Heavy monsoon rains due to multiple cloudbursts triggered the flash floods in Himachal Pradesh, causing widespread damage to properties and loss of life.
- The Indira Priyadarshini Hydroelectric Project has been impacted.
| Indira Priyadarshini Hydroelectric Project – The 4.8 MW (2.4 x 2) run-of-the-river hydroelectric plant is being developed on the Manuni Khad stream. |
About Cloudburst
- A cloudburst is defined as “Rainfall of 10 cm or more in one hour over a roughly 10 km x 10 km area.”
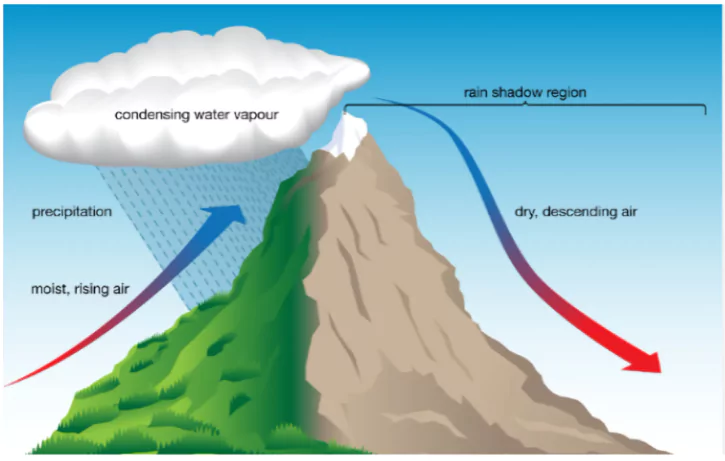 Mechanism: Common in hilly areas due to a process called orographic lift:
Mechanism: Common in hilly areas due to a process called orographic lift:-
- Warm air rises along mountain slopes.
- It expands due to low pressure at altitude and cools.
- Cooling causes condensation and release of moisture.
- If warm moist air keeps rising, it may delay rainfall until a large volume suddenly condenses and falls as torrential rain.
- Occurrence in India: In India, cloudbursts are frequently observed during the monsoon season, particularly over regions like the Himalayas, the Western Ghats, and the northeastern hill states.
- Linkage with Flash floods: Cloudbursts often result in flash floods and have become increasingly common from May-September when the southwest monsoon season prevails in much of the country.
- Impacts:
- Sudden, localized heavy rain.
- Often leads to flash floods and landslides due to drainage overload and rapid water accumulation.
- Prediction: Difficult to detect due to the small area and short time frame.
Flash Floods
- According to the India Meteorological Department (IMD), a flash flood is a sudden, rapid flooding event that typically occurs within a short period, generally less than 6 hours, due to intense rainfall, often associated with cloudbursts or heavy thunderstorms.
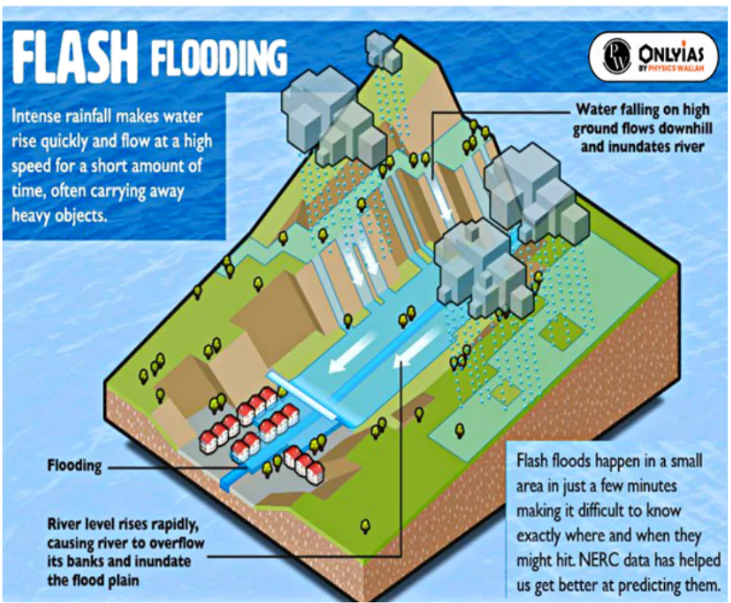
Causes of Flash Flood
Flash floods can be caused by factors other than rainfall
- Dam or Levee Failures: Structural breaches can unleash massive water flows, causing sudden downstream flooding.
- Cloud Bursts: In India, flash floods are often associated with cloud bursts, which are sudden, intense rainfall events that occur within a short duration.
- Melting Glaciers: Himalayan states face the challenge of overflowing glacial lakes, formed due to the melting of glaciers.
- Debris Flows & Mudslides: Landslides or debris jams can divert or block water, triggering flash floods.
- Urbanization and Poor Drainage Systems: Urban areas with extensive concrete surfaces and inadequate drainage systems are prone to flash floods. Impervious surfaces prevent water from infiltrating the ground, resulting in rapid runoff and increased flood risk.
- Topography & Soil Type: Steep slopes, poor soil absorption, and obstructive structures further heighten flash flood risk.
Causes of Increased Cloudbursts and Flash Floods in Himalayan Regions
The increased frequency and severity of cloudbursts and flash floods in Himalayan states are a result of several natural and anthropogenic factors.
- These factors are interconnected and exacerbate each other, contributing to the vulnerability of the region.
1. Orographic and Topographical Factors
- The Himalayan region’s steep slopes and narrow valleys are particularly susceptible to cloudbursts.
- When moist air masses from the Bay of Bengal are forced to ascend over the mountains, they cool and condense, leading to intense rainfall over short periods.
- Recent Example: In June 2025, multiple cloudbursts in the Kullu and Kangra districts of Himachal Pradesh caused severe flash floods, destroying infrastructure and causing loss of life.
2. Climate Change and Global Warming
- Rising global temperatures have intensified the water cycle, increasing evaporation rates and atmospheric moisture content.
- The Himalayan region is warming at a rate higher than the global average, exacerbating the occurrence of cloudbursts and the intensity of rainfall.
- Recent Example: The glacial melt and increased rainfall intensity observed in regions like Sikkim and Uttarakhand have been linked to global warming.
- The Lhonak Lake outburst in Sikkim in October 2023 is a significant example of climate-induced natural disasters.
3. Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs)
- The rapid melting of glaciers due to rising temperatures has resulted in the formation of glacial lakes in the Himalayas. These lakes are particularly dangerous as their natural dams may fail, releasing massive volumes of water downstream.
- Recent Example: The Lhonak Lake outburst in Sikkim in 2023 caused significant flooding, infrastructure damage, and loss of life.
4. Deforestation and Land Use Changes
- Unregulated construction, deforestation, and encroachment on riverbeds have reduced the natural absorption capacity of the land.
- Urban sprawl and infrastructure development in flood-prone areas exacerbate the effects of heavy rains by increasing runoff.
- Recent Example: In August 2024, the Kullu-Manali region in Himachal Pradesh experienced devastating flash floods triggered by multiple cloudbursts.
- In Hilly States, the construction of roads, buildings, and other infrastructure in flood-prone areas has heightened the region’s vulnerability to such natural disasters.
|
Way Forward
- Enhanced Weather Forecasting and Monitoring: Implement advanced meteorological systems to provide real-time weather updates and early warnings to authorities and tourists.
- Emergency Response Drills: Regularly conduct mock drills involving all stakeholders to ensure preparedness for unforeseen events.
- Community Awareness: Conduct awareness programs to educate local populations about disaster preparedness and response.
- Infrastructure Planning: Ensure that infrastructure development in the Himalayan region adheres to environmental guidelines to minimize disaster risks.
- International Cooperation: to share best practices in disaster management.
Conclusion
The increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events, such as cloudbursts and flash floods, poses significant risks to both life and infrastructure in the Himalayan region.
- The urgent need for improved disaster management strategies and sustainable development practices is clear, to mitigate the effects of such disasters in the future.
![]() 27 Jun 2025
27 Jun 2025

 Mechanism: Common in hilly areas due to a process called orographic lift:
Mechanism: Common in hilly areas due to a process called orographic lift:
