Recently, a US military plane carrying 104 Indian deportees landed in Amritsar, with many of the returnees complaining about being handcuffed throughout the journey and allowed limited access to washrooms.
- Deportation of Indian Immigrants: Dozens of Indians, believed to be illegal immigrants, deported from the U.S.
- U.S. Immigration Crackdown: Intensified Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) operations under the Trump administration (post-January 2025 swearing-in).
- Scale of Deportations:
- Between June and October 2024, 1,60,000 individuals deported on 495 international flights to 145+ countries, including India.
- India has an estimated 7,25,000 undocumented immigrants in the U.S., making it one of the largest populations of illegal immigrants.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Methods of Illegal Migration
- Overstaying Visas: Individuals enter legally but fail to return, often via:
- Tourist visas converted into illegal work.
- Student visas overstayed to seek employment.
- H-1B visa fraud, where applicants fail to secure legitimate jobs.
- Crossing Borders Illegally
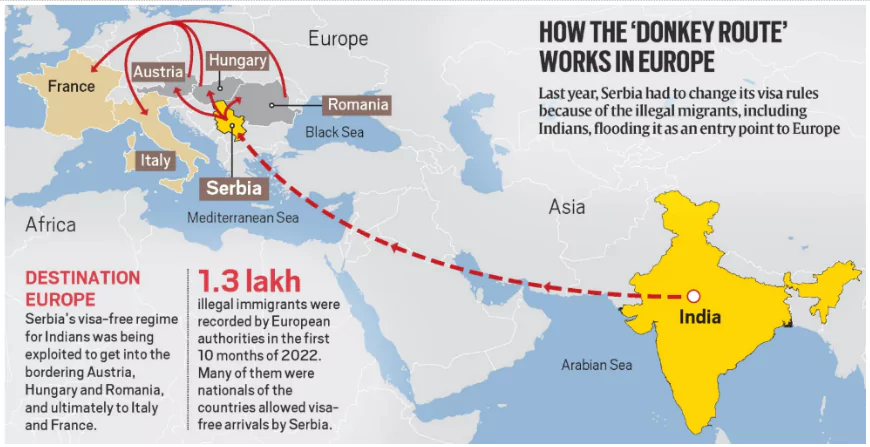
- The ‘Dunki Route’ – A Dangerous Path: “Dunki” (meaning “donkey” journey) refers to the hazardous, multi-country path taken by migrants to illegally enter developed nations.
- Often involves fake visas, human smugglers, and perilous crossings.
- Darién Gap (Panama-Colombia): One of the most dangerous migration routes, with high rates of crime, death, and exploitation.
- The Northern Route to the U.S. (Via Canada): A rising alternative to the Mexico-U.S. route
- The Schengen Visa Fraud Route (To Europe & U.K.): Used by illegal migrants heading to the U.K., Germany, France, and Italy.
- Marriage & Birthright Citizenship
- Marriage fraud: Fake marriages to obtain residency.
- Birth tourism: Children born in the U.S. granted automatic citizenship, encouraging unauthorized stays.
Key Trends in Illegal Emigration from India
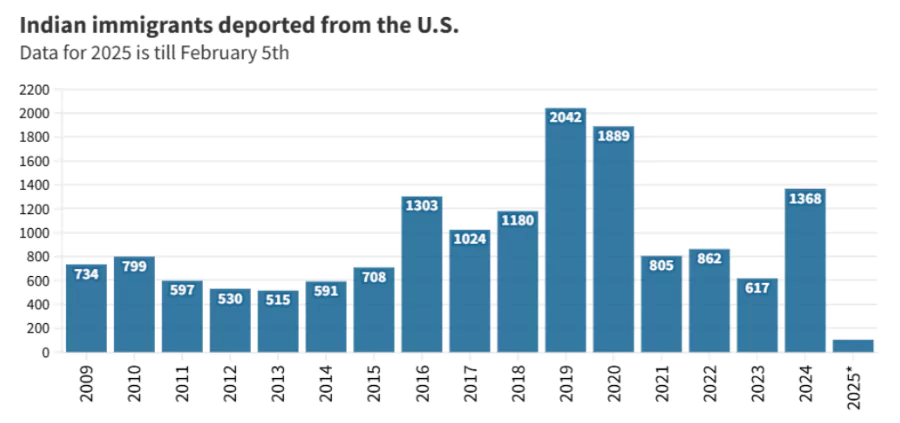
Growing Deportations from the U.S.
- U.S. repatriations of Indian nationals have increased steadily:
- FY 2024 (October 2023 – September 2024): Over 1,000 Indian nationals deported via chartered and commercial flights.
- 2025: Use of military aircraft for deportation, focusing on Punjab, Haryana, and Gujarat.
- Canada is now an emerging entry route: The visa processing time for the U.S. exceeds a year, whereas Canada’s 76-day processing time offers an easier route to enter and potentially cross into the U.S. illegally.
Causes of Illegal Emigration from India
- Unemployment & Economic Hardship: Many migrants take the risk of illegal travel because even a low-paying job in the U.S. (e.g., $10–15/hour) offers higher earnings than a decent job in India.
- In states like Punjab, Haryana, and Gujarat, lack of white-collar job opportunities has pushed youth towards illegal migration routes such as the Dunki route to the U.S.
- Agricultural Distress & Rural Migration: Over 60% of India’s workforce depends on agriculture, but farm incomes are stagnant.
- In Punjab, declining wheat and rice MSP growth, coupled with rising debts, has forced thousands of youth to sell land and migrate illegally to the U.S. and Canada.
- The National Sample Survey (NSS) 2022 reported that 50% of rural households are under debt stress, increasing the push factor for illegal emigration.
- Wage Disparity & Better Opportunities Abroad: The average monthly wage in India is significantly lower than an average American earning several thousand dollars per month.
- The World Bank Migration Report 2024 stated that India received $111 billion in remittances, proving that wage differences encourage large-scale migration.
- Social Aspiration & Status Symbol: Having a family member in a foreign country is considered a symbol of success in Punjab and Gujarat.
- Many Punjabi and Gujarati families take huge loans to send their children to the U.S. or Canada, often using fake education visas or Dunki routes.
- Human Trafficking & Fake Travel Agents: India ranks in the top 10 for human trafficking victims (Global Slavery Index 2023).
- A fake visa racket worth over Rs 300 crore, producing 5,000 counterfeit visas over the last five years, has been uncovered by the Delhi police in 2024.
- Legal & Bureaucratic Hurdles in Migration: The wait time for U.S. tourist visas for Indians is 600+ days, making legal migration difficult.
- H-1B visa restrictions imposed by the Trump administration forced many skilled Indians to seek illegal entry into the U.S. via Mexico and Canada.
- Political Instability & Religious Persecution: India’s minority communities (e.g., Sikhs, Dalits, LGBTQ individuals) face social discrimination in certain regions.
- Many Sikh asylum seekers from Punjab attempt illegal entry into the U.S. and Canada, citing religious persecution and farmer protests.
- Influence of the “Dunki Route” Culture: More than 90,000 Indians attempted illegal crossings into the U.S. in 2023 via Mexico’s southern border (U.S. Customs & Border Protection Report).
- Gujarati & Punjabi youth are inspired by successful migrants who took illegal routes and settled in the U.S..
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Difference Between Emigration, Immigration, and Migration
| Term |
Definition |
Key Focus |
Example |
| Emigration |
When a person leaves their home country to settle in another country. |
Exit from a country (departure). |
An Indian worker moving from Punjab to Canada for a job is an emigrant from India. |
| Immigration |
When a person enters a new country to live permanently or temporarily. |
Entry into a country (arrival). |
The same worker is an immigrant in Canada once he arrives there. |
| Migration |
A broad term that includes both movement within a country (internal migration) and between countries (international migration). |
Movement from one place to another. |
A farmer moving from Bihar to Delhi for work (internal migration) or an Indian moving to the U.S. (international migration). |
Impact of Illegal Emigration from India
Impact on India
- Economic Impact
- Loss of Skilled & Semi-Skilled Workforce: Many young and productive workers migrate illegally, leading to a brain drain.
- Large-scale illegal migration from Punjab, Gujarat, and Haryana results in a shortage of skilled labor in India.
- Dependency on Remittances: India received $111 billion in remittances in 2022 (World Bank), making it the highest globally.
- However, remittances from illegal migrants are unreliable due to their unstable status abroad.
- Financial Burden on Families: Families in Punjab and Gujarat take loans of ₹30–₹50 lakh per person to send migrants illegally to the U.S. or Canada, often leading to debt traps if deported.
- Social Impact
- Disruption of Family Structures: Young men migrate illegally, leaving behind broken families and an aging rural population.
- In Punjab’s Doaba region, many villages have only women, children, and elderly people as men have migrated abroad.
- Rise in Fake Migration Agencies & Human Trafficking: Fake visa agents and human smuggling networks exploit desperate families.
- In 2024, Delhi Police busted a fake Schengen visa racket smuggling Indians to Europe.
- Mental Health Issues Among Migrants & Families: Fear of deportation, economic stress, and exploitation lead to depression and trauma.
- Example: Many Punjabi migrants stuck in U.S. detention centers suffer mental distress.
- Legal & Administrative Challenges
-
- Increase in Fake Documents & Identity Fraud: Illegal migrants often forge passports, visas, and education certificates.
- Example: The Indian government has cancelled thousands of fake passports since 2022.
- Crackdown on Illegal Agents: Under the Bharatiya Nyaya Samhita (BNS), 2023, fake migration agents face 7 years in prison.
- Challenges in Handling Deportations: India faces diplomatic pressure to accept deported nationals.
- India was labeled “uncooperative” by U.S. authorities in accepting deportees.
Impact on Destination Countries (U.S., Canada, Europe, Gulf Nations)
- Economic Impact
- Cheap Labor Supply: Illegal migrants work in low-paying jobs like construction, restaurants, and domestic work.
- U.S. cities like New York & Boston depend on undocumented workers in informal sectors.
- Strain on Public Resources: Illegal migrants use healthcare, education, and welfare benefits, increasing public spending.
- California spends over $1 billion annually on services for undocumented immigrants.
- Social & Political Impact
- Rise in Anti-Immigrant Sentiments: Trump’s 2025 immigration policy is driven by public anger against illegal migration.
- Right-wing groups in Canada & the U.S. blame Indian migrants for job losses.
- Security Concerns & Border Control Issues: The Swanton Sector (U.S.-Canada border) recorded 2,715 Indian crossings in June 2024, leading to stricter U.S. border security policies.
- Pressure on Legal Immigration: Stricter H-1B visa rules in the U.S. due to rise in illegal migration cases from India.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
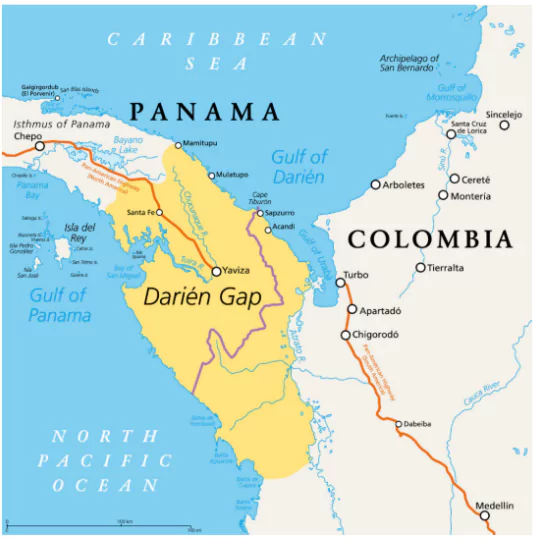
About Darien Gap
- Location: A dense, jungle-covered region spanning northern Colombia and southern Panama, approximately 60 miles (97 kilometers) wide.
- Despite its challenging terrain and lack of infrastructure, Darien Gap has become a major route for global human migration.
- Migrants traverse the gap to reach North America, particularly the United States and Canada.
- The journey involves walking for several days through mountains, rivers, and mud, often with children and belongings, relying on paid guides due to the absence of paved roads and cellphone service.
|
Impact on Migrants
- Humanitarian Crisis & Exploitation
- Deaths Due to Dangerous Routes: Hundreds of migrants die annually in the Darién Gap (Panama-Colombia border) due to violence, starvation, and natural dangers.
- Patel family from Gujarat froze to death in Canada just 12m from the U.S. border (2022).
- Exploitation by Human Traffickers: Many illegal migrants fall into forced labor and sex trafficking.
- Thousands of Indian workers stranded in the UAE and Saudi Arabia in 2023 due to fake job contracts.
- Risk of Arrest, Deportation & Blacklisting
- Deportation & Legal Penalties: Over 1,500+ Indians deported from the U.S. in 2024 alone.
- Blacklisting: Many deported migrants face a lifetime ban on re-entering the U.S., Canada, and Europe.
- Detention & Abuse in Foreign Jails: 2,647 Indians currently detained in U.S. immigration centers (2025), awaiting deportation.
- Indian migrants detained in Mexican and Guatemalan jails face human rights abuses.
- Psychological & Social Trauma:
-
- Mental Health Issues: Fear of deportation, economic failure, and exploitation leads to depression, anxiety, and trauma.
- Many deported migrants from the U.S. return to India in shame and financial ruin, often facing social stigma.
- Family Separation: Children of deported migrants born in the U.S. (birthright citizens) are separated from parents, leading to legal limbo and trauma.
Legal and Policy Framework for Illegal Emigration from India
India’s Legal Framework on Emigration
- Emigration Act, 1983 (To be replaced by the Overseas Mobility Bill, 2024): Regulates overseas employment of Indians, particularly in Gulf nations.
- Key Provisions:
- Mandatory emigration clearance for workers traveling to 18 ECR (Emigration Check Required) countries.
- Regulation of recruiting agents to prevent fraud.
- Punishment for unauthorized recruitment (imprisonment extends to one year or a fine, or both).
- Passports Act, 1967: Regulates issuance of passports and punishes forgery.
- Key Provisions:
- Forging documents for illegal migration punishable with imprisonment up to 2 years.
- Confiscation of passports of illegal migrants.
- Bharatiya Nyaya Samhita (BNS), 2023 (Replaces IPC): New provisions to curb illegal migration:
- Section 336: Forgery of documents for illegal migration punishable with up to 7 years in prison, along with a fine..
- Stricter penalties for human trafficking networks involved in fake visa scams.
- Proposed Overseas Mobility (Facilitation & Welfare) Bill, 2024 (To replace Emigration Act, 1983)
- Objective:
- Promote safe, legal, and orderly migration for overseas employment.
- Prevent fraud by fake recruiting agents.
- Modernize migration regulations for skilled professionals.
- Key Features:
- Single-window clearance system for overseas employment.
- Stronger penalties for fake travel agents.
- Awareness campaigns on illegal migration risks.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
U.S. Immigration Laws and Policies on Illegal Migration
- Immigration and Nationality Act (INA), 1952: Main U.S. immigration law regulating visas, deportations, and asylum.
- Allows expedited deportation of illegal entrants.
- 2024: 1,368 Indian nationals deported under this policy.
- H-1B Visa Reforms (2025): H-1B visas are issued to skilled Indian professionals.
- Under Trump 2.0, restrictions on H-1B have increased:
- Stricter eligibility requirements.
- Preference for American workers over Indian IT professionals.
- Delays in Green Card processing for Indians.
- U.S.-Canada Border Enforcement (2025): Canada is now a major illegal entry route for Indians.
- Swanton Sector (U.S.-Canada border) saw 2,715 Indian crossings in June 2024 alone.
The H-1B Visa
- It is for “specialty occupations” that require “a high level of skill” and at least a bachelor’s degree for a maximum of 6 years or longer if they are in line for a green card. It is presently capped at 65,000 H-1B visas per year
- As per the US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), Indians accounted for 72.3% (2.79 lakh of a total of 3.86 lakh) H-1B visa holders in 2023.
|
International Efforts to Curb Illegal Migration
- India-U.S. Migration Dialogue (2025): Ensure humane deportation procedures and prevent human trafficking.
- Faster verification of Indian nationals in U.S. detention centers.
- India working on “blacklist” policies for repeat offenders.
- UN Global Compact for Migration: Focus on safe, orderly, and legal migration.
- India is a signatory
- India is working to increase legal migration routes to reduce dependence on illegal ones.
Way Forward for India: Addressing Illegal Emigration
- Strengthening Legal Migration Pathways: Replace the outdated Emigration Act, 1983 to regulate migration more efficiently.
- Faster visa processing: Reduce long wait times (600+ days for U.S. visas) to prevent illegal migration attempts.
- Cracking Down on Human Trafficking & Fake Migration Agents: Mandate government registration & background checks for all migration consultants.
- AI-based tracking & biometric verification at airports to detect fraudulent visa applicants.
- Addressing Economic Push Factors in High Migration States: Job creation & skilling programs in Punjab, Gujarat, Haryana, and Andhra Pradesh to reduce migration dependency.
- Financial literacy campaigns to prevent families from taking high-interest loans for illegal migration.
- Diplomatic Engagement for Humane Deportation & Legal Migration: Stronger border security agreements with transit countries (Mexico, Guatemala, Ecuador) to curb human smuggling.
- Expand India’s role in the UN Global Compact for Migration to advocate for migrant rights & ethical recruitment practices.
- Public Awareness & Education on Risks of Illegal Migration: Mass awareness campaigns in high-migration districts on legal migration routes & dangers of Dunki networks.
- Government helpline & online portals to provide real-time migration information.
- Strengthening Border & Airport Security: Better screening of high-risk passengers at international airports using AI-based profiling.
- Increased intelligence-sharing with transit nations (Mexico, Canada, UAE, Turkey) to intercept illegal migration attempts.
- Reintegration Support for Deported Migrants: Skill training & employment support for deported returnees to prevent reattempts.
- Financial assistance for families of deported migrants who face economic hardship.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
Illegal immigration is a complex socio-economic issue driven by economic distress, aspirations, and trafficking networks. India must balance international diplomacy with measures to protect legal migration pathways while cracking down on human smuggling. Strengthening legal job migration channels and creating employment opportunities in India is the key to reducing illegal emigration.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 10 Feb 2025
10 Feb 2025




