The role of the Global South is changing in the global economy and to boost its growth, it needs better financial support, digital infrastructure and climate financing that highlights the need for reforms in the global financial system.
About Global South
- Refers: Global South refers to various countries around the world that are sometimes described as ‘developing’, ‘less developed’ or ‘underdeveloped’.
- The term Global South was first used in 1969 by Carl Oglesby, but gained momentum after the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991.
- The term ‘Global South’ is not geographical. In fact, the Global South’s two largest countries — China and India — lie entirely in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Its usage denotes a mix of political, geopolitical and economic commonalities between nations.
- Regional Spread: Many of the Global South countries are in the Southern Hemisphere, largely in Africa, Asia and Latin America.
- Characteristics of Global South Countries:
- Poverty ridden with higher levels of income inequality.
- Lower life expectancy and harsh living conditions.
- Variations within the Global South Countries:
- Population Level: 4 out of the 5 most populous nations of the world are in Asia (including China and India).
- Economic Growth: In recent decades, Asian economies (especially in East Asia) have grown the fastest and are expected to do so in the future as well.
- Income Level: Latin American countries, except Venezuela are either upper-middle or high-income, while the African members of the Global South region are generally poorer with 7 of the 20 countries having per capita income of less than $1,000.
- Conflict Situation: 3 large African nations- Ethiopia, Democratic Republic of the Congo and Sudan have been affected by long and bloody civil conflicts.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Global North
- Global North consists of richer nations that are located mostly in North America and Europe, with some additions in Oceania and elsewhere.
- ‘Global North’ refers loosely to countries like the US, Canada, Europe, Russia, Australia and New Zealand.
Classification of Countries as per the Cold War metrics
- First World: It referred to the advanced capitalist nations.
- Example: USA, UK, France, Germany, etc.
- Second World: It referred to the socialist nations led by the Soviet Union.
- Example: USSR, China, Cuba, etc.
- Third World: It referred to developing nations, many of whom were still under the colonial yoke.
- Example: Countries in Asia, Africa like India, Indonesia, etc.
World Systems Approach
- It was introduced by sociologist Immanuel Wallerstein in 1974, emphasising an interconnected perspective of looking at world politics.
- As per this system, there are three major zones of production: core, peripheral and semi-peripheral.
- The core zones reap profits, being the owners of cutting-edge technologies such as the US or Japan.
- Peripheral zones engage in less sophisticated production that is more labour-intensive. In the middle are countries like India and Brazil.
- Semi-peripheral zones sometimes exploit other countries but are sometimes exploited themselves such as Argentina and Iran.
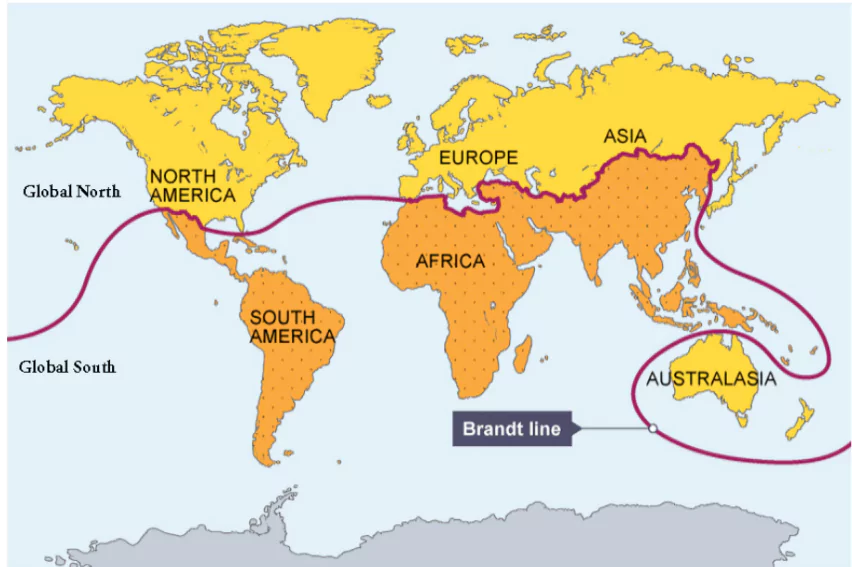
About the Brandt Line
- Proposed by Willy Brandt in the 1980s.
- It is an imaginary line that divides the world into richer countries (mainly in the Northern Hemisphere) and poorer countries (mostly in the Southern Hemisphere).
- It basically shows the socio-economic divide between northern countries and southern countries.
|
Recent Economic Forecasts about Global South
- Growth and Development: The latest World Bank/IMF forecasts indicate that growth of the Global South will hold steady at around 3% and is the lowest in decades.
- Regional Achievements: For the next two to three decades, nearly three-fourths of the global growth will come from middle- and low-income countries, with Asia leading the way.
- Reasons for Growth: Decades of supportive geopolitics, demographics, globalisation and technological advances resulted in a period of high growth.
Impact of Recent Global Events on the Global South
- Globalisation and Social Safety Nets: As globalisation deepened, safety nets in individual countries did not keep pace with the accompanying displacement of livelihoods, impacting social cohesion and support for the multilateral system.
- Impact of Pandemic: COVID-19 disrupted markets, trade, supply chains, financial globalisation, impacting global growth.
- Geopolitical Concerns: The war in Ukraine, worsening geopolitics, and the rise of strategic competition risks entrenched policy-driven fragmentation, impacting global cooperation and economic stability.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Initiatives by India for the Global South
- The New Delhi Declaration: It serves as a testament to the collaborative efforts of G20 member countries in addressing global challenges and striving for a more prosperous, peaceful, and sustainable world.
- Non-Aligned Movement (NAM): India played a pivotal role in founding the Non-Aligned Movement in 1961.
- Aim: To promote the interests of countries that are not aligned with any major power bloc and advocates for the rights of the Global South.
- South-South Cooperation: India has engaged in various bilateral agreements and partnerships with countries in Africa, Latin America, and Asia.
- These agreements focus on trade, technology transfer, and capacity-building.
- BRICS: India is a member of BRICS, a group of emerging economies that advocate for a more equitable global order.
- Group of 77 (G77): India is an active participant in the G77, a coalition of developing countries at the United Nations.
- It works to address economic and developmental challenges faced by the Global South.
- Climate Change Negotiations: India has played a significant role in climate change negotiations, advocating for the principle of “common but differentiated responsibilities”.
-
- It highlights the need for developed countries to take the lead in addressing climate change.
- Recently established Loss and Damage Fund at COP28 will provide urgent assistance to vulnerable communities living on the frontlines of the climate crisis. All wealthy and high emitting countries now have a responsibility to step up and contribute to the fund.
- World Trade Organization (WTO) and Trade Issues: India has been a key advocate for the Doha Development Agenda in the WTO that emphasises the importance of addressing trade imbalances and development concerns.
- Peacekeeping Operations: India has consistently been one of the largest contributors to UN peacekeeping operations, demonstrating its commitment to global peace and security.
- In 2023, the Indian Prime Minister announced the following five initiatives in the “Voice of Global South Summit” hosted by India:
- The Global South Centre of Excellence: For research development solutions and best practices.
- The Global South Science and Technology Initiative: To share Indian expertise in areas such as space technology and nuclear energy.
- The Aarogya Maitri Project: To provide essential medical supplies to any developing country affected by natural disasters or humanitarian crises.
- The Global South Young Diplomats Forum: To connect young officers of foreign ministries.
- The Global South Scholarships: To provide higher education opportunities in India for students from developing countries.
- The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) Treaty on intellectual property, Genetic resources and Associated Traditional Knowledge: It is a significant win for countries of the global South and for India, which is a mega biodiversity hotspot with abundance of traditional knowledge, and wisdom.
- Others:
- Vaccine Diplomacy during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Humanitarian assistance in times of natural disasters and crises.
- Demand for UNSC Reforms to make it more representative and inclusive, reflecting the interests of the Global South.
- Soft Power Diplomacy through initiatives like the Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) and hosting cultural festivals.
|
Significance of the Global South
- Shifting Economic and Political Power: The Global South has experienced a significant shift in both political and economic powers.
- The World Bank (WB) has acknowledged a “shift in wealth” from the North Atlantic to the Asia-Pacific region.
- By 2030 it is projected that three of the four largest economies will be from the Global South — with the order being China, India, the U.S. and Indonesia.
- Already the GDP in terms of purchasing power of the Global South dominated BRICS nations surpasses that of the Global North’s G7 club.
- The combined GDP of the BRICS nations (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) already surpasses that of the G-7 nations.
- These are increasingly asserting themselves on the global scene — be it China’s brokering of Iran and Saudi Arabia’s rapprochement or Brazil’s attempt to push a peace plan to end the war in Ukraine.
- Impact on Geopolitics: Asian nations are predicted to play a significant role and is known by experts as the “Asian Century”.
- Increased participation within important North-created international institutions, such as IMF, WTO and UN agencies.
- Increased cooperation in various organisations such as OPEC, ASEAN, and the African Union.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Challenges Faced by the Global South
- Vulnerability to Global Headwinds: Headwinds to growth emanating from several sources such as climate change, cost of living crisis, out-of-reach Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) goals, declining productivity, absence of liquidity financing, and a broken debt architecture impact the Global South the most.
- Financial Challenges in Global South:
- Absence of Deep Financial Markets: Without deep financial markets, the availability of sustainable financing will be a binding constraint for growth in the Global South and by extension for global growth because the Global South attracts capital at prohibitive rates and at short tenure.
- Inadequate Financial Systems: The present international financial architecture is seemed to be ill-suited to support the growth potential of the Global South.
- As per various experts, the global financial system is not providing financing at scale and in time to emerging markets.
- Technological Disparities: Countries lacking digital public infrastructure (DPI) struggled during the pandemic, while those with effective DPI could provide emergency services. It highlights the need for development of more DPIs.
- Others:
- Inadequate Access to Resources: Global North-South divide has been due to major gaps in the access to resources that is required for crucial development.
- Interference by China: It is through making inroads in the region through the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) for developing infrastructure, while it is still a question whether BRI will profit all respective regions or only of China.
- US Hegemony: The world is now considered to be multipolar but still the US alone dominates international affairs due to its largest economy and dominance in trade and currency.
Way Forward
- Technological Advancements: With the surge in technological innovations including Artificial Intelligence (AI), the digital transformation of daily lives in a positive manner is observed in all sectors such as education, emergency responses, health systems, commerce, etc.
- Advances in AI give it great potential to boost global growth and inclusion.
- Establishment of a Common Repository: The DPI architecture requires a centre and a firmer common structure to realise gains and ensure data and cyber security across multiple usages.
- An international effort to bring together a coalition of the willing to create a repository of best practices and provide a forum for sharing technical advances would avert system-wide incompatibilities.
- With reliable and consistent data, shareholders and civil society groups will be in a better position to channel their activism more efficiently.
- It will provide the means for corporate boards to develop effective long-term plans for their organisations and large money managers will have the data to act on their sustainability-related goals.
- Improved Climate Financing: As regards climate financing, several proposals envisage leveraging public and multilateral resources.
- A recent Bretton Woods Committee Report proposes a complementary approach to focus more forcefully on capital markets. Research shows that 1% of publicly listed companies are responsible for 40% of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Need to Adopt: Such a solution would entail three elements:
- Mandatory disclosure requirements applied globally for publicly listed companies and large state-owned enterprises.
- A digital public infrastructure that translates data disclosed by companies into machine-readable data.
- New rating agencies need to rate corporations on the sustainability front.
- Enhancement of Liquidity Provisions: A strengthened and reformed IMF is required to achieve this liquidity goal. It could address the lack of US dollar swap lines for countries like India and Indonesia.
- In its absence, countries self-insure by amassing large reserves which could have been used for other developmental purposes.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Conclusion
The recent resurgence of the Global South reflects the evolving geopolitical landscape and the growing influence of developing nations in global affairs. India’s leadership exemplifies this transition through its championing of the interests of the Global South and advocating for a recalibration of the global economic and political order.
![]() 21 Jun 2024
21 Jun 2024
