Context:
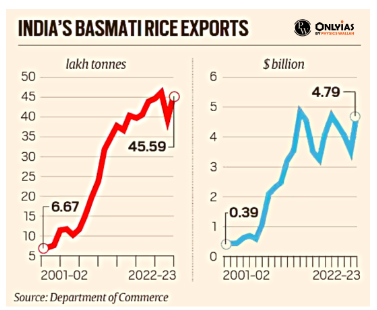
Over the past three decades, India’s annual Basmati rice exports have surged from 0.3-0.35 million tonnes valued at $200-250 million to 4.5-4.6 million tonnes worth $4.7-4.8 billion.
Three Basmati Rice Revolutions in India:
- Until the late 1980s, traditional basmati rice varieties in India had tall plants (150 – 160 cm) that were prone to bending when laden with grains.
- Basmati Rice yielded only about 10 quintals of paddy per acre over 155-160 days.
- Some of these traditional varieties of Basmati Rice included Taraori and Dehraduni.
| The First Revolution: Pusa Basmati-1 (PB-1) |
- In 1989, the breakthrough came with Pusa Basmati-1 (PB-1), a crossbreed between Karnal Local and a high-yielding non-basmati line.
- PB-1 had a shorter plant height, didn’t bend, and yielded 25-26 quintals of grain per acre in a shorter time, making it a game-changer for basmati rice.
- At the turn of the century, India was exporting 0.6-0.7 mt of basmati rice fetching $400-450 million annually, with PB-1’s share at roughly 60%.
|
| The Second Revolution: Pusa Basmati-1121 (PB-1121) |
- In 2003, Pusa Basmati-1121 (PB-1121) was introduced. While it yielded (20-21 quintal/acre) slightly less and took longer to mature (140-145 days).
- Its grain quality was exceptional, with longer kernels that expanded significantly upon cooking. This variety transformed basmati exports, becoming a global hit.
- Between 2001-02 and 2013-14, India basmati rice exports surged from 0.7 mt to 3.7 mt, and from $390 million to $4.9 billion in value terms. Over 70% of that was from PB-1121.
|
| The Third Basmati Revolution: Pusa Basmati-1509 (PB-1509) |
- In 2013, the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) released PB-1509.
- It offered similar yields to PB-1 but with a shorter seed-to-grain duration (115-120 days).
- Farmers could now grow an additional crop, increasing their income.
|
What are the benefits of the Basmati crop?
About Basmati Rice:
- Basmati rice is a long-grain aromatic rice known for its extra-long slender grains, fluffy texture, delightful taste, superior aroma, and distinct flavor.
- Varieties of Basmati Rice: 34 varieties recognized under the Seeds Act, 1966.
- Cultivation Areas: Grown in J&K, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Uttarakhand, and western Uttar Pradesh.
- Export Leader: India is the top exporter, with 4,558,972.23 MT of Basmati Rice exported in 2022-23, valued at Rs. 38,524.11 crores (4,787.50 million US dollars).
- Key Export Destinations (2022-23): Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, UAE, and Yemen.
|
News Source: The Indian Express
![]() 18 Sep 2023
18 Sep 2023
