Context:
Scientists at CSIR-Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine (IIIM), Jammu, have found that phytocannabinoids, a class of compounds found in the cannabis plant, possess some hitherto unexplored antibiotic properties.
THCBD and Its Antibiotic Properties
- In the new study, published in the journal ACS Infectious Diseases revealed, the antibacterial properties of tetrahydrocannabinol (THCBD), a semisynthetic phytocannabinoid, against Staphylococcus aureus, the bacteria responsible for the second most number of deaths due to AMR.
- According to a senior principal scientist at the CSIR-National Chemical Laboratory (NCL), Pune, bacteria have developed certain sophisticated ‘shields’ over many decades to resist the effects of antibiotic medications.
- These include the formation of biofilms – thin sheets of bacterial colonies that are more resistant to antibiotics than when separated – and cellular mechanisms called efflux pumps that flush drugs out from cells.
- The resulting AMR increases the risk of disease spread, severe illness, and death.
About Cannabis Sativa
- It is an herbaceous plant that belongs to the family Cannabinaceae.
- It has been used by humans for over 5,000 years for medicinal and recreational uses, firstly in Central and Northeast Asia and subsequently spreading worldwide.
- Cannabis, or marijuana, is undoubtedly one of the most widely used illicit drugs.
- It has a complex chemical composition that includes cannabinoids which are a group of secondary metabolites, several of which are responsible for the psychotropic effects.
|
What is India’s AMR burden?
- AMR Capital of the World: According to one estimate, India reported 2.97 lakh deaths in 2019 that could be attributed to AMR and 10.42 lakh others that could be associated with AMR.
- Reasons:
-
- Overuse of antibiotics in India (Due to Over-the-counter sales).
- Misuse in animal husbandry
- Poor Biowaste disposal management.
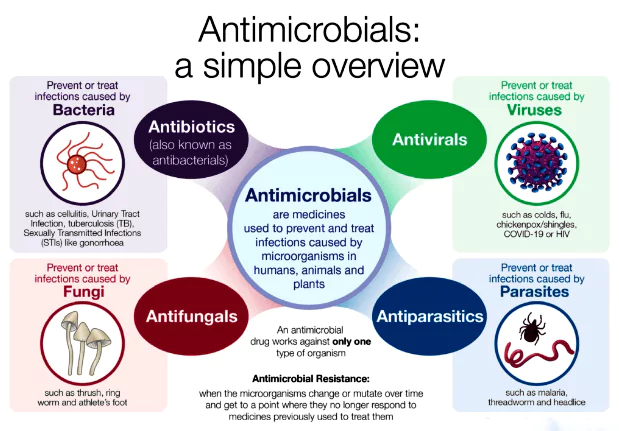
About Antibiotics:
- These are chemical compounds isolated from one microorganism and used to kill another.
- Since their discovery, they have saved millions of lives but are falling short against AMR bacteria.
|
Need for Alternative Solutions
- Numerous antibiotics exist for S. aureus, the emergence of the MRSA strain necessitates alternative solutions.
- “S. aureus includes a strain known as MRSA, for methicillin-resistant S. aureus, resistant to the last line of antibiotics called methicillin.’’
How is THCBD made?
- The prefix ‘phyto’ in phytocannabinoid means it comes from a plant.
- Cannabinoids are a class of compounds found in the cannabis plant. Cannabinoids bind to receptors in the bodies of animals to produce a variety of neurological effects.
- The researchers extracted cannabidiol from a cannabis plant and made it react with hydrogen, using palladium as a catalyst.
- This process yielded a mixture of molecules with the same composition and order of atoms but different structures. One of them was THCBD.
What Were THCBD’s Effects?
- Researchers tested THCBD against bacterial cultures in the lab and found THCBD “demonstrated strong effectiveness” against efflux pump overexpression and MRSA strains.
- The minimum quantity found to be efficacious against a strain of Gram-positive S. aureus used commonly in AMR research was 0.25 μg/ml, which the researchers called “potent”.
- It “significantly reduced” the number of viable microbial cells of S. aureus skin infections in mice.
- They also found that the compound either complemented or was indifferent to the effects of other common antibiotics like mupirocin, penicillin G, and ciprofloxacin.
Significance of Study
- It will help the development of new therapeutics against AMR.
- It can be a good preclinical candidate, which needs further fine-tuning as far as its drug likeness is concerned
Challenges
- Collaboration and Coordination: THCBD comes from cannabis, which is notorious for its intoxicating properties.
What is the Solubility Challenge?
- It is an important consideration for a drug. It must dissolve in an aqueous solution. If it doesn’t dissolve properly, the body won’t be able to absorb it as intended.
- The properties of the solvent influence the solubility of a drug.
- For example, a molecule can be too hydrophilic (water-loving) or lipophilic (fat-loving).
- In a biological system, the cytoplasm – which fills the inside of a cell – is a gelatinous liquid and the cell’s wall is primarily composed of lipids.
- A drug molecule in this milieu should be neither hydrophilic nor lipophilic but in between.
|
-
- As a result, it hasn’t been easy to collaborate on phytocannabinoid research with other institutes.
- Legal Constraints: There is a need to adhere to specific regulations when studying this plant.
- For example, Section 20 of the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act 1985 restricts the use of cannabis and doesn’t make exceptions for research.
- Lack of Approval to Conduct Research: Many universities lack approval to research the plant, and efforts are underway to secure government authorisation.
- The solubility challenge of THCBD: THCBD “leans slightly towards lipophilicity”, achieving a “drug-like” balance is crucial for it to be appropriately soluble.
Way Forward: What next for THCBD?
- Collaborations to speed up drug development progress: Faster approval and dispersal of funds.
- Unified National Policy: Establishing a framework for cannabis research and transportation agreement
- Conducting a comprehensive safety profile assessment for THCB to use as a drug.
Conclusion
Highlighting the anti-bacterial nature of cannabis, the project will go a long way towards circumventing the taboo around it and transforming it into a valuable resource.
- The researchers’ work on cannabis will “yield significant contributions to the healthcare system,” “but will also directly benefit J&K by establishing related industries that will create a sustainable demand for jobs.”
Also Read: New Class Of Antibiotic Against A Drug-Resistant Bacterium
![]() 23 Jan 2024
23 Jan 2024
