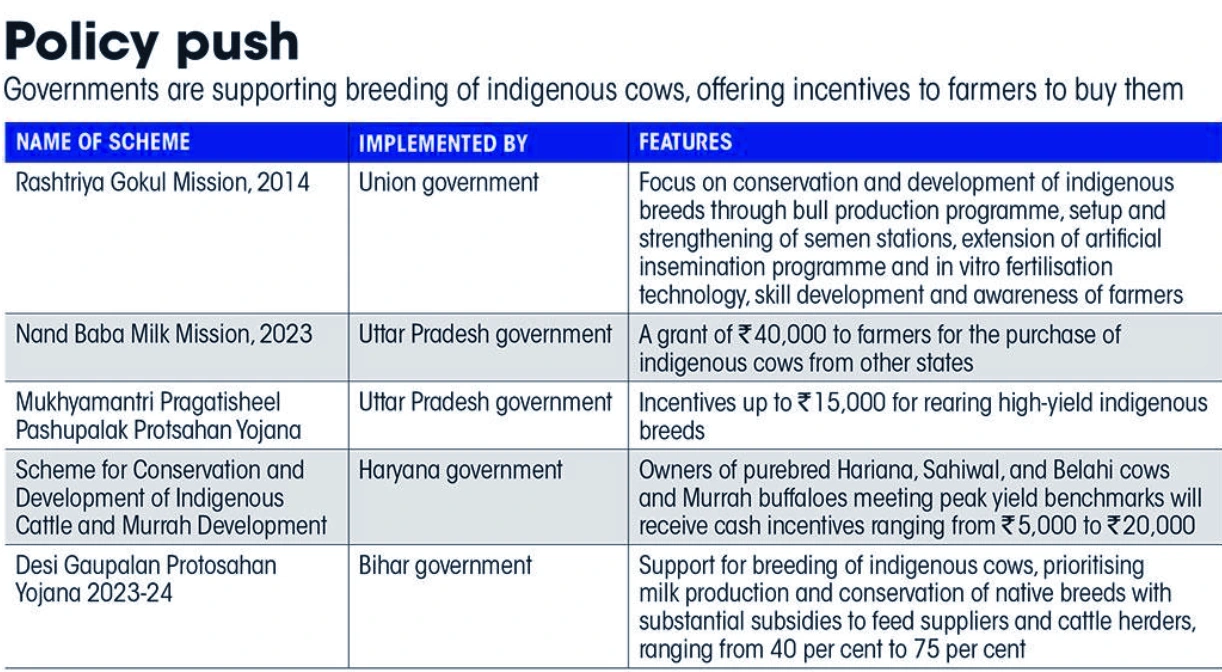
Also Read: Centre To Depute National Level Monitors (NLMs) to Oversee Livestock Schemes
Prioritizing indigenous cattle breeds over exotic crossbreeds in India’s dairy sector is essential for sustainability, economic viability, and preserving cultural significance, requiring concerted efforts in awareness, research, and inclusive development initiatives.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>